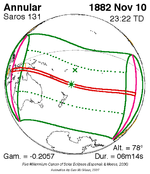
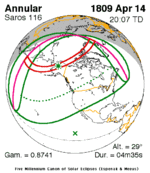
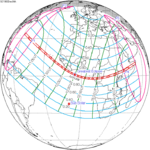
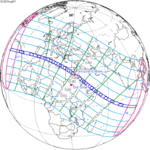
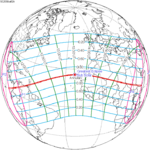
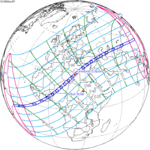
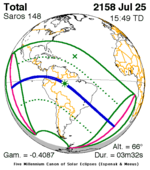
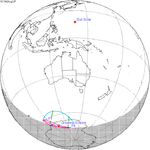
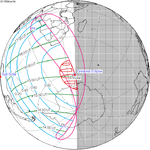
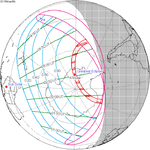
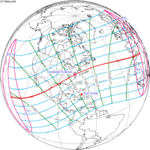
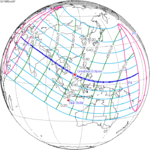
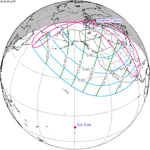
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, May 30, 1984, with a magnitude of 0.998. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in Mexico, the United States, Azores Islands, Morocco and Algeria. It was the first annular solar eclipse visible in the US in 33 years. The Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because it occurred 6.7 days after apogee and 7.8 days before perigee.
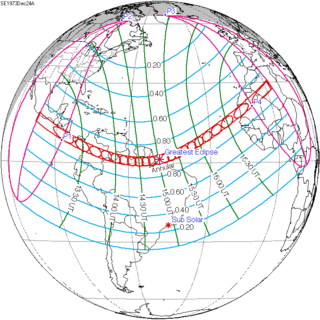
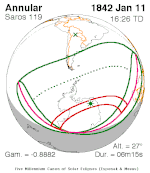
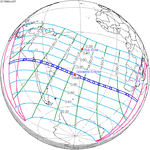
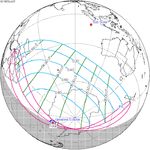
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Monday, December 24, 1973, with a magnitude of 0.9174. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from southern Mexico, southwestern Nicaragua, Costa Rica including the capital city San José, Panama, Colombia including the capital city Bogotá, southern Venezuela, Brazil, southern Guyana, southern Dutch Guiana, southern French Guiana, Portuguese Cape Verde including the capital city Praia, Mauritania including the capital city Nouakchott, Spanish Sahara, Mali, and Algeria.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, July 2, 2038, with a magnitude of 0.9911. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

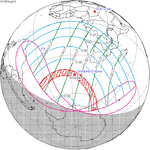
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Sunday, August 10, 1980, with a magnitude of 0.9727. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in Tabuaeran of Kiribati, Peru, Bolivia, northern Paraguay and Brazil. Occurring 5 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. At greatest eclipse, the Sun was 79 degrees above horizon.

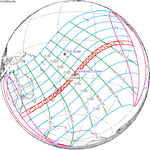
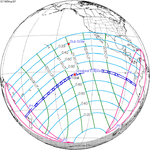
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Thursday, September 11, 1969, with a magnitude of 0.969. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from the Pacific Ocean, Peru, Bolivia and the southwestern tip of Brazilian state Mato Grosso. Places west of the International Date Line witnessed the eclipse on Friday, September 12, 1969.

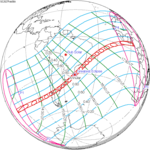
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, March 18, 1969, with a magnitude of 0.9954. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from part of Indonesia, and two atolls in the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands which belongs to the Federated States of Micronesia now.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Sunday, September 22, 2052, with a magnitude of 0.9734. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
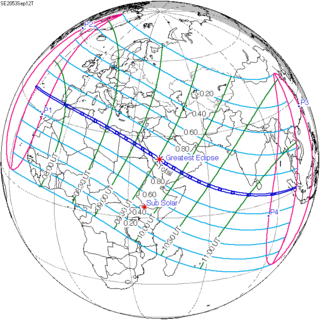
A total solar eclipse will take place at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, September 12, 2053, with a magnitude of 1.0328. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, July 12, 2056, with a magnitude of 0.9878. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, December 6, 2067, with a magnitude of 1.0011. It is a hybrid event, beginning and ending as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Sunday, December 16, 2085, with a magnitude of 0.9971. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. If a moon with same apparent diameter in this eclipse near the Aphelion, it will be Total Solar Eclipse, but in this time of the year, just 2 weeks and 4 days before perihelion, it is an Annular Solar Eclipse.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, July 24, 2074, with a magnitude of 0.9838. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
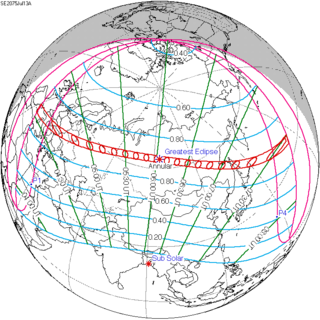
An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Saturday, July 13, 2075, with a magnitude of 0.9467. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometers wide.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Saturday, January 27, 2074, with a magnitude of 0.9798. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
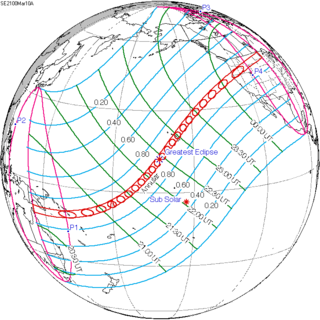
An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Wednesday, March 10 and Thursday, March 11, 2100, with a magnitude of 0.9338. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometers wide. The path of annularity will move from Indonesia at sunrise, over the islands of Hawaii and Maui around noon, and through the northwestern United States at sunset.
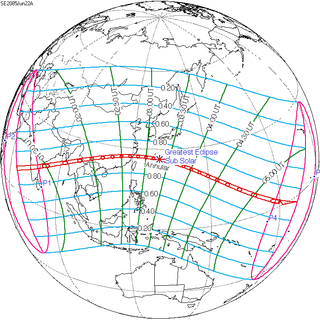
An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Friday, June 22, 2085, with a magnitude of 0.9704. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Sunday, June 28, 1908, with a magnitude of 0.9655. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Thursday, July 20, 1944, with a magnitude of 0.97. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from British Uganda, Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, British Kenya, Ethiopia, British Somaliland, British Raj, Burma, Thailand, French Indochina, Philippines, South Seas Mandate in Japan the Territory of New Guinea.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, February 24, 1933, with a magnitude of 0.9841. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from Chile, Argentina, Portuguese Angola, French Equatorial Africa, Belgian Congo, Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Ethiopia, French Somaliland, southeastern Italian Eritrea, and Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen, Aden Protectorate and Aden Province in British Raj.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, July 9, 1926, with a magnitude of 0.968. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from the islands of Pulo Anna and Merir in Japan's South Seas Mandate and Wake Island on July 10 (Saturday), and Midway Atoll on July 9 (Friday).