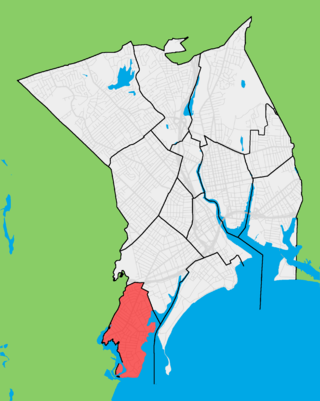
Black Rock is a neighborhood in the southwestern section of the city of Bridgeport, Connecticut. It borders Fairfield and the Ash Creek tidal estuary on the west, the West Side/West End of Bridgeport on the north and east, and Black Rock Harbor and Long Island Sound on the south. Black Rock comprises census tracts 701 and 702 and part of census tract 703. It includes two historic districts listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Residences comprise 86% of properties in Black Rock, 10% are commercial, and 4% are industrial or other property classes.

The history of Bridgeport, Connecticut was, in the late 17th and most of the 18th century, one of land acquisitions from the native inhabitants, farming and fishing. From the mid-18th century to the mid-19th century, Bridgeport's history was one of shipbuilding, whaling and rapid growth. Bridgeport's growth accelerated even further from the mid-19th century to the mid-20th century with the advent of the railroad, Industrialization, massive immigration, labor movements until, at its peak population in 1950, Bridgeport with some 159,000 people was Connecticut's second most populous city. In the late 20th century, Bridgeport's history was one of deindustrialization and declining population, though it overtook Hartford as the state's most populous city by 1980.

The Black Rock Historic District is a predominantly residential historic district in the Black Rock section of Bridgeport, Connecticut. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979. At that time it included 109 contributing buildings. The historic district surrounds at the upper reaches of Black Rock Harbor.

The Sterling Hill Historic District in Bridgeport, Connecticut is a historic district that was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1992. The district is a two-block area of 43 urban residential structures dating as far back as 1821. Most of the buildings are from later in the 19th century when the neighborhood was largely occupied by Irish working-class residents. Most of the early buildings are vernacular wood-frame structures with modest Federal, Greek Revival, or Gothic Revival details, while the later additions include multiunit tenement-style buildings. The area includes the oldest urbanized part of the city.

Bridgeport is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Connecticut and the fifth-most populous city in New England, with a population of 148,654 in 2020. Located in eastern Fairfield County at the mouth of the Pequonnock River on Long Island Sound, it is a port city 60 miles (97 km) from Manhattan and 40 miles (64 km) from The Bronx. It is bordered by the towns of Trumbull to the north, Fairfield to the west, and Stratford to the east. Bridgeport and other towns in Fairfield County make up the Greater Bridgeport Planning Region, as well as the Bridgeport-Stamford-Norwalk-Danbury metropolitan statistical area, the second largest metropolitan area in Connecticut. The Bridgeport-Stamford-Norwalk-Danbury metropolis forms part of the New York metropolitan area.

Bassickville Historic District is a historic district encompassing a well-preserved late 19th-century residential development on the west side of Bridgeport, Connecticut. Located on Bassick, Howard, and Fairview Avenues, the area was developed as a residential subdivision of worker housing by Edmund Bassick. The development is characterized by nearly identical 1-1/2 story frame cottages exhibiting the Stick style of architecture. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1987.

The United States Housing Corporation Historic District is a residential historic district located on the west side of New London, Connecticut. It contains a relatively uniform collection of Colonial Revival houses, most of them built in 1919 and 1920 by the United States Housing Corporation, a United States federal government agency founded to provide housing for workers in strategically significant war-related industries. The development of this district was overseen by the noted landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted Jr. The district is bounded on the west by Colman Avenue, the south by West Pleasant Street, the east by Jefferson Street, and on the north by Fuller Street. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on April 16, 1990.

The Barnum–Palliser Historic District is a 5.9-acre (2.4 ha) residential historic district in Bridgeport, Connecticut. The area, bounded roughly by Austin Street, Myrtle Avenue, Atlantic Street, and Park Avenue, was developed by P.T. Barnum to provide worker housing in the 1880s. Many of the houses were designed by Palliser, Palliser & Co., and are interesting examples of Italianate, Queen Anne, and Stick/Eastlake architecture. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1982.

