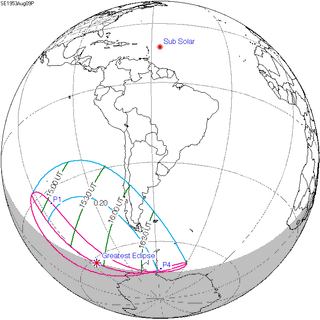
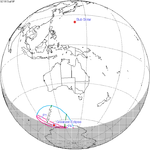
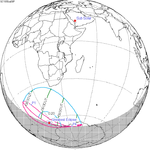
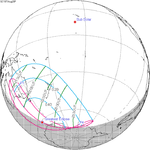
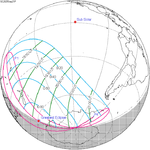
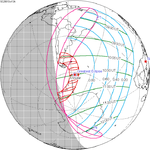
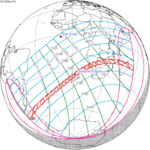
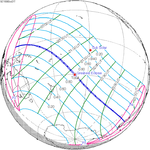
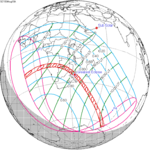
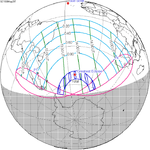
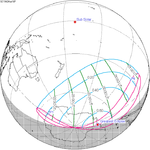
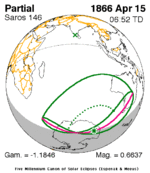
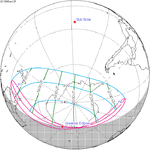
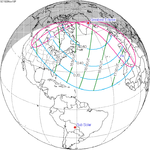
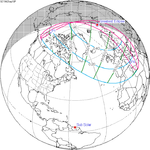
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of orbit on Tuesday, September 11, 2007, with a magnitude of 0.7507. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
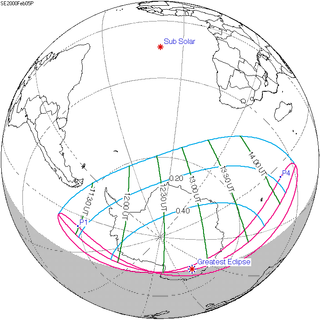
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of orbit on Saturday, February 5, 2000, with a magnitude of 0.5795. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

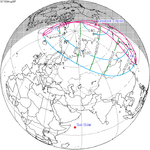
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Thursday, February 15, 2018, with a magnitude of 0.5991. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
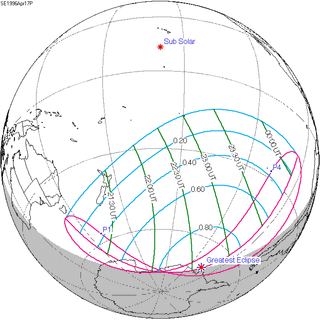
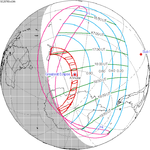
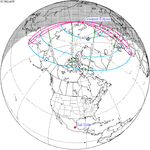
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit between Wednesday, April 17 and Thursday, April 18, 1996, with a magnitude of 0.8799. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
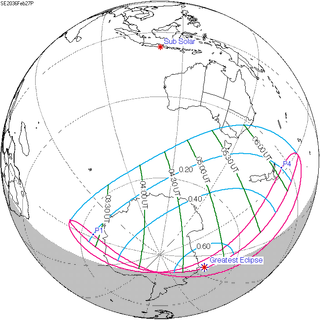
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, February 27, 2036, with a magnitude of 0.6286. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
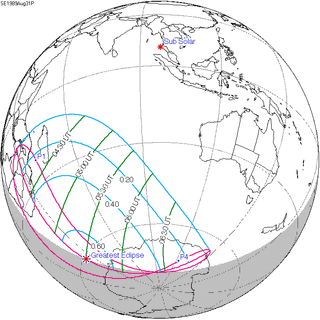
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Thursday, August 31, 1989, with a magnitude of 0.6344. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
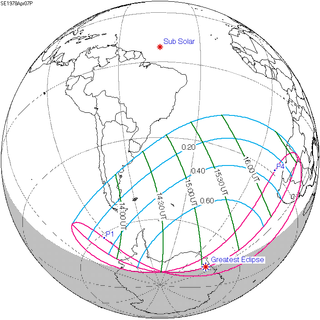
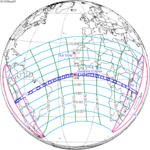
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Friday, April 7, 1978, with a magnitude of 0.7883. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
