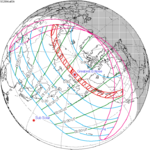
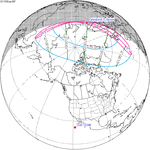
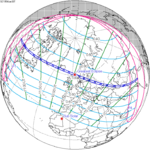
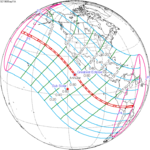
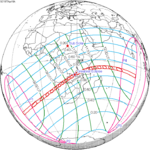
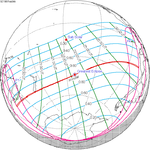
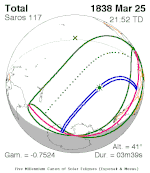
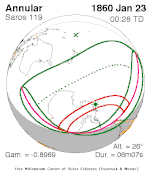
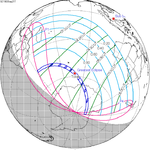
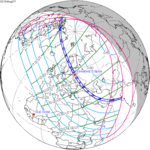
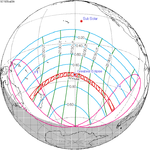
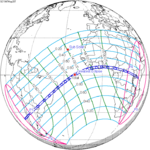
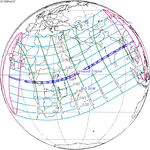
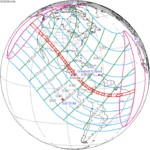
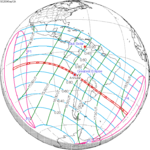
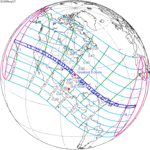
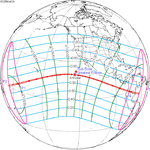
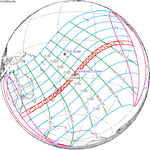
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, December 4, 2002, with a magnitude of 1.0244. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.9 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Thursday, June 21, 2001, with a magnitude of 1.0495. It was the first solar eclipse of the 21st century. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 2.25 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit between Saturday, March 8 and Sunday, March 9, 1997, with a magnitude of 1.042. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 18.5 hours after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

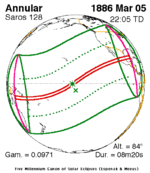
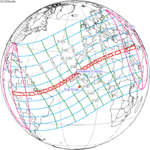
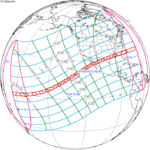
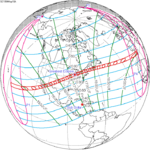
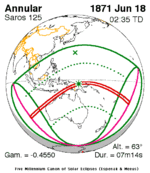
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Thursday, April 29, 1976, with a magnitude of 0.9421. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.9 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, October 24, 1995, with a magnitude of 1.0213. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 2.7 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Saturday, June 11, 1983, with a magnitude of 1.0524. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 2.1 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.
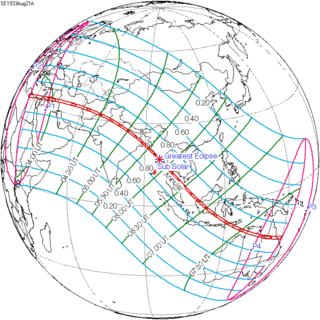
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Monday, August 21, 1933, with a magnitude of 0.9801. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 5.6 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, September 23, 1987, with a magnitude of 0.9634. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 5 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Sunday, September 22, 1968, with a magnitude of 1.0099. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 3.4 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.
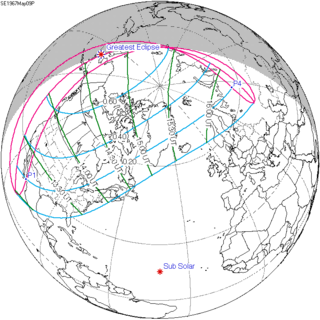
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, May 9, 1967, with a magnitude of 0.7201. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
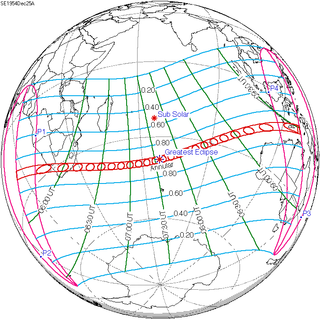
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Saturday, December 25, 1954, with a magnitude of 0.9323. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometers wide. Occurring about 4.9 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.
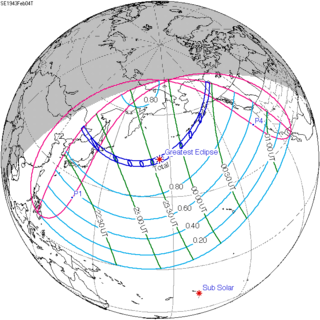
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit between Thursday, February 4 and Friday, February 5, 1943, with a magnitude of 1.0331. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 22 hours after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.
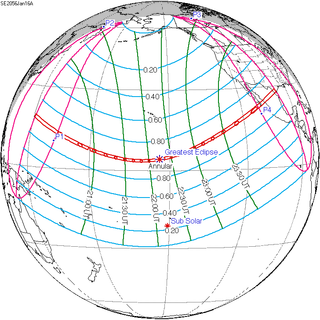
An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit between Sunday, January 16 and Monday, January 17, 2056, with a magnitude of 0.9759. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter will be near the average diameter because it will occur 6.25 days after perigee and 7.2 days before apogee.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Sunday, September 21, 1941, with a magnitude of 1.0379. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 2.25 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, July 24, 2074, with a magnitude of 0.9838. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 5.6 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be larger.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Thursday, October 14, 2088, with a magnitude of 0.9727. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 6.3 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be smaller.
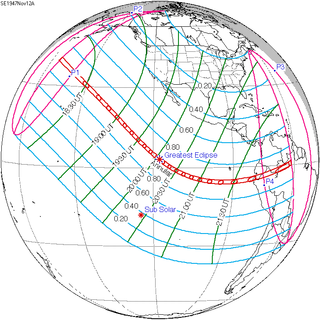
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, November 12, 1947, with a magnitude of 0.965. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 6.1 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Saturday, May 8 and Sunday, May 9, 1948, with a magnitude of 0.9999. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because it occurred 7 days after apogee and 6.7 days before perigee.

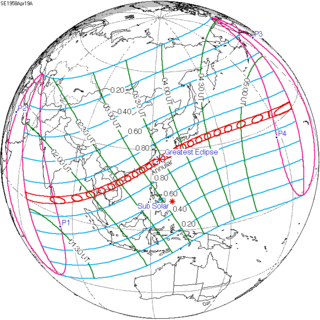
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, April 19, 1939, with a magnitude of 0.9731. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 6.3 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Friday, July 9 and Saturday, July 10, 1926, with a magnitude of 0.968. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 4.3 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.