
Barnstaple is a river-port town and civil parish in the North Devon district of Devon, England. The town lies at the River Taw's lowest crossing point before the Bristol Channel. From the 14th century, it was licensed to export wool from which it earned great wealth. Later it imported Irish wool, but its harbour silted up and other trades developed such as shipbuilding, foundries and sawmills. A Victorian market building survives, with a high glass and timber roof on iron columns.

North Devon is a local government district in Devon, England. Its council is based just outside Barnstaple, the district's largest town. The district also includes the towns of Ilfracombe, Lynton and Lynmouth and South Molton along with numerous villages, seaside resorts and surrounding rural areas.

Braunton is a large village, civil parish, ecclesiastical parish and former manor in Devon. The village is situated 5 miles (8 km) west of Barnstaple. It is one of the largest villages in Devon with a population at the 2021 census of 10,217 people. There are two electoral wards. Their joint population at the above census was 8,218. Within the parish is the fertile, low-lying Braunton Great Field, which adjoins the undulating Braunton Burrows, the Core Area in North Devon Biosphere Reserve, the largest psammosere in England. It confronts the Atlantic Ocean at the west of the parish at the large beach of Saunton Sands, one of the South West's international-standard surfing beaches.

The Lynton and Barnstaple Railway (L&B) was a single track, 1 ft 11+1⁄2 in narrow gauge railway. It opened in May 1898 and ran for slightly more than 19 miles (31 km) through the area bordering Exmoor in North Devon, England. Although it opened after the Light Railways Act 1896 came into force, it was authorised and constructed before that act. It was authorised under its own Act of Parliament and built to higher standards than similar railways of the time. It was notable as the only narrow gauge railway in Britain that was required to use main-line standard signalling. For a short period, it earned a modest return for shareholders, but for most of its existence it made a loss. In 1923, the L&B was taken over by the Southern Railway, and eventually closed in September 1935.

Pilton is a suburb of the town of Barnstaple, it is located about quarter of a mile north of the town centre, in the civil parish of Barnstaple, in the North Devon district, in the county of Devon, England. It was formerly a separate village. The civil parish of Pilton West covers the more rural parts of the ancient parish of Pilton that have not been incorporated into the town of Barnstaple. In 2009, the Pilton (Barnstaple) ward had a population of 4,239 living in some 1,959 dwellings. It has its own infants and junior school, houses one of Barnstaple's larger secondary schools, and one of Barnstaple's SEN specialist schools. North Devon Hospital is also within West Pilton parish. It has a Church Hall, two public houses, two hotels, and residential homes. It has residential estates of both private and public housing including flats. It also has a historic Church that dates back to at least the 11th Century.

Barnstaple Town railway station was an intermediate station on the L&SWR line to Ilfracombe, England.
Pilton Yard, in Barnstaple was, between 1898 and 1935, the main depot and operating centre of the Lynton and Barnstaple Railway ('L&B'), a narrow gauge line that ran through Exmoor from Barnstaple to Lynton and Lynmouth in north Devon, England. Pilton station was served by regular passenger services advertised between 1898 and 1904 after which only goods facilities were provided. Passengers were catered for at the nearby LSWR station, Barnstaple Town, which provided connections with trains on the standard gauge branch line to Ilfracombe. The L&B's main offices were also based at Pilton, in a building formerly belonging to the Tannery which had earlier occupied the site, and which took over the site after the railway closed.
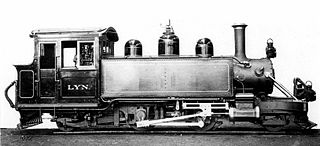
Lyn was a 2-4-2 tank steam locomotive built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1898 for the Lynton and Barnstaple Railway in England. While the original Lyn was scrapped in 1935, a complete recreation of the locomotive exists, having been completed in 2017, and bears the same name as its precursor.
The Chumhill railway accident occurred 26 February 1913 in England, killing two. The Lynton & Barnstaple Railway maintained an exemplary safety record throughout its short existence, from 1898 to 1935, and no passengers or members of the public were ever killed or injured.

Knowle is a village near Braunton located on the A361 road between Ilfracombe and Barnstaple in North Devon, England. It is in the civil parish of Braunton. Knowle is situated near to the Iron Age fortification of Knowle Hill Castle.

Mullacott is a small settlement on the A361 road between Ilfracombe and Barnstaple, in Devon, England. It is referred to as 'Mullacott Cross' and forms the crossroads between routes toward Woolacombe, Ilfracombe, Lynton and Braunton. There is an industrial estate, restaurant and horse riding stables.
The North Devon Railway connected Barnstaple to the growing railway network in 1854 and as Ilfracombe developed as a watering place, it was obvious a railway connection to the town was needed. The hilly terrain was very difficult, but an Ilfracombe Railway was authorised in 1864 but failed when a major shareholder was unable to respond to a subscription call. After several false starts the Barnstaple and Ilfracombe Railway, soon taken over by the London and South Western Railway, opened in 1870.

Lieutenant-Colonel William Harding of Upcott in the parish of Pilton in Devon, was a British antiquary, geologist and army officer. He was a Fellow of the Geological Society and after his retirement from the Army was an active member of the Exeter Diocesan Architectural and Archaeological Society. He is known for his History of Tiverton published in 1845 and 1847.

Lyd is a narrow gauge steam locomotive built by the Ffestiniog Railway in their own Boston Lodge shops over a period of 15 years.

Benjamin Incledon (1730–1796) of Pilton House, Pilton, near Barnstaple in North Devon, was an English antiquarian and genealogist. He served as Recorder of Barnstaple (1758–1796).

Pilton House in the parish of Pilton, near Barnstaple, North Devon, Ex31, is an historic grade II listed Georgian mansion house built in 1746 by Robert Incledon (1676-1758), twice Mayor of Barnstaple, who was from nearby Braunton. It is situated almost in the centre of the ancient town of Pilton, but had formerly extensive grounds covering at least 20 acres, which extended down "Pilton Lawn", now built over, to the River Yeo. It later served as the residence for various Members of Parliament for Barnstaple, for which it was well suited being only a 10-minute walk from the centre of that town, yet in a secluded situation with extensive grounds, and sufficiently large and grand for entertaining borough officials and electors.

Robert Incledon (1676–1758) of Pilton House, Pilton, near Barnstaple in North Devon, was a lawyer of New Inn, London, a Clerk of the Peace for Devon, Deputy Recorder of Barnstaple and was twice Mayor of Barnstaple, in 1712 and 1721. In 1713 as mayor he supervised the building of the Mercantile Exchange on Barnstaple Quay, as recorded on the building by a contemporary brass plaque and sculpture of his armorials. He built Pilton House in 1746.

Queen Anne's Walk is a grade I listed building in the town of Barnstaple, North Devon, completed in 1713 as a meeting place for the town's merchants. It is believed to have been designed by the architect William Talman, on the basis of its similarity to his work at the Hall in Drayton, Northamptonshire. It was promoted and financed by the thirteen members of the Corporation of Barnstaple whose armorials are sculpted on and above the parapet, and the work was overseen by Robert Incledon (1676–1758), Mayor of Barnstaple in 1712–13. It has been owned for many decades by North Devon District Council, which currently (2014) leases it to Barnstaple Town Council, and now trades as The Cafe on the Strand.

Sir Nicholas II Hooper (1654-1731) of Fullabrook, Braunton and Raleigh, Pilton in Devon, was a lawyer who served as Tory Member of Parliament for Barnstaple 1695-1715.















