| Annular eclipse | |
| Gamma | −0.9243 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 0.9484 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 219 s (3 min 39 s) |
| Coordinates | 63°24′S160°36′W / 63.4°S 160.6°W |
| Max. width of band | 495 km (308 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 18:11:21 |
| References | |
| Saros | 154 (10 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9686 |
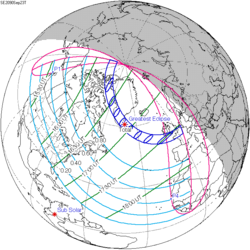
An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Tuesday, October 24, 2079, [1] with a magnitude of 0.9484. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 5.25 days before apogee (on October 29, 2079, at 23:40 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter will be smaller. [2]
Contents
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 2079
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 154
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 2076–2079
- Saros 154
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- References
- External links
The path of annularity will be visible from parts of New Zealand and Antarctica. A partial solar eclipse will also be visible for parts of Oceania, Antarctica, and southern South America.