| Total eclipse | |
 Totality of eclipse | |
| Gamma | 0.883 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 1.036 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 165 s (2 min 45 s) |
| Coordinates | 47°24′N40°00′E / 47.4°N 40°E |
| Max. width of band | 258 km (160 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 8:19:48 |
| References | |
| Saros | 120 (58 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9422 |
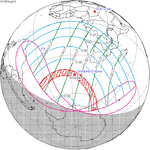
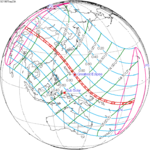
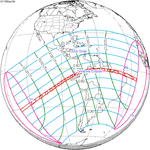
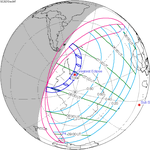
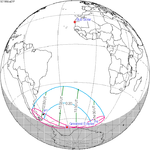
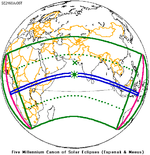
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, February 15, 1961, [1] with a magnitude of 1.036. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 21 hours after perigee (on February 14, 1961, at 11:30 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. [2]
Contents
- Observation
- In popular culture
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 1961
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 120
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 1961–1964
- Saros 120
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- See also
- Notes
- References
Totality was visible from France, Monaco, Italy, San Marino, Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia (parts now belonging to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia and Kosovo, North Macedonia), Albania, Bulgaria including the capital city Sofia, Romania including the capital city Bucharest, and the Soviet Union (parts now belonging to Ukraine, Russia and Kazakhstan). The maximum eclipse was recorded near Novocherkassk (Russian SFSR). A partial eclipse was visible for parts of Europe, North Africa, Northeast Africa, West Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia.