
John Alexander Logan was an American soldier and politician. He served in the Mexican–American War and was a general in the Union Army in the American Civil War. He served the state of Illinois as a State Senator, a Congressman, and a U.S. Senator and was an unsuccessful candidate for Vice President of the United States with James G. Blaine in the election of 1884. As the 3rd Commander-in-Chief of the Grand Army of the Republic, he is regarded as the most important figure in the movement to recognize Memorial Day as an official holiday.

Starved Rock State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of Illinois, characterized by the many canyons within its 2,630 acres (1,064 ha). Located just southeast of the village of Utica, in Deer Park Township, LaSalle County, Illinois, along the south bank of the Illinois River, the park hosts over two million visitors annually, the most for any Illinois state park.
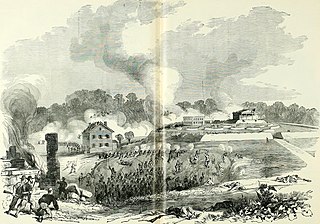
The Siege of Lexington, also known as the Battle of First Lexington, was a minor conflict of the American Civil War. The siege took place from September 13 to 20, 1861 between the Union Army and the pro-Confederate Missouri State Guard in Lexington, county seat of Lafayette County, Missouri. The victory won by the Missouri Guard bolstered the considerable Southern sentiment in the area, and briefly consolidated Missouri State Guard control of the Missouri River Valley in the western part of the state.

Fort Frederick State Park is a public recreation and historic preservation area on the Potomac River surrounding the restored Fort Frederick, a fortification active in the French and Indian War (1754–1763) and the American Revolutionary War (1775-1783). The state park lies south of the town of Big Pool, Maryland. The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal runs through the park grounds. The site was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1973.

Camp Randall is an historic U.S. Army site in Madison, Wisconsin, named after Wisconsin governor Alexander Randall, who served from 1858 to 1861. It was a training facility of the Union army during the Civil War, where more than 70,000 recruits were trained. The army also established a hospital and prisoner-of-war camp here.

Camp Butler National Cemetery is a United States National Cemetery located a few miles northeast of Springfield and a few miles southwest of Riverton, a small town nearby to Springfield, in Sangamon County, Illinois. It was named for Illinois State Treasurer at the time of its establishment, William Butler. Administered by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, it occupies approximately 53 acres (21 ha), and is the site of 19,825 interments as of the end of 2005. Camp Butler National Cemetery was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1997.

Fort Ward is a former Union Army installation now located in the city of Alexandria in the U.S. state of Virginia. It was the fifth largest fort built to defend Washington, D.C. in the American Civil War. It is currently well-preserved with 90-95% of its earthen walls intact.

Fort Selden was a United States Army post, occupying the area in what is now Radium Springs, New Mexico. The site was long a campground along the El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro. It was the site of a Confederate Army camp in 1861. The U. S. Army established Fort Selden in 1865 for the purpose of protecting westward settlers from Native American raids, the post fell into disrepair after the American Civil War. It was ultimately abandoned in 1891, due in large part to the decision to expand Fort Bliss and the lack of any expenditures for repair of the facility.

Fort McKavett State Historic Site is located in Menard County, Texas, United States. Fort McKavett was a frontier fort established as Camp on the San Saba in 1852 to protect settlers from Indian raids. The camp was renamed in honor of Captain Henry McKavett, who was killed in the Mexican–American War battle of Monterrey.

Liendo Plantation is an historic cotton plantation in Waller County, Texas, United States. Named after its original owner, José Justo Liendo, the plantation was purchased in 1873 by sculptor Elisabet Ney and her husband, physician Edmund Montgomery. The plantation is a Recorded Texas Historic Landmark and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The New Haven Battlefield is the area of American Civil War military engagements at the intersection of the Rolling Fork and the former Louisville and Nashville Railroad line between Knoxville and New Haven, Kentucky. The geographic area includes the James Howell Farm and additional combat areas of December 30, 1862.

Michael Kelly Lawler was a volunteer militia soldier in the Black Hawk War, 1831–1832, an officer in the United States Army in both the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War. In the latter conflict, as a brigadier general he commanded a brigade of infantry in the Western Theater and served in several battles.

Major General John A. Logan, also known as the General John A. Logan Monument and Logan Circle Monument, is an equestrian statue in Washington, D.C. that honors politician and Civil War general John A. Logan. The monument is sited in the center of Logan Circle, a traffic circle and public park in the Logan Circle neighborhood. The statue was sculpted by artist Franklin Simmons, whose other prominent works include the Peace Monument and statues in the National Statuary Hall Collection. The architect of the statue base was Richard Morris Hunt, designer of prominent buildings including the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City and The Breakers in Newport, Rhode Island. Prominent attendees at the dedication ceremony in 1901 included President William McKinley, members of his cabinet, Senator Chauncey Depew, Senator Shelby Moore Cullom, and General Grenville M. Dodge.

Historic Blenheim is a ca. 1859 brick farm house designed in the Greek Revival style and located in City of Fairfax, Virginia. During the American Civil War, Union soldiers were often encamped on the grounds surrounding the house and utilized it as part of a reserve hospital system. As a result, more than 115 of these soldiers inscribed words and pictures on the first and second floor walls, as well as the attic of the house. Blenheim was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2001.

The U.S. state of Illinois during the American Civil War was a major source of troops for the Union Army, and of military supplies, food, and clothing. Situated near major rivers and railroads, Illinois became a major jumping off place early in the war for Ulysses S. Grant's efforts to seize control of the Mississippi and Tennessee rivers. Statewide, public support for the Union was high despite Copperhead sentiment.

The Stephenson Grand Army of the Republic Memorial, also known as Dr. Benjamin F. Stephenson, is a public artwork in Washington, D.C. honoring Dr. Benjamin F. Stephenson, founder of the Grand Army of the Republic, a fraternal organization for Union veterans. The memorial is sited at Indiana Plaza, located at the intersection of 7th Street, Indiana Avenue, and Pennsylvania Avenue NW in the Penn Quarter neighborhood. The bronze figures were sculpted by J. Massey Rhind, a prominent 20th century artist. Attendees at the 1909 dedication ceremony included President William Howard Taft, Senator William Warner, and hundreds of Union veterans.

The Camp White Sulphur Springs Confederate Cemetery is an American Civil War cemetery in Arkansas. It is located northeast of the village of Sulphur Springs, also known as White Sulphur Springs, in Jefferson County.

The Alton Military Prison was a prison located in Alton, Illinois and originally built in 1833 as the first state penitentiary in Illinois and later closed in 1857. During the American Civil War, the prison was reopened in 1862 to accommodate the growing population of Confederate prisoners of war and ceased to be prison at the end of the war in 1865. The prison building was demolished not long after the Civil War. All that remains of the former prison site is a section of ruin wall that is maintained by the State of Illinois as an historic site. The prison site is included in the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

The Camp Harlan-Camp McKean Historic District, also known as the Hugh B. and Mary H. Swan Farmstead and the Springdale Stock Farm, is a nationally recognized historic district located northwest of Mount Pleasant, Iowa, United States. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2013. At the time of its nomination it consisted of eight resources, which includes two contributing buildings, one contributing site, one contributing object and four non-contributing buildings.





















