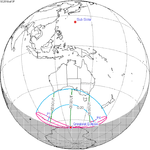
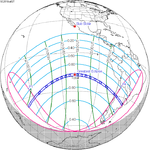
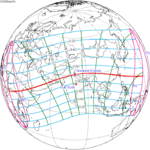
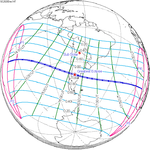
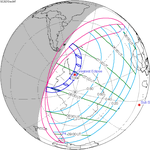
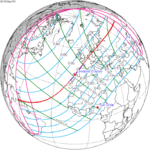
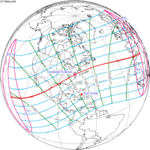
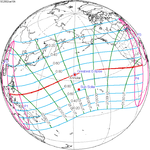
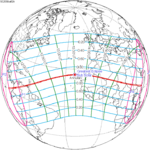
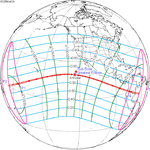
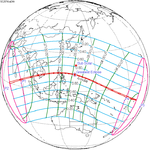
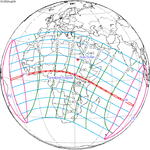
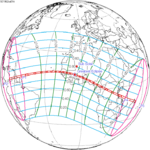
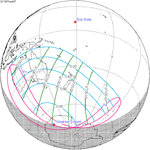
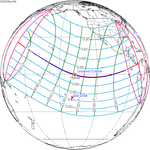
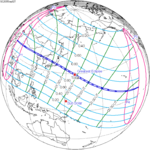
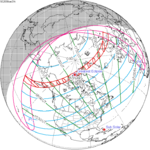
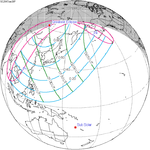
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of the orbit on Thursday, July 11, 1991. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality began over the Pacific Ocean and Hawaii moving across Mexico, down through Central America and across South America ending over Brazil. It lasted for 6 minutes and 53.08 seconds at the point of maximum eclipse. There will not be a longer total eclipse until June 13, 2132. This was the largest total solar eclipse of Solar Saros series 136, because eclipse magnitude was 1.07997.

The solar eclipse of May 20, 2012 was an annular solar eclipse that was visible in a band spanning through Eastern Asia, the Pacific Ocean, and North America. As a partial solar eclipse, it was visible from northern Greenland to Hawaii, and from eastern Indonesia at sunrise to northwestern Mexico at sunset. The moon's apparent diameter was smaller because the eclipse was occurring only 32 1/2 hours after apogee.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the ascending node of the Moon's orbit on Tuesday, July 2, 2019, with an eclipse magnitude of 1.0459. Totality was visible from the southern Pacific Ocean east of New Zealand to the Coquimbo Region in Chile and Central Argentina at sunset, with the maximum of 4 minutes 33 seconds visible from the Pacific Ocean. The Moon was only 2.4 days before perigee, making it fairly large.

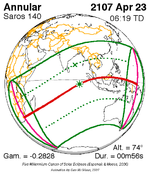
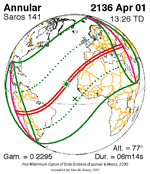
An annular solar eclipse took place at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on May 9–10 (UTC), 2013, with a magnitude of 0.9544. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on September 22, 2006. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The path of annularity of this eclipse passed through Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, the northern tip of Roraima and Amapá of Brazil, and the southern Atlantic.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node on 3 November 2013. It was a hybrid eclipse of the Sun with a magnitude of 1.0159, with a small portion over the western Atlantic Ocean at sunrise as an annular eclipse, and the rest of the path as a narrow total solar eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A hybrid solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's in sunrise and sunset, but at Greatest Eclipse the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's.

An annular solar eclipse took place on February 26, 2017. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 4.7 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. The moon's apparent diameter was just over 0.7% smaller than the Sun's.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on December 4, 1983. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in Cape Verde, Annobón Island of Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the People's Republic of Congo, Zaire, northern Uganda, southern Sudan, northwestern Kenya, Ethiopia and Somalia. The Sun's altitude was 66°. Occurring 6.5 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the moon's descending node of its orbit on Tuesday, May 10, 1994. It was visible over a wide swath of North America, from Baja California across the Midwest of the United States up through Ontario and Nova Scotia in Canada. Occurring only 1.6 days after apogee, the moon's apparent diameter was smaller than the sun. This solar eclipse belonged to Saros series 128.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on Thursday, June 10, 2021, when the Moon passed between Earth and the Sun, thereby partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. During the eclipse, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller than the Sun's, so it caused the Sun to look like an annulus. The annular eclipse was visible from parts of northeastern Canada, Greenland, the Arctic Ocean, and the Russian Far East, whilst the eclipse appeared partial from a region thousands of kilometres wide, which included northeastern North America, most of Europe, and northern Asia.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on May 30, 1984. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in Mexico, the United States, Azores Islands, Morocco and Algeria. It was the first annular solar eclipse visible in the US in 33 years. The moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because occurs 6.7 days after apogee and 7.8 days before perigee.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on June 11, 1983. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 48 hours before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred on November 22, 1984. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and southern Pacific Ocean. West of the International Date Line the eclipse took place on November 23, including all land in the path of totality. Occurring only 2.1 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was fairly larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred on June 30, 1992. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southeastern Uruguay and southern tip of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.

A hybrid solar eclipse occurred on Thursday, April 20, 2023. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun thereby totally or partly obscuring the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A hybrid solar eclipse is a rare type of solar eclipse that changes its appearance from annular to total and back as the Moon's shadow moves across the Earth's surface. Totality occurs in a narrow path across the surface of the Earth, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometers wide. Hybrid solar eclipses are extremely rare, occurring in only 3.1% of solar eclipses in the 21st century.
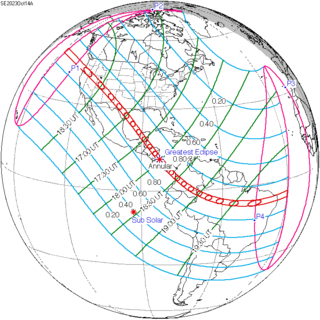
An annular solar eclipse will occur on Saturday, October 14, 2023. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres or miles wide. Occurring only 4.6 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be small.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on December 14, 1955. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse will occur on Friday, October 25, 2041. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
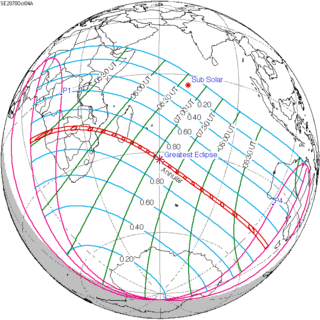
An annular solar eclipse will occur on October 4, 2070. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Saturday, May 22, 2077. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.