| Total eclipse | |
 Totality as viewed from Gorbea, Chile | |
| Gamma | −0.2939 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 1.0254 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 130 s (2 min 10 s) |
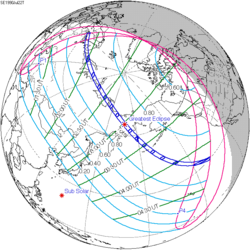
| Coordinates | 40°18′S67°54′W / 40.3°S 67.9°W |
| Max. width of band | 90 km (56 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 16:14:39 |
| References | |
| Saros | 142 (23 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9554 |
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Monday, December 14, 2020, [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] with a magnitude of 1.0254. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's and the apparent path of the Sun and Moon intersect, blocking all direct sunlight and turning daylight into darkness; the Sun appears to be black with a halo around it. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.8 days after perigee (on December 12, 2020, at 20:40 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. [7]
Contents
- Visibility
- Chile
- Argentina
- Eclipse timing
- Places experiencing total eclipse
- Places experiencing partial eclipse
- Scientific observations
- Gallery
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 2020
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 142
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 2018–2021
- Saros 142
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- References
- External links
Totality was visible from parts of southern Chile and Argentina. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of central and southern South America, Southern Africa, and Antarctica. A total solar eclipse crossed a similar region of the Earth about a year and a half earlier on July 2, 2019.