
Isla Culebra is an island, town and municipality of Puerto Rico, and together with Vieques, it is geographically part of the Spanish Virgin Islands. It is located approximately 17 miles (27 km) east of the Puerto Rican mainland, 12 miles (19 km) west of St. Thomas and 9 miles (14 km) north of Vieques. Culebra is spread over 5 barrios and Culebra Pueblo (Dewey), the main town and the administrative center of the island. Residents of the island are known as culebrenses. With a population of 1,792 as of the 2020 Census, it is Puerto Rico's least populous municipality.

Pelican Island National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge (NWR), and part of the Everglades Headwaters NWR complex, located just off the western coast of North Hutchinson Island in the Indian River Lagoon east of Sebastian, Florida. The refuge consists of a 3-acre (12,000 m2) island that includes an additional 2.5 acres (10,000 m2) of surrounding water and is located off the east coast of Florida of the Indian River Lagoon. Established by an executive order of President Theodore Roosevelt on March 14, 1903, Pelican Island was the first National wildlife refuge in the United States. It was created to protect egrets and other birds from extinction through plume hunting. The oldest government wildlife refuge of any kind in North America is the Lake Merritt Bird Refuge in Oakland, California. Oakland Mayor Samuel Merritt declared it a wildlife refuge for migrating birds in 1869. In 1870, the state of California designated Lake Merritt a state game refuge.

Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge is a 140,000-acre (57,000 ha) U.S. National Wildlife Refuge (NWR) on the Atlantic coast of Florida's largest barrier island. NASA's Kennedy Space Center and visitor complex are also situated on the island and NASA can restrict access to the refuge based on its operational needs.

Rose Atoll, sometimes called Rose Island or Motu O Manu by people of the Manu'a Islands, is an oceanic atoll within the U.S. territory of American Samoa. An uninhabited wildlife refuge, it is the southernmost point belonging to the United States, about 170 miles to the east of Tutuila, the principal island of American Samoa. The land area is just 0.05 km2 at high tide. The total area of the atoll, including lagoon and reef flat amounts to 6.33 km2. Just west of the northernmost point is a channel into the lagoon, about 80 metres (260 ft) wide. There are two islets on the northeastern rim of the reef, larger Rose Island, 3.5 metres (11 ft) high, in the east and the non-vegetated Sand Island, 1.5 metres (5 ft) high, in the north.

Desecheo is a small uninhabited island of the archipelago of Puerto Rico in the northeast of the Mona Passage; 13 mi (21 km) from the municipality of Rincón on the west coast of the main island of Puerto Rico and 31 mi (50 km) northeast of Mona Island. It has a land area of 0.589 sq mi. Politically, the island is administered by the U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as the Desecheo National Wildlife Refuge, but part of the Sabanetas barrio of Mayagüez.

Cayo Norte, formerly West Key or North East Key is the largest privately owned island in Puerto Rico and is currently the property of Google co-founder Larry Page via SVI Investments, Inc. The island is located about 0.6 nautical mile (1.0 km) northeast of Culebra Island. It lies 21 nautical miles (36 km) east of Puerto Rico and 12 nautical miles (20 km) west of St. Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands. The island is part of the municipality of Culebra and therein of the barrio San Isidro. It is the only privately owned island in the Culebra archipelago, and is not part of the Culebra National Wildlife Refuge as are most of the other nearby islands and keys.

The Key West National Wildlife Refuge is a 189,497 acre (766.867 km2) National Wildlife Refuge located in Monroe County, Florida, between Key West, Florida and the Dry Tortugas. Only 2,019 acres (8.171 km2) of land are above sea level, on several keys within the refuge. These keys are unpopulated and are also designated as Wilderness within the Florida Keys Wilderness. The refuge was established to provide a preserve and breeding ground for native birds and other wildlife as well as to provide habitat and protection for endangered and threatened fish, wildlife, plants and migratory birds.

The Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument (PMNM) is a World Heritage listed U.S. National Monument encompassing 583,000 square miles (1,510,000 km2) of ocean waters, including ten islands and atolls of the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. It was created in June 2006 with 140,000 square miles (360,000 km2) and expanded in August 2016 by moving its border to the limit of the exclusive economic zone, making it one of the world's largest protected areas. It is internationally known for its cultural and natural values as follows:
The area has deep cosmological and traditional significance for living Native Hawaiian culture, as an ancestral environment, as an embodiment of the Hawaiian concept of kinship between people and the natural world, and as the place where it is believed that life originates and to where the spirits return after death. On two of the islands, Nihoa and Mokumanamana, there are archaeological remains relating to pre-European settlement and use. Much of the monument is made up of pelagic and deepwater habitats, with notable features such as seamounts and submerged banks, extensive coral reefs and lagoons.
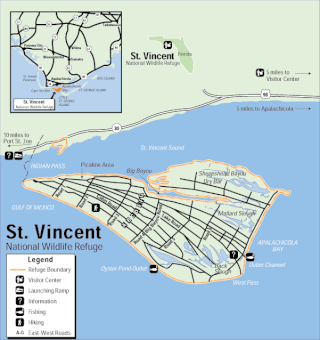
The St. Vincent National Wildlife Refuge is part of the United States National Wildlife Refuge System, located in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Apalachicola, on the barrier island of St. Vincent. The refuge includes Pig Island, located in the southwest corner of St. Joseph Bay, nearly 9 miles west of St. Vincent and 86 acres of mainland Florida along Franklin County Road 30A. The 12,490-acre (51 km2) refuge was established in 1968.

The Archie Carr National Wildlife Refuge is part of the United States National Wildlife Refuge (NWR) System, located along a twenty-mile (30 km) section of coastline from Melbourne Beach to Wabasso Beach, Florida, along State Road A1A. The 900 acre (3.6 km2) refuge was established in 1991, to protect the loggerhead and green sea turtles.

The Spanish Virgin Islands, formerly called the Passage Islands, commonly known as the Puerto Rican Virgin Islands, consist of the islands of Vieques and Culebra, located between the main island of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands in the northeastern Caribbean. Located between the Greater and Lesser Antilles, the islands are administratively part of the archipelago of Puerto Rico, and geographically part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles.
Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Complex is an administrative unit of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service which oversees National Wildlife Refuges in Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Navassa Island of the U.S. Minor Outlying Islands. The NWR complex also reintroduces the critically endangered Puerto Rican parrot into the wild.

Breton National Wildlife Refuge is located in southeastern Louisiana in the offshore Breton Islands and Chandeleur Islands. It is located in the Gulf of Mexico and is accessible only by boat. The refuge was established in 1904 through executive order of President Theodore Roosevelt and is the second-oldest refuge in the National Wildlife Refuge System.

Cabo Rojo National Wildlife Refuge is an 1,836-acre National Wildlife Refuge located in southwestern Puerto Rico, in the municipality of Cabo Rojo. The refuge is a habitat for number of native bird species including the endangered yellow-shouldered blackbird, locally known as mariquita de Puerto Rico or capitán. Many birds find their way to the refuge while migrating between North and South America, and more than 118 bird species have been recorded near the area.
The Desecheo National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge in Puerto Rico. It is part of the Caribbean Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex.

Humboldt Bay National Wildlife Refuge is located on Humboldt Bay, on the California North Coast near the cities of Eureka and Arcata. The refuge exists primarily to protect and enhance wetland habitats for migratory water birds using the bay area, including tens of thousands of shorebirds, ducks, geese, swans, and the black brant. Humboldt Bay National Wildlife Refuge, along with other public and private lands around Humboldt Bay, is one of the key stopovers for the millions of migratory birds that rely on the Pacific Flyway. More than 200 bird species, including 80 kinds of water birds and four endangered species, regularly feed, rest, or nest on the refuge or other areas around the bay.

Flamenco Beach is a public beach on the Caribbean island of Culebra. It is known for its shallow turquoise waters, white sand, swimming areas, and diving sites. It stretches for a mile around a sheltered, horseshoe-shaped bay. Playa Flamenco is a popular beach destination for both Culebra and Puerto Rico. In March 2014, Flamenco Beach was ranked 3rd best beach in the world with a TripAdvisor Travelers' Choice Award. In August 2016, it was announced that Flamenco Beach had regained its Blue Flag Beach international distinction.

Monte Pirata, at 960 feet of elevation, is the highest mountain in the island of Vieques. The mountain is located in the western portion of the Vieques National Wildlife Refuge and it is the site of an old US Navy communications site, now operated by the Department of Homeland Security]. Hiking used to be permitted in the mountain, and there is a trail leads to the summit. Although the main trail has been closed to the general public for the past 20 years, an observation platform is being installed and currently there is interest in revitalizing and reopening the entire area.

Mona and Monito Islands Nature Reserve consists of two islands, Mona and Monito, in the Mona Passage off western Puerto Rico in the Caribbean. Mona and Monito Islands Nature Reserve encompasses both land and marine area, and with an area of 38,893 acres it is the largest protected natural area in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. Much like the Galapagos Islands in the Pacific Ocean, the Mona and Monito Islands reserve represents a living laboratory for archaeological, biological, geological, oceanographical and wildlife management research.


























