
A total lunar eclipse occurred on February 20 and February 21, 2008. It was visible in the eastern evening sky on February 20 for all of North and South America, and on February 21 in the predawn western sky from most of Africa and Europe. Greatest Eclipse occurring on Thursday, February 21, 2008, at 03:26:03 UTC, totality lasting 49 minutes and 45.6 seconds.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on 16 August 2008, the second of two lunar eclipses in 2008, with the first being a total eclipse on 20 February 2008. The next lunar eclipse was a penumbral eclipse occurring on 9 February 2009, while the next total lunar eclipse occurred on 21 December 2010.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Sunday 9 November 2003, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 2003, the first being on 16 May 2003. It is the first total lunar eclipse of 21st century which happened on a micromoon day. The Moon barely edged into total eclipse for 21 minutes and 58 seconds. With the Moon just 1.78% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, the Moon may have been quite bright, but even so, this should have been worth seeing. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 31 minutes and 25 seconds. Occurring only 1.4 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 6.4% smaller than average.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Sunday 26 May 2002, the first of three lunar eclipses in 2002.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Sunday 30 December 2001, the last of three lunar eclipses in 2001. At maximum eclipse, 89.477% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a slight shadow gradient across its disc; this subtle effect may have been visible to careful observers. No part of the Moon was in complete shadow. The eclipse lasted 4 hours, 4 minutes and 17.7 seconds overall. This lunar eclipse followed the Annular Solar Eclipse on 14 December 2001.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, October 28, 1985, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1985, the first being on May 4, 1985.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, March 3, 1988, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1988, the second being on August 27, 1988. Earlier sources compute this as a 0.3% partial eclipse lasting under 14 minutes, and newest calculations list it as a penumbral eclipse that never enters the umbral shadow. In a rare total penumbral eclipse, the entire Moon was partially shaded by the Earth, and the shading across the Moon should have been quite visible at maximum eclipse. The penumbral phase lasted for 4 hours, 53 minutes and 50.6 seconds in all, though for most of it, the eclipse was extremely difficult or impossible to see. The Moon was 2.2 days after apogee, making it 6.1% smaller than average.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, November 8, 1984, the last of three lunar eclipses in 1984. This subtle penumbral eclipse may have been visible to a skilled observer at maximum eclipse. 90% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a gentle shadow gradient across its disc at maximum; the eclipse as a whole lasted 4 hours and 28 minutes.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, May 15, 1984, the first of three lunar eclipses in 1984. This was a deep penumbral eclipse, with the southern limb of the Moon close to the Earth's shadow.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, December 20, 1983, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1983. At the maximum eclipse, 89% of the Moon's disk was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a slight shadow gradient across its disc; this subtle effect may have been visible to careful observers. No part of the Moon was in complete shadow. The eclipse lasted 4 hours and 2 minutes overall.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, January 20, 1981, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1981. In a rare total penumbral eclipse, the entire Moon was partially shaded by the Earth, and the shading across the Moon should have been quite visible at maximum eclipse. The penumbral phase lasted for 4 hours and 24 minutes in all, though for most of it, the eclipse was extremely difficult or impossible to see. The moon's apparent diameter was larger because the eclipse occurred 5.2 days after perigee.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, November 29, 1974, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1974. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 15 minutes and 45 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 28.961% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 28 minutes and 58.7 seconds in total. The penumbral eclipse lasted for 5 hours, 33 minutes and 11.6 seconds. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 28 minutes and 58.7 seconds. The total eclipse lasted for 1 hour, 15 minutes and 45 seconds. Occurring only 3.6 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 1.4% larger than average.

A partial lunar eclipse occurred on 19 November 2021. The eclipse occurred towards a micromoon. This was the longest partial lunar eclipse since 18 February 1440, and the longest until 8 February, 2669; however, many eclipses, including the November 2022 lunar eclipse, have a longer period of umbral contact at next to 3 hours 40 minutes. It was often referred to as a "Beaver Blood Moon" although not technically fulfilling the criteria for a true blood moon (totality).

A total lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday, October 18, 1967, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1967, the first being on April 24, 1967.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, September 15, 1913. The moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.
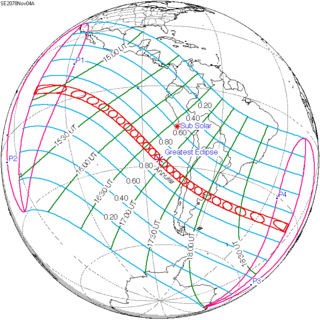
An annular solar eclipse will occur on Friday, November 4, 2078. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The path of annularity will cross Pacific Ocean, South America, and Atlantic Ocean. The tables below contain detailed predictions and additional information on the Annular Solar Eclipse of 4 November 2078.

Saros cycle series 114 for lunar eclipses occurs at the moon's ascending node, 18 years 11 and 1/3 days. It contains 71 member events, with 13 total eclipses, starting in 1458 and ending in 1674. Solar saros 121 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.

Saros cycle series 129 for lunar eclipses occurs at the moon's descending node, repeats every 18 years 11+1/3 days. The 129th lunar saros is associated with Solar Saros 136.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, October 7, 1949, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1949.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, September 26, 1931. The Moon passed through the central of the Earth's shadow. This was the last central lunar eclipse of Saros cycle 126.




































