A total lunar eclipse took place on May 4, 2004, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2004, the second being on October 28, 2004.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on April 24, 2005, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2005. At maximum eclipse, 86.5% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a slight shadow gradient across its disc; this subtle effect may have been visible to careful observers. No part of the Moon was in complete shadow. The eclipse lasted 4 hours and 6 minutes overall, and was visible from east Asia, Australia, and the Americas.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, September 27, 1996, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1996, the first being on Thursday, April 4. This is the 41st member of Lunar Saros 127. The previous event is the September 1978 lunar eclipse. The next event is the October 2014 lunar eclipse.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday 8 October 2014. It is the second of two total lunar eclipses in 2014, and the second in a tetrad. Other eclipses in the tetrad are those of 15 April 2014, 4 April 2015, and 28 September 2015. Occurring only 2.1 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger, 1960.6 arcseconds.

A total lunar eclipse took place on 4 April 2015. It is the former of two total lunar eclipses in 2015, and the third in a tetrad. Other eclipses in the tetrad are those of 15 April 2014, 8 October 2014, and 28 September 2015.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place at the Moon's ascending node on 11 February 2017, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2017. It was not quite a total penumbral lunar eclipse. It occurred the same day as comet 45P/Honda–Mrkos–Pajdušáková made a close approach to Earth. It also occurred on the Lantern Festival, the first since 9 February 2009. Occurring only 4.4 days after perigee, the moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, April 4, 1996, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1996, the other being on Friday, September 27. The moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, March 24, 1978, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1978. The moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 30 minutes and 40.2 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 45.179% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 38 minutes and 34.5 seconds in total.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, April 24, 1986, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1986, the second being on October 17, 1986. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 3 minutes and 34.8 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 20.217% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 18 minutes and 46.8 seconds in total. The Moon was just 1.2 days before perigee, making it 5.3% larger than average.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, December 21, 1991, the last of four lunar eclipses in 1991. The moon grazed the northern edge of the umbral shadow.
A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on Monday, March 25, 2024. It will be visible to the naked eye as 95.57% of the Moon will be immersed in Earth's penumbral shadow.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, September 16, 1978, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1978. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 18 minutes and 39 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 32.683% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 27 minutes and 11.6 seconds in total.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, November 6, 1976, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1976, the first being on May 13. This subtle penumbral eclipse may have been visible to a skilled observer at maximum eclipse. 83.827% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a gentle shadow gradient across its disc at maximum; the eclipse as a whole lasted 4 hours, 25 minutes and 52.1 seconds. Occurring only 0.3 days after apogee, the moon's apparent diameter was 6.5% smaller than average.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, April 24, 1967, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1967, the second being on October 18, 1967.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday, October 18, 1967, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1967, the first being on April 24, 1967.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, December 19, 1964. A shallow total eclipse saw the Moon in relative darkness for 58 minutes and 54 seconds. The Moon was 17% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, and should have been significantly darkened. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours and 16 minutes in total. The eclipse afforded astrophysicist J. M. Saari the opportunity to make infrared pyrometric scans of the lunar surface with improved equipment, following up on Richard W. Shorthill's discovery of "hot spots" in the Tycho crater during the March 13, 1960 eclipse.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, September 5, 1960. The moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, November 29, 1955 with an umbral eclipse magnitude of 0.11899. A partial lunar eclipse happens when the Earth moves between the Sun and the Full Moon, but they are not precisely aligned. Only part of the Moon's visible surface moves into the dark part of the Earth's shadow. A partial lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth moves between the Sun and Moon but the three celestial bodies do not form a straight line in space. When that happens, a small part of the Moon's surface is covered by the darkest, central part of the Earth's shadow, called the umbra. The rest of the Moon is covered by the outer part of the Earth's shadow called the penumbra. It was the second of two lunar eclipses in 1955, first being the penumbral lunar eclipse on June 5.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on May 6, 2050.
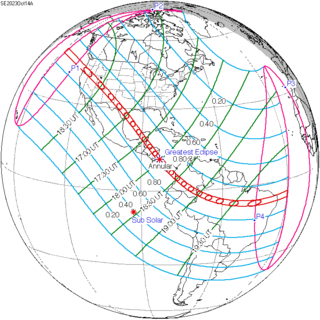
An annular solar eclipse will occur on Saturday, October 14, 2023. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres or miles wide. Occurring only 4.6 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be small.