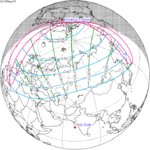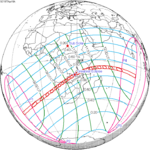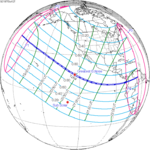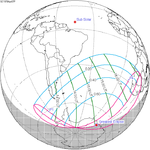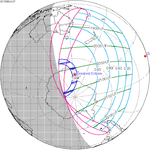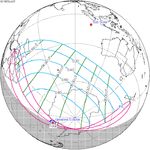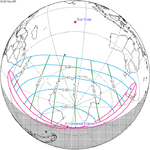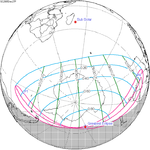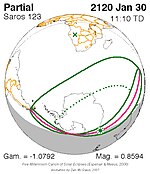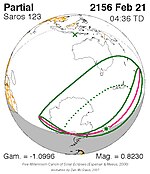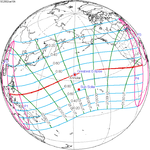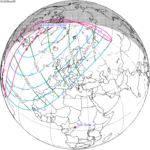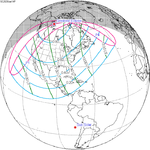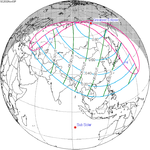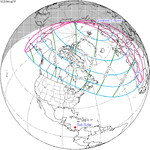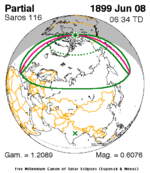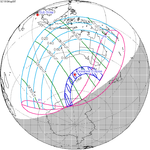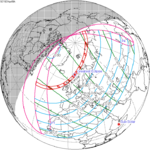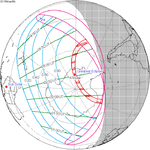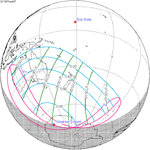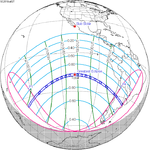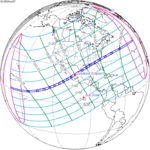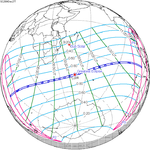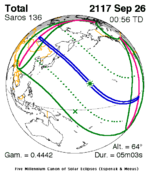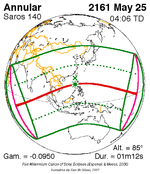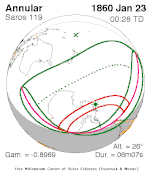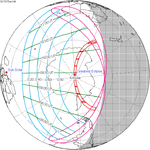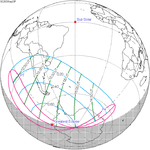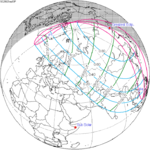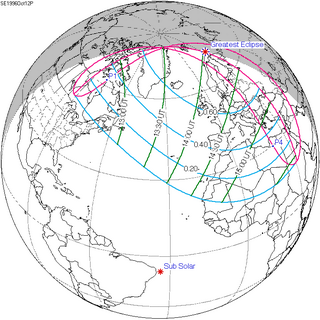
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Saturday, October 12, 1996, with a magnitude of 0.7575. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

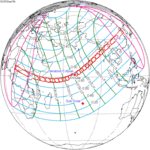
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Saturday, November 13 and Sunday, November 14, 1993, with a magnitude of 0.928. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
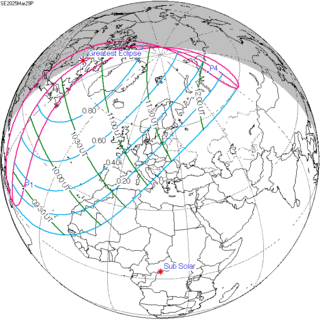
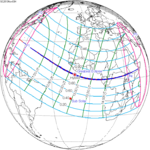
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit on Saturday, March 29, 2025, with a magnitude of 0.9376. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
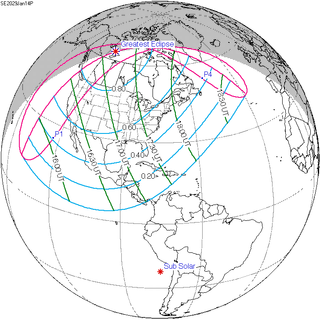
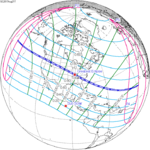
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Sunday, January 14, 2029, with a magnitude of 0.8714. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
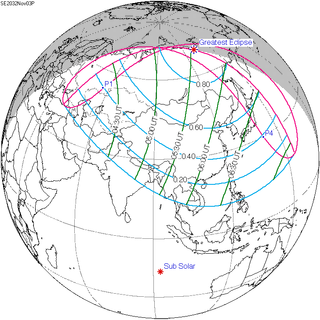