The Capen-Clark Historic District encompasses a residential neighborhood area in the North End of Hartford, Connecticut. Centered on Capen Street between Main and Enfield Streets, it contains a cross-section of post-Civil War Victorian vernacular housing styles, and shows in its development patterns the ebb and flow of the city's economy between about 1865 and 1910. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1982.

Historic Seaside Village Co-operative encompasses a primarily residential area in the South End of Bridgeport, Connecticut. It is bounded on the east by Iranistan Avenue, the north by South Avenue, the south by Forest Court and by the west by Alsace Street. The property consists of a densely built collection of brick rowhouses, arranged in irregular combinations. The village was developed during World War I to alleviate a housing shortage caused by an influx of workers hired to work in the city's munitions factories. It is a good example of an early government-funded project of this type, and was a collaborative design effort by R. Clipston Sturgis, Skinner & Walker, and Arthur Shurtleff. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1990.

The Imlay and Laurel Streets District is a residential historic district on portions of Imlay, Laurel, Hawthorn and Sigourney Streets in Hartford, Connecticut. The area is a densely built residential neighborhood developed between about 1870 and 1895, with predominantly brick Italianate and Queen Anne construction. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979.

The Civic Park Historic District is a primarily residential historic district roughly bounded by Welch and Brownell Boulevards Trumbull Avenue, Dupont Street, and Dartmouth Street, in Flint, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979.

The Cassidy House is a historic house at 691 Ellsworth Street in Bridgeport, Connecticut. Built in 1849, it is a well-preserved example of early Italianate residential architecture, and the only documented building in the city from that period which retains its original board and batten siding. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2011.

The Deacon's Point Historic District encompasses a historic 19th-century residential area of eastern Bridgeport, Connecticut. Roughly bounded by Seaview Avenue and Williston, Bunnell and Deacon Streets, the district was first laid out for development shortly after the American Civil War, and contains modest examples of residential architecture dating from 1866 to the early 20th century. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1992.

The Division Street Historic District encompasses one of the best-preserved 19th-century residential areas of Bridgeport, Connecticut. Now separated from downtown Bridgeport by the Connecticut Route 25 highway, the area includes a cross-section of 19th-century architectural styles, as well as a diversity of sophistication, from working-class accommodations to high-style Victorian mansions. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1982.

The Gateway Village Historic District encompasses a World War I-era housing project on the east side of Bridgeport, Connecticut. Centered on Alanson Road, the project was developed in the later years of the war to provide emergency housing for workers in the city's munitions factories. It is a rare design attributed to the female-led architectural firm Mead & Schenk, led by Marcia Mead and Anna P. Schenk. Gateway Village is an early example of Garden City movement design. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1990.

The Lakeview Village Historic District encompasses a historic World War I-era housing project on the east side of Bridgeport, Connecticut. Located northeast of Boston Avenue and west of Lakeview Cemetery, the development was built in 1918–20 to provide emergency housing for an influx of workers to the city's war production industries, and is a good early example of a Garden City movement subdivision. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1990.

The Park Apartments are a historic apartment building at 59 Rennell Street in Bridgeport, Connecticut. Built in 1916 during the First World War, it was the first development of the Bridgeport Housing Corporation, established to provide emergency housing for workers in the city's war-related industries. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1990.

The Remington City Historic District encompasses a World War I-era housing development in northeastern Bridgeport, Connecticut. Bounded by Stewart, Tudor, and Bond Streets, and Palisade Avenue, the area was developed by the Remington Arms company to attract workers to its nearby munitions factory. The complex is a well-preserved example of wartime housing in the city, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1990.

The Remington Village Historic District encompasses a World War I-era housing development in northeastern Bridgeport, Connecticut. Located on Willow Street and East Avenue between Boston and Barnum Avenues, the area was developed by the Remington Arms company to attract workers to its nearby munitions factory. The complex is a well-preserved example of wartime housing in the city, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1990.






















