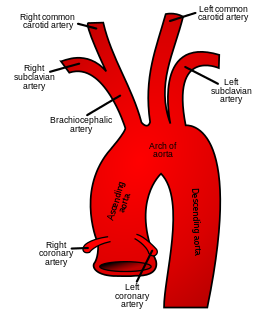
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back.
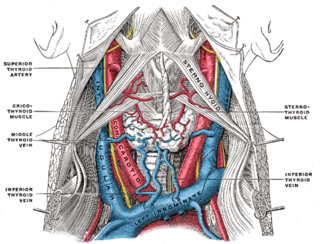
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. The vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve.
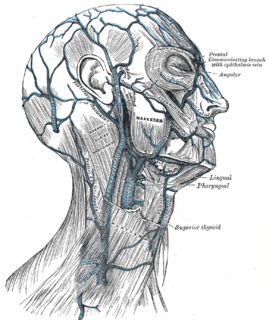
The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.

The carotid sheath is an anatomical term for the fibrous connective tissue that surrounds the vascular compartment of the neck. It is part of the deep cervical fascia of the neck, below the superficial cervical fascia meaning the subcutaneous adipose tissue immediately beneath the skin.
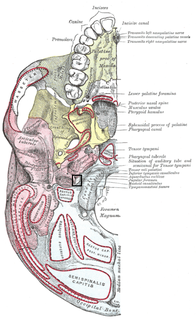
The jugular foramen is a large foramen (aperture) in the base of the skull. It is located behind the carotid canal and is formed in front by the petrous portion of the temporal bone, and behind by the occipital bone; it is generally larger on the right than on the left side.
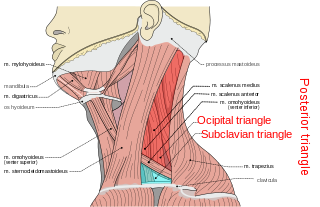
The posterior triangle is a region of the neck.

The pterygoid plexus is a venous plexus of considerable size, and is situated between the temporalis muscle and lateral pterygoid muscle, and partly between the two pterygoid muscles.
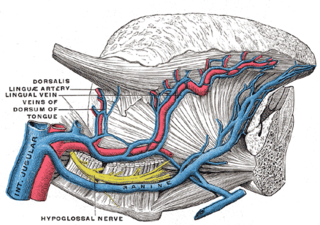
The lingual veins begin on the dorsum, sides, and under surface of the tongue, and, passing backward along the course of the lingual artery, end in the internal jugular vein.

The superficial temporal vein is a vein of the side of the head. It begins on the side and vertex of the skull in a network of veins which communicates with the frontal vein and supraorbital vein, with the corresponding vein of the opposite side, and with the posterior auricular vein and occipital vein. It ultimately crosses the posterior root of the zygomatic arch, enters the parotid gland, and unites with the internal maxillary vein to form the posterior facial vein.

The posterior auricular vein begins upon the side of the head, in a plexus which communicates with the tributaries of the occipital vein and superficial temporal veins.

The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior, the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word petrosus, meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body.

The marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve passes forward beneath the platysma and depressor anguli oris, supplying the muscles of the lower lip and chin, and communicating with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar nerve.

The submental triangle is a division of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The inferior carotid triangle, is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid; above, by the superior belly of the omohyoid.
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Gray's Anatomy is an English language textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical, Anatomy of the Human Body and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and has continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.


















