| Annular eclipse | |
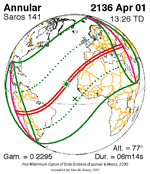
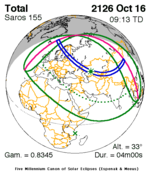
| Gamma | 0.4171 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 0.9174 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 722 s (12 min 2 s) |
| Coordinates | 1°06′N48°30′W / 1.1°N 48.5°W |
| Max. width of band | 345 km (214 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 15:02:44 |
| References | |
| Saros | 141 (21 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9451 |
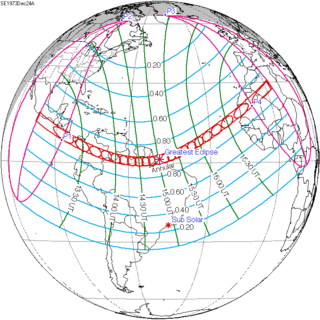
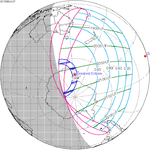
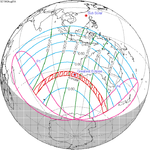
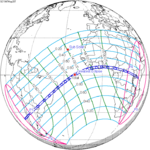
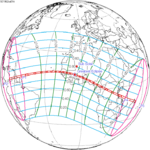
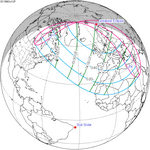
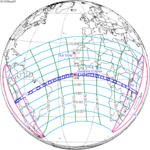
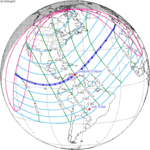
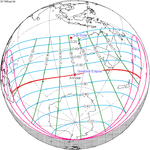
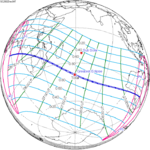
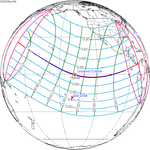
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Monday, December 24, 1973, [1] with a magnitude of 0.9174. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.25 days before apogee (on December 25, 1973, at 21:30 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. [2]
Contents
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 1973
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 141
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 1971–1974
- Saros 141
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- Notes
- References
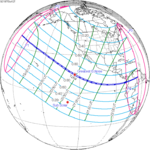
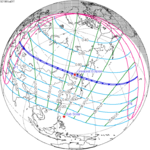
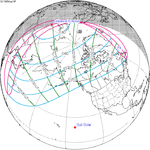
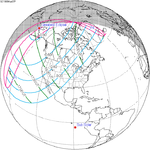
The duration of annularity at maximum eclipse (closest to but slightly shorter than the longest duration) was 12 minutes, 2.37 seconds in the Atlantic Ocean near the Brazilian coast. It was the longest annular solar eclipse until January 14, 3080, but the Solar eclipse of December 14, 1955 lasted longer. [3]
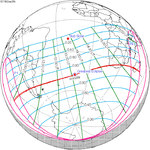
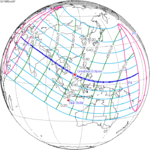
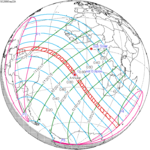
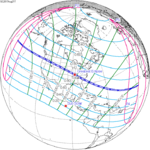
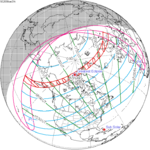
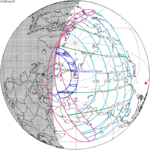
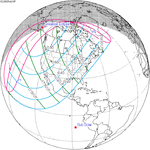
Annularity was visible from southern Mexico, southwestern Nicaragua, Costa Rica including the capital city San José, Panama, Colombia including the capital city Bogotá, southern Venezuela, Brazil, southern Guyana, southern Dutch Guiana (today's Suriname), southern French Guiana, Portuguese Cape Verde (today's Cape Verde) including the capital city Praia, Mauritania including the capital city Nouakchott, Spanish Sahara (today's Western Sahara), Mali, and Algeria. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of eastern North America, Central America, the Caribbean, northern and central South America, Western Europe, and West Africa.