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, November 3, 2032, with a magnitude of 0.8554. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, March 7, 1989, with a magnitude of 0.8268. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, April 9, 1986, with a magnitude of 0.8236. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Monday, June 21, 1982, with a magnitude of 0.6168. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Monday, October 2, 1978, with a magnitude of 0.6905. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
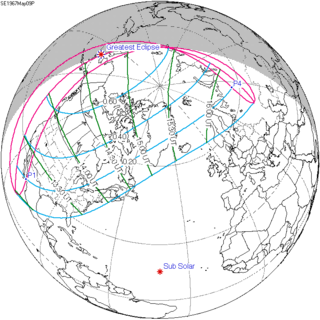
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, May 9, 1967, with a magnitude of 0.7201. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Tuesday, September 20 and Wednesday, September 21, 1960, with a magnitude of 0.6139. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
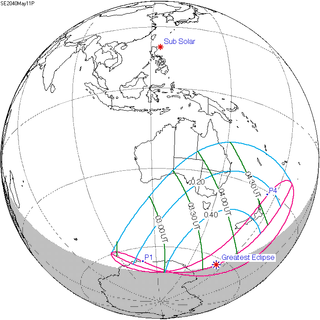
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, May 11, 2040, with a magnitude of 0.5306. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Monday, December 16 and Tuesday, December 17, 2047, with a magnitude of 0.8816. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Monday, November 14, 2050, with a magnitude of 0.8874. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
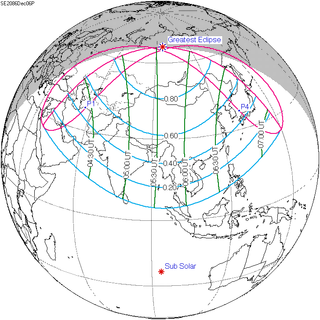
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, December 6, 2086, with a magnitude of 0.9271. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
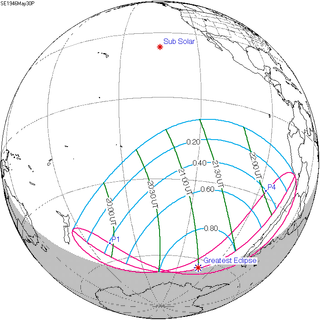
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Thursday, May 30, 1946, with a magnitude of 0.8865. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
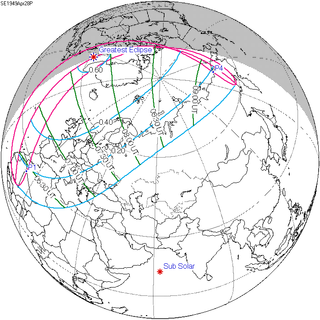
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Thursday, April 28, 1949, with a magnitude of 0.6092. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

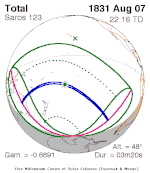
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Friday, April 17 and Saturday, April 18, 1931, with a magnitude of 0.5107. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
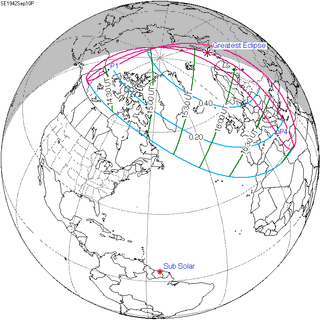
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Thursday, September 10, 1942, with a magnitude of 0.523. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Saturday, August 30, 1924, with a magnitude of 0.4245. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.