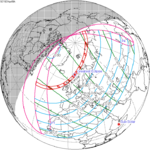
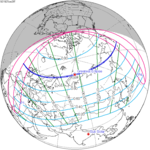
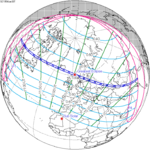
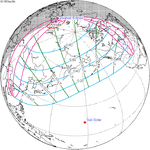
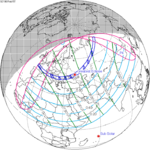
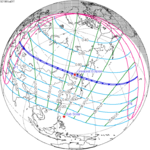
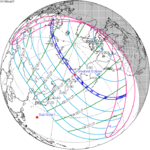
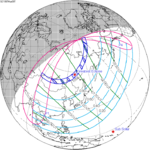
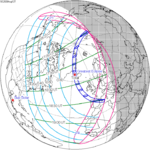
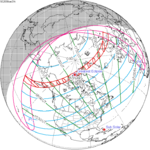
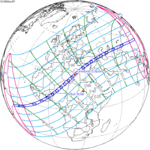
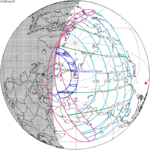
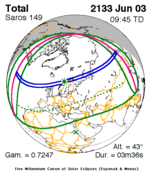
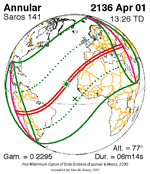
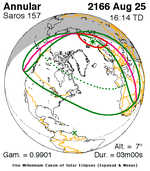
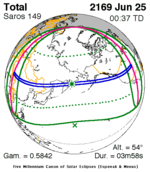
A total lunar eclipse occurred on 28 August 2007, lasting just over 90 minutes. The Moon entered the Earth's penumbra at 7:53:40 UTC. The first partial phase began in earnest at 8:51:16 UTC when the Moon entered the Earth's umbra. It exited the penumbra at 13:20:57 UTC.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Sunday 24 April 2005, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2005. At maximum eclipse, 86.5% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a slight shadow gradient across its disc; this subtle effect may have been visible to careful observers. No part of the Moon was in complete shadow. The eclipse lasted 4 hours and 6 minutes overall, and was visible from east Asia, Australia, and the Americas.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Sunday 30 December 2001, the last of three lunar eclipses in 2001. At maximum eclipse, 89.477% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a slight shadow gradient across its disc; this subtle effect may have been visible to careful observers. No part of the Moon was in complete shadow. The eclipse lasted 4 hours, 4 minutes and 17.7 seconds overall. This lunar eclipse followed the Annular Solar Eclipse on 14 December 2001.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Sunday, January 31, 1999, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1999.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place at the Moon's ascending node on 11 February 2017, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2017. It was not quite a total penumbral lunar eclipse. It occurred the same day as comet 45P/Honda–Mrkos–Pajdušáková made a close approach to Earth. It also occurred on the Lantern Festival, the first since 9 February 2009. Occurring only 4.4 days after perigee, the moon's apparent diameter was larger.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, April 14, 1987, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1987, the second being on October 7, 1987. This subtle penumbral eclipse may have been visible to a skilled observer at maximum eclipse. 77.703% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a gentle shadow gradient across its disc at maximum; the eclipse as a whole lasted 3 hours, 54 minutes and 12.8 seconds. The Moon was just 4.6 days before perigee, making it 0.5% larger than average.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, December 20, 1983, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1983. At the maximum eclipse, 89% of the Moon's disk was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a slight shadow gradient across its disc; this subtle effect may have been visible to careful observers. No part of the Moon was in complete shadow. The eclipse lasted 4 hours and 2 minutes overall.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, January 20, 1981, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1981. In a rare total penumbral eclipse, the entire Moon was partially shaded by the Earth, and the shading across the Moon should have been quite visible at maximum eclipse. The penumbral phase lasted for 4 hours and 24 minutes in all, though for most of it, the eclipse was extremely difficult or impossible to see. The moon's apparent diameter was larger because the eclipse occurred 5.2 days after perigee.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the ascending node of the Moon's orbit on Tuesday, July 2, 2019, with an eclipse magnitude of 1.0459. Totality was visible from the southern Pacific Ocean east of New Zealand to the Coquimbo Region in Chile and Central Argentina at sunset, with the maximum of 4 minutes 33 seconds visible from the Pacific Ocean. The Moon was only 2.4 days before perigee, making it fairly large.

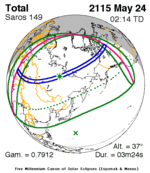
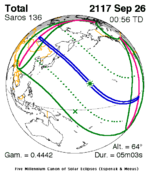
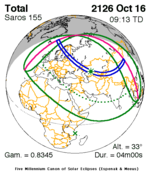
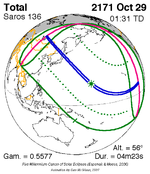
A total solar eclipse will occur on Wednesday, March 30, 2033. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse occurred on Sunday, July 22, 1990. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southern Finland, the Soviet Union, and eastern Andreanof Islands and Amukta of Alaska.

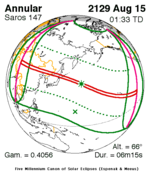
An annular solar eclipse occurred on Sunday, June 21, 2020. An annular solar eclipse is a solar eclipse whose presentation looks like a ring, or annulus; it occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most, but not all, of the Sun's light. In this instance, the Moon's apparent diameter was 0.6% smaller than the Sun's.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on Thursday, June 10, 2021, when the Moon passed between Earth and the Sun, thereby partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. During the eclipse, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller than the Sun's, so it caused the Sun to look like an annulus. The annular eclipse was visible from parts of northeastern Canada, Greenland, the Arctic Ocean, and the Russian Far East, whilst the eclipse appeared partial from a region thousands of kilometres wide, which included northeastern North America, most of Europe, and northern Asia.

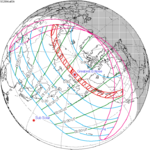
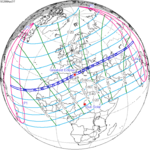
Saros cycle series 112 for lunar eclipses occurs at the moon's ascending node, 18 years 11 and 1/3 days. It contains 72 events, with 15 total eclipses, starting in 1364 and ending in 1616. Solar Saros 119 interleaves with this lunar Saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.

A total solar eclipse occurred on August 18, 1868, also known as "The King of Siam's eclipse". A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.