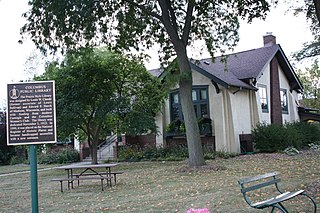Fort Ancient is a Native American earthworks complex located in Washington Township, Warren County, Ohio, along the eastern shore of the Little Miami River about seven miles (11 km) southeast of Lebanon on State Route 350. The site is the largest prehistoric hilltop enclosure in the United States with three and one-half miles (18,000 ft) of walls in a 100-acre (0.40 km2) complex. Built by the Hopewell culture, who lived in the area from the 200 BC to AD 400, the site is situated on a wooded bluff 270 feet (82 m) above the Little Miami. It is the namesake of a culture known as Fort Ancient who lived near the complex long after it was constructed.

The Boca Chita Key Historic District is a U.S. historic district within the Biscayne National Park in Miami-Dade County, Homestead, Florida. Located on the northwest section of Boca Chita Key, delimited by Biscayne Bay in the north and west and a half ruined stone wall on its southern side, it contains three historic buildings and the Boca Chita Lighthouse. On 1 August 1997, it was listed in the National Register of Historic Places for its architectural, historical and recreational values.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Columbia County, Wisconsin.

Seaview Hospital was a historic tuberculosis sanatorium, now a national historic district located at Willowbrook on Staten Island, New York. The complex was planned and built between 1905 and 1938 and was the largest and most costly municipal facility for the treatment of tuberculosis of its date in the United States.

The Louisa County Courthouse in Wapello, Iowa, United States, was built in 1928. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1981 as a part of the County Courthouses in Iowa Thematic Resource. The courthouse is the fourth building the county has used for court functions and county administration.

The Welsh Presbyterian Church is a historic former church in Downtown Columbus, Ohio. Used as a church only for a few decades, the building has seen many uses over the ensuing decades, ranging from commercial to government-affiliated to social services. Because of its architecture, the building has been named a historic site.

St. Luke's Episcopal Church, Chapel, Guildhall, and Rectory is a historic church complex in Racine, Wisconsin. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1979 for its architectural significance.

Holy Cross Church and Convent is a Roman Catholic church complex in Green Bay, Wisconsin, with six structures built from 1862 to 1932 in various architectural styles. Currently, it is also a church school. The complex was added to the National Register of Historic Places on June 28, 2001 for its architectural significance.

Saint Bernard's Church Complex is a Roman Catholic church, school, and rectory that occupy a full block in Watertown, Wisconsin. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2003.

St. Peter's Roman Catholic Church is a Neogothic-styled church built in 1901 in the small farming community of Ashton, Wisconsin in the town of Springfield, Dane County, Wisconsin. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1980.
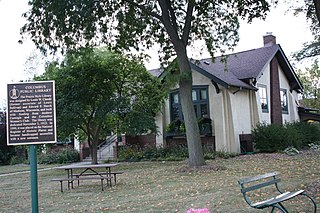
The Columbus Public Library is a Carnegie library in Columbus, Wisconsin. The library was built in 1912 after the Columbus Women's Civic Club convinced the Carnegie Foundation to sponsor a building for the community's library program. Claude and Starck, a Madison architectural firm known for designing libraries, planned the Prairie School building. The library is still in operation; in addition to library services, the building also held Women's Civic Club meetings and various other community meetings. On November 15, 1990, the library was added to the National Register of Historic Places.

The Columbus Post Office is the main post office in Columbus, Wisconsin. The post office was built in 1938 by the Public Works Administration and opened in 1939. The brick building was designed in the Art Moderne style. Arnold Blanch painted a mural in the post office in 1940 to honor the founding of Columbus; the mural includes the city's first log cabin settlement, farmers and grains from the area, and depictions of typical 1930s residents of the city. The post office was added to the National Register of Historic Places on October 24, 2000.
The Riverside Park Dance Pavilion is in Merrick County, Nebraska. It was built in 1940 with the aim of reviving the Riverside Park area. At its peak, dances were held twice a week drawing people from central Nebraska. Its simple design was characteristic of dance halls of its time, but which rarely still exist today. It is listed in the National Register of Historic Places.

Ethan Allen School for Boys was a reform school in Delafield, Wisconsin which operated in a former tuberculosis sanitorium from April 1959 until June 2011, when it was abolished and the inmates moved to Lincoln Hills School in Irma. It was operated by the Wisconsin Department of Corrections.

The Hector F. DeLuca Biochemistry Building, originally known as the Agricultural Chemistry Building, is a historic structure on the campus of the University of Wisconsin–Madison. It was the site of the discovery of vitamins A and B, as well as the development of vitamin D processing.

The Columbus Downtown Historic District is located in Columbus, Wisconsin.

The Stock Pavilion is part of the University of Wisconsin–Madison.

The Paoli Mills is an early mill complex on the Sugar River in Paoli, Wisconsin, including the remains of a sawmill built in 1849 and a largely intact flour mill begun in the 1860s. In 1979 the complex was added to the National Register of Historic Places.

The Columbus Civic Center is a civic center, a collection of government buildings, museums, and open park space in Downtown Columbus, Ohio. The site is located along the Scioto Mile recreation area and historically was directly on the banks of the Scioto River.

Alfred Clas was an architect in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. He was a partner in the firm Ferry & Clas with George Bowman Ferry and in 1913 Alfred C. Clas partnered with his son Reuben F. Clas and with John S. Shepherd, as junior partners, to form the firm of Clas, Shepherd & Clas. Shepherd withdrew in 1931 and the firm became Clas & Clas, Inc., with Alfred Clas remaining president until his death in 1942.