
Puerto Rico, officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is an archipelagic island U.S. territory comprised of the eponymous main island of Puerto Rico and 142 smaller islands, including Vieques, Culebra, and Mona. It is located between the Greater and Lesser Antilles in the northeastern Caribbean Sea, east of Hispaniola, west of Saint Thomas, north of Venezuela, and south of the Puerto Rico Trench. Measuring 177 km in length and 65 km in width with a land area of 8,868 sq km, the main island is the 3rd largest in the U.S., 4th in the Caribbean, 29th in the Americas, and 81st in the world, making it the 174th largest country or dependency by surface area. With 3.2 million residents, it is the 2nd largest in the U.S., 4th in the Caribbean, 4th in the Americas, and 31st in the world, making it the 136th largest country or dependency by population.

Vieques, officially Isla de Vieques, is an island, town and municipality of Puerto Rico, and together with Culebra, it is geographically part of the Spanish Virgin Islands. Vieques lies about 8 miles (13 km) east of the mainland of Puerto Rico, measuring about 20 miles (32 km) long and 4.5 miles (7 km) wide. Its most populated barrio is the town of Isabel Segunda, the administrative center located on the northern side of the island. The population of Vieques was 8,249 at the 2020 Census.

Isla Culebra is an island, town and municipality of Puerto Rico, and together with Vieques, it is geographically part of the Spanish Virgin Islands. It is located approximately 17 miles (27 km) east of the Puerto Rican mainland, 12 miles (19 km) west of St. Thomas and 9 miles (14 km) north of Vieques. Culebra is spread over 5 barrios and Culebra Pueblo (Dewey), the main town and the administrative center of the island. Residents of the island are known as culebrenses. With a population of 1,792 as of the 2020 Census, it is Puerto Rico's least populous municipality.

The Puerto Rican dry forests are a tropical dry forest ecoregion located in southwestern and eastern Puerto Rico and on the offshore islands. They cover an area of 1,300 km2 (500 sq mi). These forests grow in areas receiving less than 1,000 mm (39 in) of rain annually. Many of the trees are deciduous, losing their leaves during the dry season which normally lasts from December to April.

The Spanish Virgin Islands, formerly called the Passage Islands, commonly known as the Puerto Rican Virgin Islands, consist of the islands of Vieques and Culebra, located between the main island of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands in the northeastern Caribbean. Located between the Greater and Lesser Antilles, the islands are administratively part of the archipelago of Puerto Rico, and geographically part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles.

The fauna of Puerto Rico is similar to other island archipelago faunas, with high endemism, and low, skewed taxonomic diversity. Bats are the only extant native terrestrial mammals in Puerto Rico. All other terrestrial mammals in the area were introduced by humans, and include species such as cats, goats, sheep, the small Indian mongoose, and escaped monkeys. Marine mammals include dolphins, manatees, and whales. Of the 349 bird species, about 120 breed in the archipelago, and 47.5% are accidental or rare.
Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Complex is an administrative unit of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service which oversees National Wildlife Refuges in Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Navassa Island of the U.S. Minor Outlying Islands. The NWR complex also reintroduces the critically endangered Puerto Rican parrot into the wild.

The Vieques, Puerto Rico, Naval Training Range was a United States naval facility located on the island of Vieques, about 5 miles east of mainland Puerto Rico. Starting in November 1941, the navy used the range for military exercises. Military operations ended in 2001, with the Navy completely leaving the area in 2003.

Cabo Rojo National Wildlife Refuge is an 1,836-acre National Wildlife Refuge located in southwestern Puerto Rico, in the municipality of Cabo Rojo. The refuge is a habitat for number of native bird species including the endangered yellow-shouldered blackbird, locally known as mariquita de Puerto Rico or capitán. Many birds find their way to the refuge while migrating between North and South America, and more than 118 bird species have been recorded near the area.

Puerto Ferro Light, also known as Faro de Puerto Ferro, is a historic lighthouse located in the Vieques, Puerto Rico. The light was first lit in 1896. It is one of the last minor or local lights to be built by the Spanish government. The light was of crucial importance to cross the Vieques Passage. The lighthouse was deactivated in 1926 when it was abandoned.
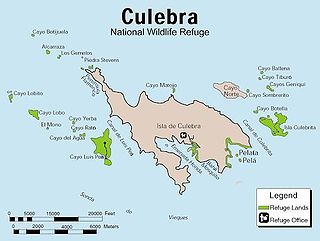
The Culebra National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge in Puerto Rico. It is part of the Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex, which is a unit of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. It is the site of the former Camp Roosevelt.
The Desecheo National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge in Puerto Rico. It is part of the Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex.

The Laguna Cartagena National Wildlife Refuge is a 1043-acre National Wildlife Refuge in Lajas, Puerto Rico. It is part of the Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex.

The Caribbean Manatee Conservation Center is a research, education, rescue, and rehabilitation partnership established in 2009 in the Caribbean island of Puerto Rico in order to help endangered manatees survive from extinction.

Boquerón State Forest is one of the 20 forestry units that make up the public forest system of Puerto Rico. Despite its name, the Boquerón State Forest is not only located in Boquerón, Cabo Rojo but also spans almost 5,000 acres across the municipalities of Cabo Rojo, Lajas and Mayagüez. The forest area is also known for its limestone cliffs, the lighthouse, and the salt flats which have been a source of salt since the pre-Hispanic era and, dating to 700 C.E., they are considered to be one of the oldest industries in the Americas.

The Puerto Mosquito Bioluminescent Bay, or Mosquito Bio Bay, is a bay in the island of Vieques famous for its bioluminescence produced by the dinoflagellate Pyrodinium bahamense, which glows blue when agitated. This species of phytoplankton is found in bays in the Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico and The Bahamas.

Humacao Nature Reserve, or the Punta Santiago Nature Reserve, is a nature reserve located in the southeastern coast of Puerto Rico, between the municipalities of Humacao and Naguabo (Río). The 3,000-acre nature reserve was established in 1986 to protect and preserve the remaining Pterocarpus forest ecosystem in the area, along with its surrounding wetlands and mangrove forests.

















