| Annular eclipse | |
 Partial from Adelaide, Australia | |
| Gamma | −1.00001 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 0.9868 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | - |
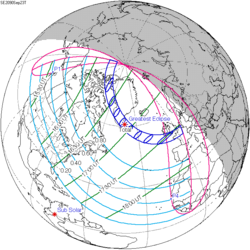
| Coordinates | 70°36′S131°18′E / 70.6°S 131.3°E |
| Max. width of band | - km |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 3:52:38 |
| (U1) Total begin | 5:47:50 |
| Greatest eclipse | 6:04:33 |
| (U4) Total end | 6:09:20 |
| (P4) Partial end | 8:14:28 |
| References | |
| Saros | 148 (21 of 75) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9539 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Tuesday, April 29, 2014, [1] [2] with a magnitude of 0.9868. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because it occurred 6.2 days after perigee (on April 23, 2014, at 1:20 UTC) and 7.2 days before apogee (on May 6, 2014, at 11:20 UTC). [3]
Contents
- Images
- Gallery
- Eclipse timing
- Places experiencing partial eclipse
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 2014
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 148
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 2011–2014
- Saros 148
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- Notes
- References
- External links
This eclipse's gamma value was closer to 1 than any other eclipse from 2000 B.C. to 3000 A.D. This means the center of the Moon's shadow passed almost exactly at the surface of the Earth, barely missing the Antarctic continent by a few kilometers, but an annular eclipse was visible from a small part of Antarctica, and a partial eclipse was visible from parts of Antarctica and Australia.