
A total lunar eclipse occurred from 5:27 to 11:06 UTC on 21 December 2010, coinciding with the date of the Winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere and Summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere. It was visible in its entirety as a total lunar eclipse in North and South America, Iceland, Ireland, Britain and northern Scandinavia.

A total lunar eclipse will take place between Monday and Tuesday, June 25-26, 2029. A central total eclipse lasting 1 hour and 41 minutes 53 seconds will plunge the full Moon into deep darkness, as it passes right through the centre of the Earth's umbral shadow. While the visual effect of a total eclipse is variable, the Moon may be stained a deep orange or red color at maximum eclipse. It will be able to be seen from most of the Americas, Western Europe and Africa. The partial eclipse will last for 3 hours and 39 minutes 32 seconds in total.

A total lunar eclipse occurred on 15–16 May 2022, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2022. The event occurred near lunar perigee; as a result, this event was referred to some in media coverage as a "super flower blood moon" and elsewhere as a "super blood moon", a supermoon that coincides with a total lunar eclipse. This was the longest total lunar eclipse visible from nearly all of North America since August 17, 1989 until the next eclipse on November 8.

A total lunar eclipse occurred on 31 January 2018. The Moon was near its perigee on 30 January and as such may be described as a "supermoon", when the Moon's distance from the Earth is less than 360,000 km. The previous supermoon lunar eclipse was in September 2015.

A partial lunar eclipse occurred on 19 November 2021. The eclipse occurred towards a micromoon. This was the longest partial lunar eclipse since 18 February 1440, and the longest until 8 February, 2669; however, many eclipses, including the November 2022 lunar eclipse, have a longer period of umbral contact at next to 3 hours 40 minutes. It was often referred to as a "Beaver Blood Moon" although not technically fulfilling the criteria for a true blood moon (totality).

A total lunar eclipse will take place on May 6, 2069. The eclipse will be a dark one with the southern tip of the Moon passing through the center of the Earth's shadow. This is the first central eclipse of Saros series 132.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Thursday, February 15, 2018, with a magnitude of 0.5991. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of orbit on Tuesday, October 25, 2022, with a magnitude of 0.8623. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
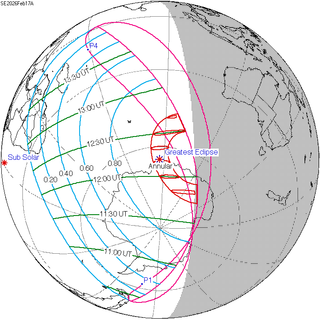
An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, February 17, 2026, with a magnitude of 0.963. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter will be near the average diameter because it will occur 6.8 days after apogee and 7.5 days before perigee.
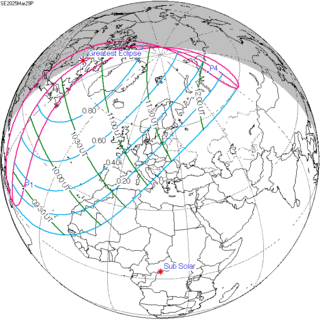
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit on Saturday, March 29, 2025, with a magnitude of 0.9376. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit on Sunday, September 21, 2025, with a magnitude of 0.855. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
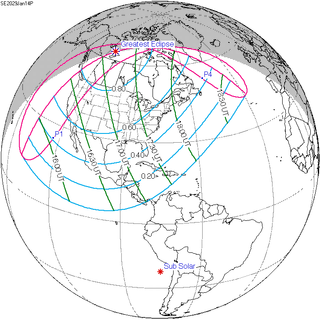
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Sunday, January 14, 2029, with a magnitude of 0.8714. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, July 11, 2029, with a magnitude of 0.2303. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Tuesday, June 12, 2029, with a magnitude of 0.4576. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
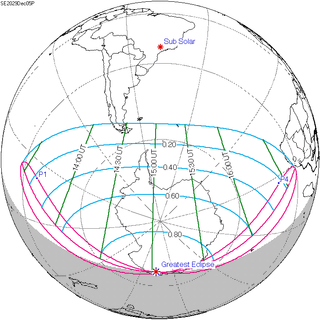
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, December 5, 2029, with a magnitude of 0.8911. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
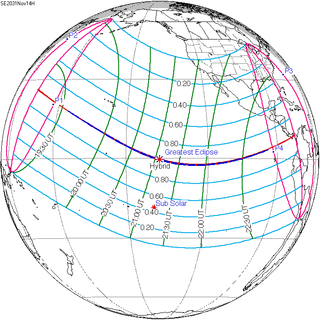
A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, November 14, 2031, with a magnitude of 1.0106. It is a hybrid event, with portions of its central path near sunrise and sunset as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 3.1 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be larger.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Sunday, May 9, 2032, with a magnitude of 0.9957. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter will be near the average diameter because it will occur 5.7 days after perigee and 7.4 days before apogee.
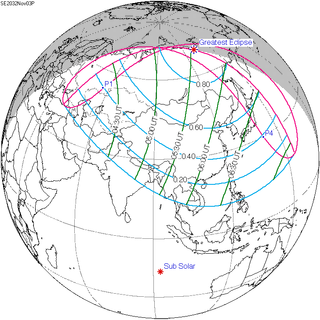
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, November 3, 2032, with a magnitude of 0.8554. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Sunday, November 4, 2040, with a magnitude of 0.8074. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
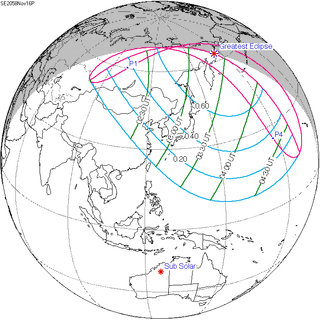
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Saturday, November 16, 2058, with a magnitude of 0.7644. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.


































































