Components
Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Complex is an administrative unit of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service which oversees National Wildlife Refuges in Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Navassa Island of the U.S. Minor Outlying Islands. The NWR complex also reintroduces the critically endangered Puerto Rican parrot into the wild. [1]

The Caribbean Ecological Services Field Office was established in 1974 as part of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service's Southeast Region (Region 4). This organization within the Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex has jurisdiction over Federal Trust Species (federally listed endangered species, including migratory birds and inter-jurisdictional fish populations) and Strategic Habitat Conservation programs. The field office is based in Cabo Rojo, Puerto Rico, and although the office is not open to the general public [2] it also hosts the Cabo Rojo National Wildlife Refuge Visitor Center. [3]

Navassa Island is a small uninhabited island in the Caribbean Sea. Located northeast of Jamaica, south of Cuba, and 40 nautical miles west of Jérémie on the Tiburon Peninsula of Haiti, it is subject to an ongoing territorial dispute between Haiti and the United States, which administers the island through the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.

Puerto Rico, officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is an archipelagic island U.S. territory comprised of the eponymous main island of Puerto Rico and 142 smaller islands, including Vieques, Culebra, and Mona. It is located between the Greater and Lesser Antilles in the northeastern Caribbean Sea, east of Hispaniola, west of Saint Thomas, north of Venezuela, and south of the Puerto Rico Trench. Measuring 177 km in length and 65 km in width with a land area of 8,868 sq km, the main island is the 3rd largest in the U.S., 4th in the Caribbean, 29th in the Americas, and 81st in the world, making it the 174th largest country or dependency by surface area. With 3.2 million residents, it is the 2nd largest in the U.S., 4th in the Caribbean, 4th in the Americas, and 31st in the world, making it the 136th largest country or dependency by population.

The United States Minor Outlying Islands is a statistical designation applying to the minor outlying islands and groups of islands that comprise eight United States insular areas in the Pacific Ocean and one in the Caribbean Sea.

Vieques, officially Isla de Vieques, is an island, town and municipality of Puerto Rico, and together with Culebra, it is geographically part of the Spanish Virgin Islands. Vieques lies about 8 miles (13 km) east of the mainland of Puerto Rico, measuring about 20 miles (32 km) long and 4.5 miles (7 km) wide. Its most populated barrio is the town of Isabel Segunda, the administrative center located on the northern side of the island. The population of Vieques was 8,249 at the 2020 Census.

Isla Culebra is an island, town and municipality of Puerto Rico, and together with Vieques, it is geographically part of the Spanish Virgin Islands. It is located approximately 17 miles (27 km) east of the Puerto Rican mainland, 12 miles (19 km) west of St. Thomas and 9 miles (14 km) north of Vieques. Culebra is spread over 5 barrios and Culebra Pueblo (Dewey), the main town and the administrative center of the island. Residents of the island are known as culebrenses. With a population of 1,792 as of the 2020 Census, it is Puerto Rico's least populous municipality.

The Puerto Rican dry forests are a tropical dry forest ecoregion located in southwestern and eastern Puerto Rico and on the offshore islands. They cover an area of 1,300 km2 (500 sq mi). These forests grow in areas receiving less than 1,000 mm (39 in) of rain annually. Many of the trees are deciduous, losing their leaves during the dry season which normally lasts from December to April.
Caborrojeños Pro Salud y Ambiente, Inc. is a non-profit environmentalist organization based in Cabo Rojo, Puerto Rico.

Desecheo is a small uninhabited island of the archipelago of Puerto Rico in the northeast of the Mona Passage; 13 mi (21 km) from the municipality of Rincón on the west coast of the main island of Puerto Rico and 31 mi (50 km) northeast of Mona Island. It has a land area of 0.589 sq mi. Politically, the island is administered by the U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as the Desecheo National Wildlife Refuge, but part of the Sabanetas barrio of Mayagüez.

The Spanish Virgin Islands, formerly called the Passage Islands, commonly known as the Puerto Rican Virgin Islands, consist of the islands of Vieques and Culebra, located between the main island of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands in the northeastern Caribbean. Located between the Greater and Lesser Antilles, the islands are administratively part of the archipelago of Puerto Rico, and geographically part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles.

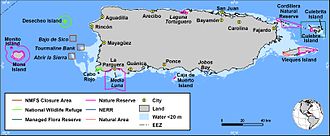
Cabo Rojo National Wildlife Refuge is an 1,836-acre National Wildlife Refuge located in southwestern Puerto Rico, in the municipality of Cabo Rojo. The refuge is a habitat for number of native bird species including the endangered yellow-shouldered blackbird, locally known as mariquita de Puerto Rico or capitán. Many birds find their way to the refuge while migrating between North and South America, and more than 118 bird species have been recorded near the area.
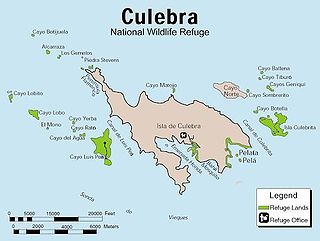
The Culebra National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge in Puerto Rico. It is part of the Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex, which is a unit of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. It is the site of the former Camp Roosevelt.

The Laguna Cartagena National Wildlife Refuge is a 1043-acre National Wildlife Refuge in Lajas, Puerto Rico. It is part of the Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex.

The Vieques National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge on the island of Vieques in the Puerto Rico archipelago. It is part of the Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex.

Sierra Bermeja is a mountain range in southwestern Puerto Rico. It forms the southern boundary of the Lajas Valley and it is bordered by La Parguera in the Caribbean Sea coast. It extends from the municipality of Cabo Rojo in the west to Lajas in the east. It consists of a combination of volcanic rocks, completely crossed by serpentinite and amphibolite faults, which could well be the oldest known rock in Puerto Rico. The mountains were used by the Taíno people as refuge from the Spanish, and then by smugglers during the Spanish colonization.

Monte Pirata, at 960 feet of elevation, is the highest mountain in the island of Vieques. The mountain is located in the western portion of the Vieques National Wildlife Refuge and it is the site of an old US Navy communications site, now operated by the Department of Homeland Security]. Hiking used to be permitted in the mountain, and there is a trail leads to the summit. Although the main trail has been closed to the general public for the past 20 years, an observation platform is being installed and currently there is interest in revitalizing and reopening the entire area.

Los Morrillos de los Cabos Rojos or more commonly known as Los Morrillos de Cabo Rojo, is a cape and tombolo landform located in southwestern Puerto Rico in the municipality of Cabo Rojo. Los Morrillos is an excellent example of a tombolo, or a tied island, with two sand pits. The cape resembles a letter Y with its two promontories or morrillos being connected through sand pits which enclose a saltwater lagoon. The landform was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1980, and the site includes mangroves, beaches, important bird nesting areas, limestone caves, cliffs and rock formations. The reddish-colored limestone cliffs give the name to the town and municipality of Cabo Rojo.

Mona and Monito Islands Nature Reserve consists of two islands, Mona and Monito, in the Mona Passage off western Puerto Rico in the Caribbean. Mona and Monito Islands Nature Reserve encompasses both land and marine area, and with an area of 38,893 acres it is the largest protected natural area in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. Much like the Galapagos Islands in the Pacific Ocean, the Mona and Monito Islands reserve represents a living laboratory for archaeological, biological, geological, oceanographical and wildlife management research.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires |journal= (help)