The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance. A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property.

Benicia Capitol State Historic Park is a state park in Benicia, California. The park is dedicated to California’s third capitol building, where the California State Legislature convened from February 3, 1853 to February 24, 1854, when they voted to move the state capital to Sacramento. It is the only pre-Sacramento capitol that remains. The park includes the Fischer-Hanlon House, an early Benicia building that was moved to the property and converted into a home in 1858, after the legislature departed. Benicia Capitol State Historic Park just off the city's main street also includes a carriage house, workers' quarters and sculptured gardens.

Malakoff Diggins State Historic Park is a state park unit preserving the largest hydraulic mining site in California, United States. The mine was one of several hydraulic mining sites at the center of the 1882 landmark case Woodruff v. North Bloomfield Mining and Gravel Company. The mine pit and several Gold Rush-era buildings are listed on the National Register of Historic Places as the Malakoff Diggins-North Bloomfield Historic District. The "canyon" is 7,000 feet (2,100 m) long, as much as 3,000 feet (910 m) wide, and nearly 600 feet (180 m) deep in places. Visitors can see huge cliffs carved by mighty streams of water, results of the mining technique of washing away entire mountains of gravel to wash out the gold. The park is a 26-mile (42 km) drive north-east of Nevada City, California, in the Gold Rush country. The 3,143-acre (1,272 ha) park was established in 1965.

The Wyoming State Capitol is the state capitol and seat of government of the U.S. state of Wyoming. Built between 1886 and 1890, the capitol is located in Cheyenne and contains the chambers of the Wyoming State Legislature as well as the office of the Governor of Wyoming. It was designated a U.S. National Historic Landmark in 1987. The Capitol underwent an extensive three-year renovation and reopened to the public on July 10, 2019.

The California State Capitol is the seat of the Government of California, located in Sacramento, the state capital of California. The building houses the chambers of the California State Legislature, made up of the Assembly and the Senate, along with the office of the governor of California. The Neoclassical structure, designed by Reuben S. Clark, was completed between 1861 and 1874. Located at the west end of Capitol Park and the east end of the Capitol Mall, the building was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1973. The California State Capitol Museum is housed on the grounds of the capitol.

The New York State Capitol, the seat of the New York State government, is located in Albany, the capital city of the U.S. state of New York. The capitol building is part of the Empire State Plaza complex on State Street in Capitol Park. Housing the New York State Legislature, the building was completed in 1899 at a cost of US$25 million, making it the most expensive government building of its time. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1971, then included as a contributing property when the Lafayette Park Historic District was listed in 1978. The New York State Capitol was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1979.

Griffith Quarry, a registered California Historical Landmark listed on the National Register of Historic Places, was a former granite quarry near Penryn, California.

The Iowa Old Capitol Building is located in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. It was once the main government building for the state of Iowa, and it now stands as the most prominent landmark at the center of the University of Iowa's campus. The building was depicted on the 1946 Iowa Centennial commemorative half dollar. It was individually listed in the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in 1972, and it was named a U.S. National Historic Landmark in 1976. In 1978 it was included as a contributing property in the Pentacrest, a historic district listed on the NRHP.

The Big Four Building is a historic 19th-century building in Downtown Sacramento, California. It is now located within Old Sacramento State Historic Park and the Old Sacramento National Historic District.
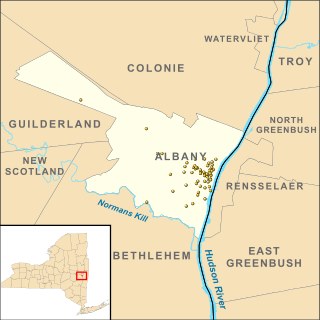
There are 70 properties listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Albany, New York, United States. Six are additionally designated as National Historic Landmarks (NHLs), the most of any city in the state after New York City. Another 14 are historic districts, for which 20 of the listings are also contributing properties. Two properties, both buildings, that had been listed in the past but have since been demolished have been delisted; one building that is also no longer extant remains listed.

The Lincoln Statue is an historic structure located on the grounds of the Greene County Courthouse in Jefferson, Iowa, United States. It was erected in 1918, and individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1993. In 2011 it was included as a contributing property in the Jefferson Square Commercial Historic District.

The statue of John Aaron Rawlins, a United States Army general who served during the Civil War and later as Secretary of War, is a focal point of Rawlins Park, a small public park in Washington, D.C.'s Foggy Bottom neighborhood. It was installed in 1874, but relocated several times between 1880 and 1931. The statue was sculpted by French-American artist Joseph A. Bailly, whose best known work is the statue of George Washington in front of Independence Hall in Philadelphia.

The Stephenson Grand Army of the Republic Memorial, also known as Dr. Benjamin F. Stephenson, is a public artwork in Washington, D.C. honoring Dr. Benjamin F. Stephenson, founder of the Grand Army of the Republic, a fraternal organization for Union veterans. The memorial is sited at Indiana Plaza, located at the intersection of 7th Street, Indiana Avenue, and Pennsylvania Avenue NW in the Penn Quarter neighborhood. The bronze figures were sculpted by J. Massey Rhind, a prominent 20th-century artist. Attendees at the 1909 dedication ceremony included President William Howard Taft, Senator William Warner, and hundreds of Union veterans.

The Provo Downtown Historic District is a 25-acre (10 ha) historic area located in Provo, Utah, United States. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

Italian Hall was a two-story commercial and recreational building in Calumet, Michigan, built in 1908 and demolished in 1984. Two prior buildings known popularly as "Italian Hall" had stood on the site. The first floor housed commercial space with a large hall on the second floor. The building served as headquarters for the Società Mutua Beneficenza Italiana and hosted community events. The hall is notorious as the site of a disaster in 1913 in which over 70 people died after a false cry of "fire" at a Christmas party. Since demolition, the site has served as a memorial park. The property is a Michigan State Historic Site and the building was formerly on the National Register of Historic Places.

Union Station is a building in Houston, Texas, in the United States. Dedicated on March 2, 1911, and formerly a hub of rail transportation, the building now serves as a cornerstone for Minute Maid Park. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places, and has since been superseded by Houston's Amtrak station.

The Stairs Station Hydroelectric Power Plant was built in 1894-1895 in Big Cottonwood Canyon, about 8 miles (13 km) southeast of Salt Lake City, Utah. The plant comprises the powerhouse, switchyard, penstocks, and a pipeline. A dam next to the site is associated with the Granite Power Plant farther downstream, and is part of neither historic district. The powerhouse is the only remaining building associated with the plant. It is an example of an intact high-head generating plant from the late 19th century.

The Memorial to Company A, Capitol Guards was an American Civil War memorial in MacArthur Park, Little Rock, Arkansas. It stood just northeast of the former Tower Building of the Little Rock Arsenal, at a junction of two of the park's internal roadways. It consisted of a bronze sculpture depicting a Confederate Army soldier in a defensive stance, holding a rifle pointed forward. The statue was 8 feet (2.4 m) in height, and was mounted in a granite column 16 feet (4.9 m) tall. The memorial was sometimes known as "Lest we forget", a line that appeared near the top of the inscription on the base. The statue was created by sculptor Rudolph Schwarz, and was installed in 1911; it was paid for by the local chapter of the Sons of Confederate Veterans, and memorializes the unit that seized the arsenal at the outset of the war.

The Downtown Cheyenne Historic District in Cheyenne, Wyoming is a historic district that was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978. It is an area of about seven blocks, in the core of the original business district of Cheyenne, and home of many of the first masonry commercial buildings in Cheyenne.



















