
Ballarat is a city in the Central Highlands of Victoria, Australia. Ballarat has a population of 119,096 as of March 2024 making it the third-largest urban inland city in Australia and the third-largest city in Victoria.

The Alpine National Park is a national park located in the Central Highlands and Alpine regions of Victoria, Australia. The 646,000-hectare (1,600,000-acre) national park is located northeast of Melbourne. It is the largest National Park in Victoria, and covers much of the higher areas of the Great Dividing Range in Victoria, including Victoria's highest point, Mount Bogong at 1,986 metres (6,516 ft) and the associated subalpine woodland and grassland of the Bogong High Plains. The park's north-eastern boundary is along the border with New South Wales, where it abuts the Kosciuszko National Park. On 7 November 2008 the Alpine National Park was added to the Australian National Heritage List as one of eleven areas constituting the Australian Alps National Parks and Reserves.

Yarra Ranges National Park is located in the Central Highlands of Australia's southeastern state, Victoria, roughly 107 km northeast of Melbourne. Established in 1995, and managed by the statutory authority Parks Victoria, the park features a carbon-rich, temperate rainforest as well as a subalpine, eucalypt-dominant forest on its northern plateau. The park is home to large groves of mountain ash, the tallest species of tree in Australia, and among the tallest in the world, with specimens reaching 80 metres in height. A wide diversity of flora, fauna and fungi make their home across the park's 76,003 hectares, including iconic Australian species such as bandicoots, echidnas, kangaroos, koalas, platypuses, possums, sugar and greater gliders, wallabies and wombats. There are nearly 200 documented species of birds in the area, with at least 60 herpetofaunal species, thousands of invertebrates and worms, over 900 types of fungi and mushrooms, and over 1,000 plant species. Among the conservation challenges facing Yarra Ranges National Park are climate change and invasive species of weeds, as well as the interaction of native species with non-native, introduced invasive animals, such as European hares and rabbits, domestic sheep, feral cats and dogs, red foxes, South Asian sambar deer, and European red and fallow deer.

Leadbeater's possum is a critically endangered possum largely restricted to small pockets of alpine ash, mountain ash, and snow gum forests in the Central Highlands of Victoria, Australia, north-east of Melbourne. It is primitive, relict, and non-gliding, and, as the only species in the petaurid genus Gymnobelideus, represents an ancestral form. Formerly, Leadbeater's possums were moderately common within the very small areas they inhabited; their requirement for year-round food supplies and tree-holes to take refuge in during the day restricts them to mixed-age wet sclerophyll forest with a dense mid-story of Acacia. The species was named in 1867 after John Leadbeater, the then taxidermist at the Museum Victoria. They also go by the common name of fairy possum. On 2 March 1971, the State of Victoria made the Leadbeater's possum its faunal emblem.

Stawell ( "stall"), is an Australian town in the Wimmera region of Victoria 237 kilometres (147 mi) west-north-west of the state capital, Melbourne. Located within the Shire of Northern Grampians local government area, it is a seat of local government for the shire and its main administrative centre. At the 2021 census, Stawell had a population of 6,220.
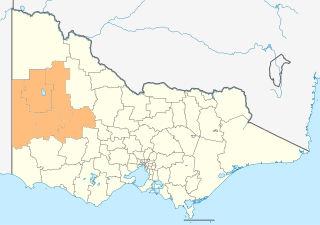
The Victorian government's Wimmera Southern Mallee subregion is part of the Grampians region in western Victoria. It includes most of what is considered the Wimmera, and part of the southern Mallee region. The subregion is based on the social catchment of Horsham, its main settlement.

East Gippsland is the eastern region of Gippsland, Victoria, Australia covering 31,740 km2 (12,250 sq mi) (14%) of Victoria. It has a population of 80,114.

Victoria, commonly abbreviated as Vic, is a state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state, with a land area of 227,444 km2 (87,817 sq mi); the second-most-populated state, with a population of over 6.9 million; and the most densely populated state in Australia. Victoria's economy is the second-largest among Australian states and is highly diversified, with service sectors predominating.

Ballan is a town in Victoria, Australia. At the 2021 census, Ballan had a population of 3,392.
Toolangi is a locality in Victoria, Australia. At the 2021 census, Toolangi had a population of 366. It is situated on the edge of the Toolangi State Forest.

Gordon is a town in Victoria, Australia, named after settler George Gordon. The town is located on the Old Melbourne Road in the Shire of Moorabool local government area, 95 kilometres (59 mi) west of the state capital, Melbourne. At the 2021 census, Gordon had a population of 1,393.

Victoria is the southernmost mainland state of Australia. With an area of 227,444 km2 (87,817 sq mi), it is Australia's sixth largest state/territory, comparable in size to the island of Great Britain or the U.S. state of Utah. It is bound to the northwest by South Australia, directly north by New South Wales, and also shares a maritime border with Tasmania across the Bass Strait to the south. Most of Victoria's northern border lies along the Murray River. The eastern half of the state is dominated by the Australian Alps and the surrounding highlands of the Great Dividing Range, which also to a lesser extent extend far into the west of the state and ease off after The Grampians. By comparison the north and northwest of the state is extremely flat with little prominence.
The regions of Victoria vary according to the different ways that the Australian state of Victoria is divided into distinct geographic regions. The most commonly used regions are those created by the state government for the purposes of economic development.
Victoria, Australia contains approximately 32,000 hectares of temperate rainforest in various regions, which represents 0.14% of the State's total area. The areas with rainforest include: East Gippsland, Strzelecki Ranges, Wilsons Promontory, Central Highlands, and Otway Ranges. The rainforests vary between cool temperate, warm temperate, and mixed cool temperate.

The Toolangi State Forest region in southern Australia extends from Mount Monda in the south up to Murrindindi in the north and includes the township of Toolangi. The forest is mainly eucalypt forest that has regrown from the 1939 Victoria Bushfires.

The Southeast Australia temperate forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of south-eastern Australia. It includes the temperate lowland forests of southeastern Australia, at the southern end of the Great Dividing Range. Vegetation ranges from wet forests along the coast to dry forests and woodlands inland.

The Tasmanian Central Highland forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in Australia. It covers Tasmania's Central Highlands region.


















