| Partial eclipse | |
| Gamma | 1.0348 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 0.9282 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 61°12′N153°42′W / 61.2°N 153.7°W |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 3:00:23 |
| References | |
| Saros | 124 (54 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9518 |
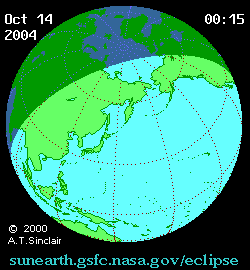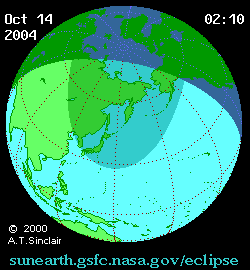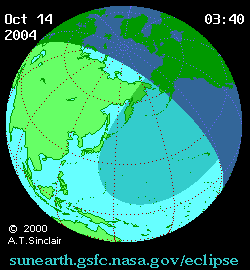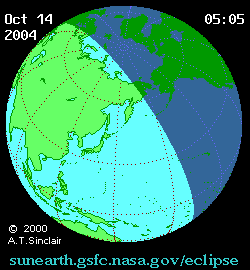
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit between Wednesday, October 13 and Thursday, October 14, 2004, [1] [2] [3] with a magnitude of 0.9282. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
Contents
- Images
- Eclipse timing
- Places experiencing partial eclipse
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 2004
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 124
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 2004–2007
- Saros 124
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- Notes
- References
- External links
A partial eclipse was visible for parts of eastern Russia, Mongolia, northeastern China, Korea, Japan, Hawaii, and western Alaska.