A total lunar eclipse occurred on February 20 and February 21, 2008. It was visible in the eastern evening sky on February 20 for all of North and South America, and on February 21 in the predawn western sky from most of Africa and Europe. Greatest Eclipse occurring on Thursday, February 21, 2008, at 03:26:03 UTC, totality lasting 49 minutes and 45.6 seconds.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Sunday 9 November 2003, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 2003, the first being on 16 May 2003. It is the first total lunar eclipse of 21st century which happened on a micromoon day. The Moon barely edged into total eclipse for 21 minutes and 58 seconds. With the Moon just 1.78% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, the Moon may have been quite bright, but even so, this should have been worth seeing. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 31 minutes and 25 seconds. Occurring only 1.4 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 6.4% smaller than average.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Thursday 5 July 2001, the second of three lunar eclipses in 2001. The Earth's shadow on the moon was clearly visible in this eclipse, with 49.614% of the Moon in shadow; the partial eclipse lasted for 2 hours, 40 minutes and 0.5 seconds. Occurring only 3.9 days before apogee, the Moon’s apparent diameter was 5.021% smaller than average.

A total lunar eclipse took place at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on Tuesday, September 16, 1997, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1997. A shallow total eclipse saw the Moon in relative darkness for 1 hour, 1 minute and 30.8 seconds. The Moon was 19.094% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, and should have been significantly darkened. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 16 minutes and 28.2 seconds in total. The penumbral eclipse lasted for 5 hours, 8 minutes and 20.1 seconds. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 16 minutes and 28.2 seconds. The total eclipse lasted for 1 hour, 1 minute and 30.8 seconds. Maximum eclipse was at 18:46:39.1 UTC. The moon's apparent diameter was extremely large because occurred only 3 hours and 21 minutes past perigee. The Moon was only 356,986 km of the Earth at greatest eclipse.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Monday, March 24, 1997, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1997.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday 8 October 2014. It is the second of two total lunar eclipses in 2014, and the second in a tetrad. Other eclipses in the tetrad are those of 15 April 2014, 4 April 2015, and 28 September 2015. Occurring only 2.1 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger, 1960.6 arcseconds.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, April 4, 1996, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1996, the other being on Friday, September 27. The Moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, June 4, 1993, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1993, the second being on Monday, November 29. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour and 36 minutes, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 56% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours and 38 minutes in total. The moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on July 7, 2047. It will last 1 hour 40 minutes and 49 seconds and will plunge the full Moon into deep darkness, as it passes right through the centre of the Earth's umbral shadow. While the visual effect of a total eclipse is variable, the Moon may be stained a deep orange or red colour at maximum eclipse. This will be a great spectacle for everyone who sees it. The partial eclipse will last for 3 hours and 39 minutes in total.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on 7-8 September 2025. The Moon will barely miss the center of the Earth's shadow. It will be the second of two total lunar eclipses. Occurring roughly 3 days before perigee, the Moon will appear larger than usual.

A partial lunar eclipse will take place on Friday 28 August 2026. The moon will be almost be inside the umbra, but not quite be contained within the umbral shadow at greatest eclipse.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, September 16, 1978, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1978. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 18 minutes and 39 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 32.683% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 27 minutes and 11.6 seconds in total.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, September 6, 1979, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1979. A shallow total eclipse saw the Moon in relative darkness for 44 minutes and 24.7 seconds. The Moon was 9.358% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, and should have been significantly darkened. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 11 minutes and 54.1 seconds in total.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, May 13, 1957, the third of fourteen total lunar eclipses of Lunar Saros 130. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour and 18 minutes, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 30% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours and 32 minutes in total.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on July 29, 2083. The Moon will be plunged into darkness for 1 hour and 30 minutes, in a deep total eclipse which will see the Moon 48.3% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may be stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse will last for 3 hours and 33 minutes in total.
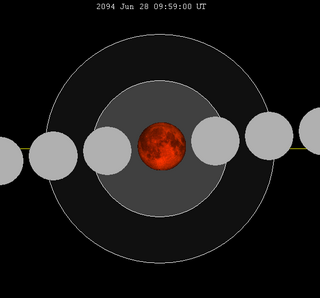
A total lunar eclipse will take place on June 28, 2094. The Moon will pass through the center of the Earth's shadow. While the visual effect of a total eclipse is variable, the Moon may be stained a deep orange or red color at maximum eclipse. With a gamma value of only 0.0288 and an umbral eclipse magnitude of 1.8234, this is the greatest eclipse in Saros series 131 as well as the second largest and darkest lunar eclipse of the 21st century.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, September 5, 1960. The Moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on September 19, 2043.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on October 30, 2050.

Saros cycle series 127 for lunar eclipses occurs at the moon's descending node, repeats every 18 years 11 and 1/3 days. It contains 72 events. Solar saros 134 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series. It consisted with 10 penumbral eclipses, 21 partial eclipses, 11 total eclipses, 21 partial eclipses, and ends with 8 penumbral eclipses.