| Annular eclipse | |
| Gamma | 0.4169 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 0.9728 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 198 s (3 min 18 s) |
| Coordinates | 2°06′N25°24′W / 2.1°N 25.4°W |
| Max. width of band | 107 km (66 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 13:47:11 |
| References | |
| Saros | 132 (47 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9592 |
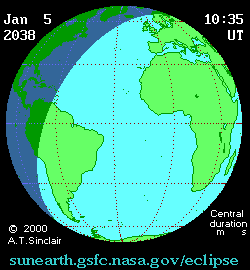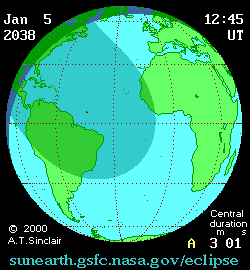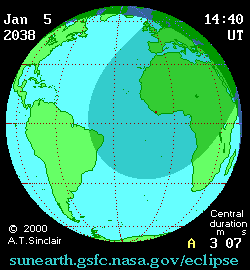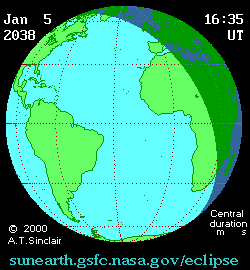
An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Tuesday, January 5, 2038, [1] with a magnitude of 0.9728. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter will be near the average diameter because it will occur 6.8 days after perigee (on December 29, 2037, at 18:50 UTC) and 7 days before apogee (on January 12, 2038, at 14:00 UTC). [2]
Contents
- Images
- Eclipse timing
- Places experiencing annular eclipse
- Places experiencing partial eclipse
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 2038
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 132
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 2036–2039
- Saros 132
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- References
- External links
Annularity will be visible from parts of Cuba, Haiti, the Dominican Republic, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Barbados, Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Togo, Benin, northwestern Nigeria, Niger, Chad, southeastern Libya, northwestern Sudan, and southwestern Egypt. A partial eclipse will be visible for parts of eastern North America, Central America, the Caribbean, northern South America, Europe, and the northern two-thirds of Africa.