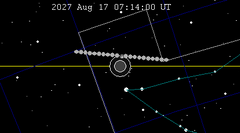
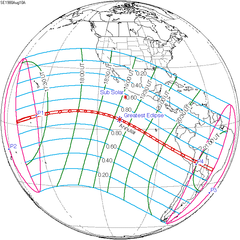
Relations to other lunar eclipses
Lunar year series
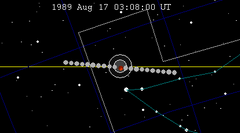
This eclipse is the second of four lunar year eclipses occurring at the Moon's ascending node.
The lunar year series repeats after 12 lunations or 354 days (Shifting back about 10 days in sequential years). Because of the date shift, the Earth's shadow will be about 11 degrees west in sequential events.
Saros series
Lunar saros series 128, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 71 lunar eclipse events including 57 umbral eclipses (42 partial lunar eclipses and 15 total lunar eclipses). Solar Saros 135 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.
| Greatest | First |
|---|

The greatest eclipse of the series occurred on 1953 Jul 26, lasting 100.7 minutes. [1] | Penumbral | Partial | Total | Central |
|---|
| 1304 Jun 18 | 1430 Sep 2 | 1845 May 21 | 1899 Jun 23 |
| Last |
|---|
| Central | Total | Partial | Penumbral |
|---|
| 2007 Aug 28 | 2097 May 21 | 2440 May 17 | 2566 Aug 2 |
Lunar Saros 128 contains 15 total lunar eclipses between 1845 and 2097 (in years 1845, 1863, 1881, 1899, 1917, 1935, 1953, 1971, 1989, 2007, 2025, 2043, 2061, 2079 and 2097). Solar Saros 135 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.
Metonic series
It is the third of five Metonic cycle eclipses, each being separated by 19 years: The Metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the Earth's shadow will in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
Tritos series
The tritos series repeats 31 days short of 11 years at alternating nodes. Sequential events have incremental Saros cycle indices.
This series produces 23 total eclipses between June 22, 1880 and August 9, 2120.
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros). [2] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 135.

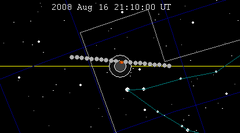
A total lunar eclipse occurred on 28 August 2007, lasting just over 90 minutes. The Moon entered the Earth's penumbra at 7:53:40 UTC. The first partial phase began in earnest at 8:51:16 UTC when the Moon entered the Earth's umbra. It exited the penumbra at 13:20:57 UTC.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday 4 May 2004, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2004, the second being on 28 October 2004.
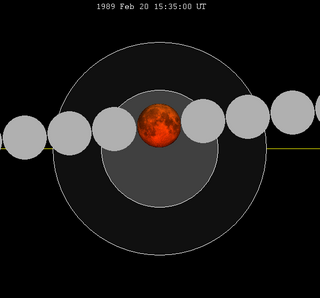
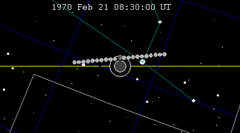
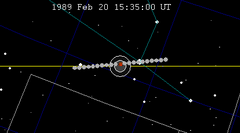
A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, February 20, 1989, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1989.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on May 26, 2040. The northern limb of the Moon will pass through the center of the Earth's shadow. This is the second central lunar eclipse of Saros series 131. This lunar event will occur near perigee, as a result, it will be referred to as a "super flower blood moon" or "super blood moon", though not quite as close to Earth as the eclipse of May 26, 2021.

A total lunar eclipse occurred on 15–16 May 2022, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2022. The event occurred near lunar perigee; as a result, this event was referred to some in media coverage as a "super flower blood moon" and elsewhere as a "super blood moon", a supermoon that coincides with a total lunar eclipse. This was the longest total lunar eclipse visible from nearly all of North America since August 17, 1989 until the next eclipse on November 8.
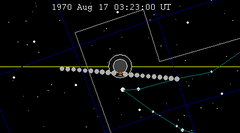
A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, August 6, 1971, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1971. A dramatic total eclipse lasting 1 hour, 39 minutes and 24.8 seconds plunged the full Moon into deep darkness, as it passed right through the centre of the Earth's umbral shadow. While the visual effect of a total eclipse is variable, the Moon may have been stained a deep orange or red colour at maximum eclipse. This was a great spectacle for everyone who saw it. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 35 minutes and 31.9 seconds in total. Occurring only 2.2 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 3.6% larger than average and the moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, April 24, 1986, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1986, the second being on October 17, 1986. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 3 minutes and 34.8 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 20.217% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 18 minutes and 46.8 seconds in total. The Moon was just 1.2 days before perigee, making it 5.3% larger than average.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on 7-8 September 2025. The Moon will barely miss the center of the Earth's shadow. It will be the second of two total lunar eclipses. Occurring roughly 3 days before perigee, the Moon will appear larger than usual.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on June 6, 2058. The Moon will pass through the center of the Earth's shadow.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday, October 18, 1967, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1967, the first being on April 24, 1967.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Sunday, July 26, 1953.

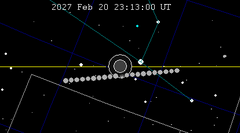
A total lunar eclipse will take place on September 19, 2043.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on May 6, 2069. The eclipse will be a dark one with the southern tip of the Moon passing through the center of the Earth's shadow. This is the first central eclipse of Saros series 132.
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Saturday, November 24, 2068, with a magnitude of 0.9109. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
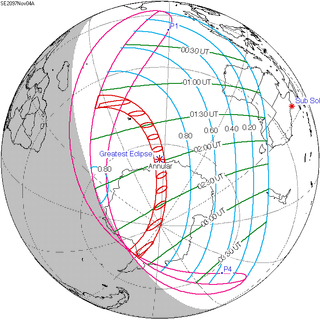
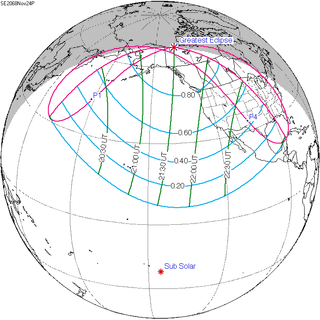
An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit between Sunday, November 3 and Monday, November 4, 2097, with a magnitude of 0.9494. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 5.4 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be smaller.
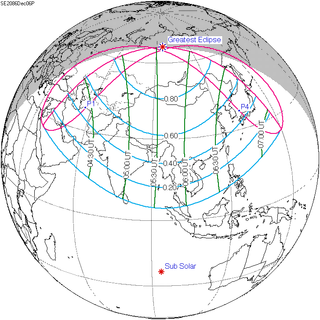
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, December 6, 2086, with a magnitude of 0.9271. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
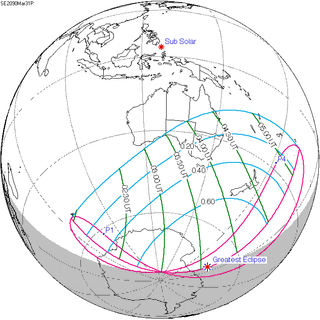
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Friday, March 31, 2090, with a magnitude of 0.7843. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

Saros cycle series 128 for lunar eclipses occurs at the moon's ascending node, repeating every 18 years 11 and 1/3 days. It contains 71 events. Solar saros 135 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, July 16, 1935. It was a central eclipse, passing through the darkest part of the shadow.

A penumbral lunar eclipse will occur on November 8, 2060. It will be too small to be visually perceptible.