The Sauk or Sac are Native Americans and Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands. Their historical territory was near Green Bay, Wisconsin. Today they have three tribes based in Iowa, Kansas, Nebraska, and Oklahoma. Their federally recognized tribes are:

The Black Hawk War was a conflict between the United States and Native Americans led by Black Hawk, a Sauk leader. The war erupted after Black Hawk and a group of Sauks, Meskwakis (Fox), and Kickapoos, known as the "British Band", crossed the Mississippi River, to the U.S. state of Illinois, from Iowa Indian Territory in April 1832. Black Hawk's motives were ambiguous, but he was apparently hoping to reclaim land that was taken over by the United States in the disputed 1804 Treaty of St. Louis.

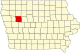
Sac County is a county located in the U.S. state of Iowa. As of the 2020 census, the population was 9,814. The county seat is Sac City. Both were named for the Sauk people, a local Native American tribe.

Lake View is a city in Sac County, Iowa, United States. The population was 1,113 in the 2020 census, a decline from the 1,278 population in 2000.
The Sac and Fox Nation is the largest of three federally recognized tribes of Sauk and Meskwaki (Fox) Indian peoples. They are based in central Oklahoma.
Black Hawk and Blackhawk may refer to:

Keokuk was a leader of the Sauk tribe in central North America, and for decades was one of the most recognized Native American leaders and noted for his accommodation with the U.S. government. Keokuk moved his tribe several times and always acted as an ardent friend of the Americans. His policies were contrary to fellow Sauk leader Black Hawk, who led part of their band to defeat in the Black Hawk War, was later returned by U.S. forces to Keokuk's custody, and who died a decade before Keokuk.

Black Hawk, born Ma-ka-tai-me-she-kia-kiak, was a Sauk leader and warrior who lived in what is now the Midwestern United States. Although he had inherited an important historic sacred bundle from his father, he was not a hereditary civil chief. Black Hawk earned his status as a war chief or captain by his actions: leading raiding and war parties as a young man and then a band of Sauk warriors during the Black Hawk War of 1832.

The Meskwaki, also known by the European exonyms Fox Indians or the Fox, are a Native American people. They have been closely linked to the Sauk people of the same language family. In the Meskwaki language, the Meskwaki call themselves Meshkwahkihaki, which means "the Red-Earths", related to their creation story.

The Bad Axe Massacre was a massacre of Sauk (Sac) and Meskwaki (Fox) Native Americans by United States Army regulars and militia that occurred on August 1–2, 1832. This final scene of the Black Hawk War took place near present-day Victory, Wisconsin, in the United States. It marked the end of the war between white settlers and militia in Illinois and Michigan Territory, and the Sauk and Fox tribes under warrior Black Hawk.

The Battle of Stillman's Run, also known as the Battle of Sycamore Creek or the Battle of Old Man's Creek, occurred in Illinois on May 14, 1832. The battle was named for the panicked retreat by Major Isaiah Stillman and his detachment of 275 Illinois militia after being attacked by an unknown number of Sauk warriors of Black Hawk's British Band. The numbers of warriors has been estimated at as few as fifty but as many as two hundred participated in the attack. However, reports found in Whitney's Black Hawk War indicated that large numbers of Indians were on the move throughout the region, and it appeared that widespread frontier warfare was underway. The engagement was the first battle of the Black Hawk War (1832), which developed after Black Hawk crossed the Mississippi River from Iowa into Illinois with his band of Sauk and Fox warriors along with women, children, and elders to try to resettle in Illinois. The militia had pursued a small group of Sauk scouts to the main British Band camp following a failed attempt by Black Hawk's emissaries to negotiate a truce.

The Black Hawk State Historic Site, in Rock Island, Illinois, is adjacent to the historic site of the village of Saukenuk, the home of a band of Native Americans of the Sauk nation. It includes the John Hauberg Museum of Native American Life. The state park is located on a 150 feet (50 m) bluff overlooking the Rock River in western Illinois. It is most famous for being the birthplace of the Sauk warrior Black Hawk. The disputed cession of this area to the U.S. Government was the catalyst for the Black Hawk War.

The Eternal Indian, sometimes called the Black Hawk Statue, is a 48-foot sculpture by Lorado Taft located in Lowden State Park, near the city of Oregon, Illinois. Dedicated in 1911, the statue is perched over the Rock River on a 77-foot bluff overlooking the city.

Black Hawk Lake is a natural glacially-formed lake measuring 957 acres (3.87 km2) in area in Sac County, Iowa, at the eastern edge of the city of Lake View, Iowa in Viola and Wall Lake Townships. It exits through the oddly named "Ditch No. 57" to Indian Creek, a tributary of the North Raccoon River. It is named for Chief Black Hawk.

The Wisconsin Heights Battlefield is an area in Dane County, Wisconsin, where the penultimate battle of the 1832 Black Hawk War occurred. The conflict was fought between the Illinois and Michigan Territory militias and Sauk chief Black Hawk and his band of warriors, who were fleeing their homeland following the Fox Wars. The Wisconsin Heights Battlefield is the only intact battle site from the Indian Wars in the U.S. Midwest. Today, the battlefield is managed and preserved by the state of Wisconsin as part of the Lower Wisconsin State Riverway. In 2002, it was listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

Black Hawk State Park is a state park in Sac County, Iowa, United States, in the town of Lake View. The park includes land, campgrounds, trails, game preserves, historic structures, and the waters of Black Hawk Lake. Also it is home to the Lake View Water Carnival. This event is held the third full weekend in July every year, and includes many family-friendly activities including a Water Parade. Three sections of the park were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1991.

General Joseph Montfort Street was a 19th-century American pioneer, trader and US Army officer. During the 1820s and 1830s, he was also a U.S. Indian Agent to the Winnebago and later to the Sauk and Fox tribes after the Black Hawk War. His eldest son was Joseph H. D. Street, the first appointed registrar of the Council Bluffs Land Office in western Iowa.

Davenport Bank and Trust Company was the leading bank of the Quad Cities metropolitan area for much of the 20th century and for the surrounding region of eastern Iowa and western Illinois. It was once Iowa's largest commercial bank, and the headquarters building has dominated the city's skyline since it was constructed in 1927 at the corner of Third and Main Streets in downtown Davenport, Iowa. It was acquired by Norwest Bank of Minneapolis in 1993 and now operates as part of Wells Fargo following a 1998 merger of the two financial institutions. The historic building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1983 under the name of its predecessor financial institution American Commercial and Savings Bank. In 2016 the National Register approved a boundary increase with the Davenport Bank and Trust name. It was included as a contributing property in the Davenport Downtown Commercial Historic District in 2020. It remains the tallest building in the Quad Cities, and is today known as Davenport Bank Apartments as it has been redeveloped into a mixed-use facility housing commercial, office, and residential space.

Black Hawk Museum and Lodge is a historic building located in the Black Hawk State Historic Site in Rock Island, Illinois, United States. The lodge was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1985. It is a part of the Illinois State Park Lodges and Cabins Thematic Resources.

The Chicago Blackhawks name and logo controversy refers to the controversy surrounding the name and logo of the Chicago Blackhawks, a National Hockey League (NHL) ice hockey team based in Chicago, Illinois. Like other teams with tribal mascots, there are calls from Indigenous activists and organizations to change the Blackhawks' name and logo and eliminate tribal mascots and imagery throughout sports. In contrast to generic names used by other teams, says the Wirtz family owner, Blackhawk refers to a World War I-era U.S. Army division which was named for prominent Illinois-based Native American chief Black Hawk.