| Total eclipse | |
| Gamma | −0.8967 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 1.0316 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 132 s (2 min 12 s) |
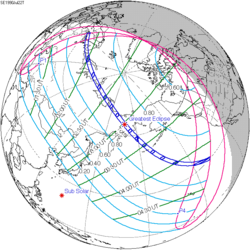
| Coordinates | 58°00′S77°12′E / 58°S 77.2°E |
| Max. width of band | 241 km (150 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 4:39:52 |
| References | |
| Saros | 123 (47 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9289 |
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Monday, September 21, 1903, [1] [2] [3] [4] with a magnitude of 1.0316. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 2.1 days after perigee (on September 19, 1904, at 2:00 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. [5]
Contents
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 1903
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 123
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 1902–1906
- Saros 123
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- Notes
- References
The path of totality crossed Antarctica and the south Indian Ocean. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of Southeast Africa, Southern Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica.