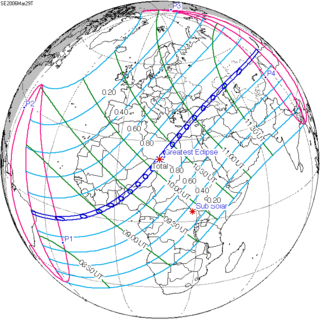
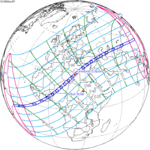
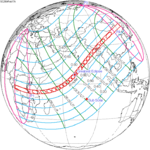
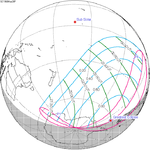
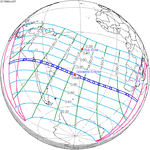
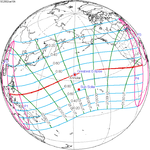
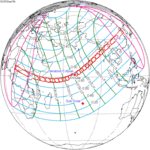
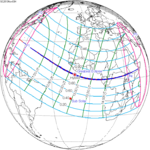
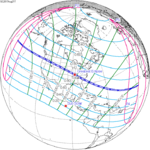
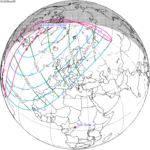
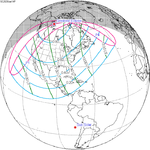
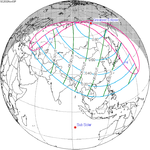
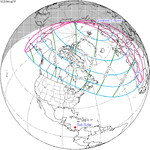
A total solar eclipse occurred on 11 August 1999 with an eclipse magnitude of 1.0286. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The path of the Moon's shadow began in the Atlantic Ocean and, before noon, was traversing the southern United Kingdom, northern France, Belgium, Luxembourg, southern Germany, Austria, Slovenia, Croatia, Hungary, and northern FR Yugoslavia (Vojvodina). The eclipse's maximum was at 11:03 UTC at 45.1°N 24.3°E in Romania ; and it continued across Bulgaria, the Black Sea, Turkey, northeastern tip of Syria, northern Iraq, Iran, southern Pakistan and Srikakulam in India and ended in the Bay of Bengal.

A total solar eclipse took place on November 23, 2003, with a magnitude of 1.0379. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It was visible from a corridor in the Antarctic region. A partial eclipse was seen from the much broader path of the Moon's penumbra, including the southern tip of South America and most of Australia.

A total solar eclipse took place on December 4, 2002, with a magnitude of 1.0244. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It was visible from a narrow corridor in southern Africa, the Indian Ocean and southern Australia. A partial eclipse was seen from the much broader path of the Moon's penumbra, including most of Africa and Australia. During the sunset after the eclipse many observers in Australia saw numerous and unusual forms of a green flash.

A total solar eclipse took place on June 21, 2001, with a magnitude of 1.0495. It was the first solar eclipse of the 21st century. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring 2.2 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. Depending on the zone it, could be seen June 20–22

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on October 3, 2005, with a magnitude of 0.958. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 4.8 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. It was visible from a narrow corridor through the Iberian peninsula and Africa and Brazil. A partial eclipse was seen from the much broader path of the Moon's penumbra, including all of Europe, Africa and southwestern Asia. The Sun was 96% covered in a moderate annular eclipse, lasting 4 minutes and 32 seconds and covering a broad path up to 162 km wide. The next solar eclipse in Africa occurred just 6 months later.

A total lunar eclipse occurred from 5:27 to 11:06 UTC on 21 December 2010, coinciding with the date of the Winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere and Summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere. It was visible in its entirety as a total lunar eclipse in North and South America, Iceland, Ireland, Britain and northern Scandinavia.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on August 1, 2008. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It had a magnitude of 1.0394 that was visible from a narrow corridor through northern Canada (Nunavut), Greenland, central Russia, eastern Kazakhstan, western Mongolia and China. Occurring north of the arctic circle, it belonged to the so-called midnight sun eclipses. The largest city in the path of the eclipse was Novosibirsk in Russia. Occurring only 2.5 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger than average.

A total lunar eclipse took place on 4 April 2015. It is the former of two total lunar eclipses in 2015, and the third in a tetrad. Other eclipses in the tetrad are those of 15 April 2014, 8 October 2014, and 28 September 2015.

A partial lunar eclipse occurred on 19 November 2021. The eclipse occurred towards a micromoon. This was the longest partial lunar eclipse since 18 February 1440, and the longest until 8 February, 2669; however, many eclipses, including the November 2022 lunar eclipse, have a longer period of umbral contact at next to 3 hours 40 minutes. It was often referred to as a "Beaver Blood Moon" although not technically fulfilling the criteria for a true blood moon (totality).

A total solar eclipse occurred on March 20, 2015. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with a partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. This total solar eclipse is notable in that the path of totality passed over the North Pole. Totality was visible in the Faroe Islands and Svalbard.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on Tuesday, April 29, 2014. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The center of the Moon's shadow missed the Earth's South Pole, but the partial eclipse was visible from parts of Antarctica and Australia, and an annular eclipse was visible from a small part of Antarctica.

A total solar eclipse took place at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on March 8–9, 2016. If viewed from east of the International Date Line, the eclipse took place on March 8 (Tuesday) and elsewhere on March 9 (Wednesday). A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's and the apparent path of the Sun and Moon intersect, blocking all direct sunlight and turning daylight into darkness; the Sun appears to be black with a halo around it. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The eclipse of March 8–9, 2016 had a magnitude of 1.0450 visible across an area of Pacific Ocean, which started in the Indian Ocean, and ended in the northern Pacific Ocean.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the ascending node of the Moon's orbit on Tuesday, July 2, 2019, with an eclipse magnitude of 1.0459. Totality was visible from the southern Pacific Ocean east of New Zealand to the Coquimbo Region in Chile and Central Argentina at sunset, with the maximum of 4 minutes 33 seconds visible from the Pacific Ocean. The Moon was only 2.4 days before perigee, making it fairly large.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node on 3 November 2013. It was a hybrid eclipse of the Sun with a magnitude of 1.0159, with a small portion over the western Atlantic Ocean at sunrise as an annular eclipse, and the rest of the path as a narrow total solar eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A hybrid solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's in sunrise and sunset, but at Greatest Eclipse the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of the orbit on Thursday, February 26, 1998. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in the Galápagos Islands, Panama, Colombia, the Paraguaná Peninsula in northwestern Venezuela, all of Aruba, most of Curaçao and the northwestern tip of Bonaire, all of Montserrat, Guadeloupe and Antigua and Barbuda.

A total solar eclipse occurred on July 22, 1990. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southern Finland, the Soviet Union, and eastern Andreanof Islands and Amukta of Alaska.

A total solar eclipse will occur on December 27, 2084. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A hybrid solar eclipse occurred on Thursday, April 20, 2023. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun thereby totally or partly obscuring the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A hybrid solar eclipse is a rare type of solar eclipse that changes its appearance from annular to total and back as the Moon's shadow moves across the Earth's surface. Totality occurs in a narrow path across the surface of the Earth, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometers wide. Hybrid solar eclipses are extremely rare, occurring in only 3.1% of solar eclipses in the 21st century.

A total solar eclipse will occur on April 11, 2070. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Saturday, May 22, 2077. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.