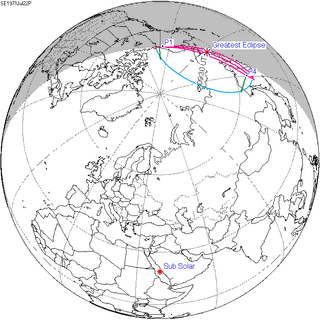
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Thursday, July 22, 1971, with a magnitude of 0.0689. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Sunday, March 27, 1960, with a magnitude of 0.7058. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Saturday, July 11, 1953, with a magnitude of 0.2015. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Sunday, November 4, 2040, with a magnitude of 0.8074. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Monday, March 9, 2054, with a magnitude of 0.6678. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
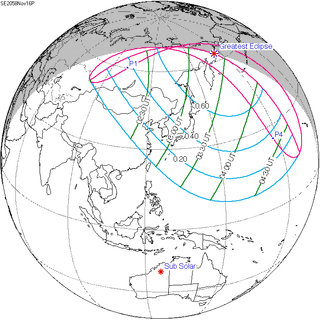
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Saturday, November 16, 2058, with a magnitude of 0.7644. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Saturday, March 19, 2072, with a magnitude of 0.7199. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit between Monday, February 6 and Tuesday, February 7, 2073, with a magnitude of 0.6768. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
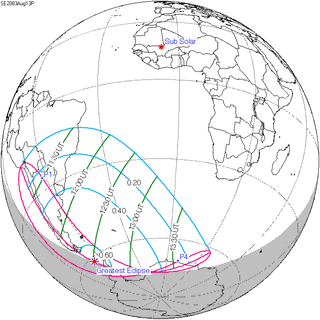
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Friday, August 13, 2083, with a magnitude of 0.6146. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
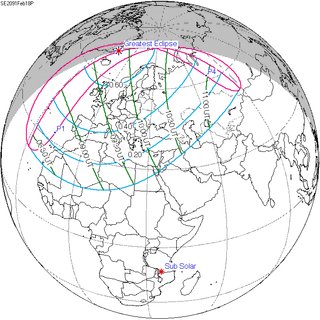
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Sunday, February 18, 2091, with a magnitude of 0.6558. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
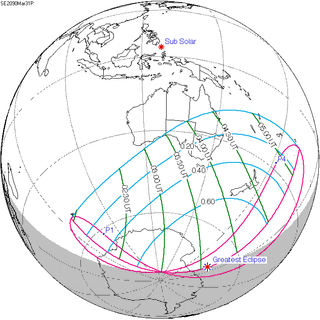
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Friday, March 31, 2090, with a magnitude of 0.7843. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
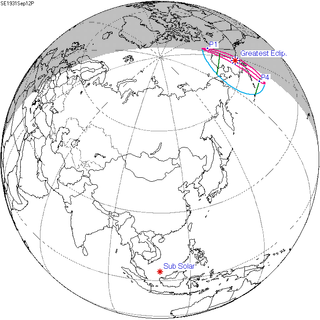
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Saturday, September 12, 1931, with a magnitude of 0.0471. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

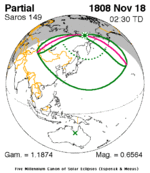
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Saturday, December 24, 1927, with a magnitude of 0.549. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.