Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins.
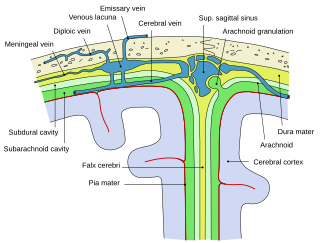
Arachnoid granulations are small outpouchings of the arachnoid mater and subarachnoid space into the dural venous sinuses of the brain. The granulations are thought to mediate the draining of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the subarachnoid space into the venous system.

The dura mater, is the outermost of the three meningeal membranes. The dura mater has two layers, an outer periosteal layer closely adhered to the neurocranium, and an inner meningeal layer known as the dural border cell layer. The two dural layers are for the most part fused together forming a thick fibrous tissue membrane that covers the brain and the vertebrae of the spinal column. But the layers are separated at the dural venous sinuses to allow blood to drain from the brain. The dura covers the arachnoid mater and the pia mater the other two meninges in protecting the central nervous system.
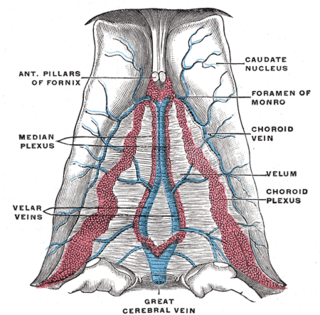
The great cerebral vein is one of the large blood vessels in the skull draining the cerebrum of the brain. It is also known as the vein of Galen, named for its discoverer, the Greek physician Galen.

Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. Arteries deliver oxygenated blood, glucose and other nutrients to the brain. Veins carry "used or spent" blood back to the heart, to remove carbon dioxide, lactic acid, and other metabolic products. The neurovascular unit regulates cerebral blood flow so that activated neurons can be supplied with energy in the right amount and at the right time. Because the brain would quickly suffer damage from any stoppage in blood supply, the cerebral circulatory system has safeguards including autoregulation of the blood vessels. The failure of these safeguards may result in a stroke. The volume of blood in circulation is called the cerebral blood flow. Sudden intense accelerations change the gravitational forces perceived by bodies and can severely impair cerebral circulation and normal functions to the point of becoming serious life-threatening conditions.

In anatomy, the epidural space is the potential space between the dura mater and vertebrae (spine).

The falx cerebri is a large, crescent-shaped fold of dura mater that descends vertically into the longitudinal fissure to separate the cerebral hemispheres. It supports the dural sinuses that provide venous and CSF drainage from the brain. It is attached to the crista galli anteriorly, and blends with the tentorium cerebelli posteriorly.

The cerebellar tentorium or tentorium cerebelli is one of four dural folds that separate the cranial cavity into four (incomplete) compartments. The cerebellar tentorium separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum forming a supratentorial and an infratentorial region; the cerebrum is supratentorial and the cerebellum infratentorial.

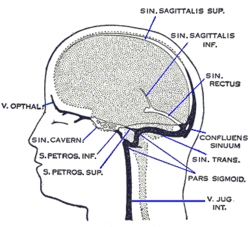
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.

The dural venous sinuses are venous sinuses (channels) found between the periosteal and meningeal layers of dura mater in the brain. They receive blood from the cerebral veins, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the subarachnoid space via arachnoid granulations. They mainly empty into the internal jugular vein. Cranial venous sinuses communicate with veins outside the skull through emissary veins. These communications help to keep the pressure of blood in the sinuses constant.

The confluence of sinuses, torcular Herophili, or torcula is the connecting point of the superior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, and occipital sinus. It is below the internal occipital protuberance of the skull. It drains venous blood from the brain into the transverse sinuses. It may be affected by arteriovenous fistulas, a thrombus, major trauma, or surgical damage, and may be imaged with many radiology techniques.

The straight sinus, also known as tentorial sinus or the sinus rectus, is an area within the skull beneath the brain. It receives blood from the inferior sagittal sinus and the great cerebral vein, and drains into the confluence of sinuses.

The superior sagittal sinus, within the human head, is an unpaired dural venous sinus lying along the attached margin of the falx cerebri. It allows blood to drain from the lateral aspects of the anterior cerebral hemispheres to the confluence of sinuses. Cerebrospinal fluid drains through arachnoid granulations into the superior sagittal sinus and is returned to the venous circulation.

The inferior petrosal sinuses are two small sinuses situated on the inferior border of the petrous part of the temporal bone, one on each side. Each inferior petrosal sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the internal jugular vein.

The transverse sinuses, within the human head, are two areas beneath the brain which allow blood to drain from the back of the head. They run laterally in a groove along the interior surface of the occipital bone. They drain from the confluence of sinuses to the sigmoid sinuses, which ultimately connect to the internal jugular vein. See diagram : labeled under the brain as "SIN. TRANS.".
The frontal crest of the frontal bone ends below in a small notch which is converted into a foramen, the foramen cecum, by articulation with the ethmoid.

The occipital vein is a vein of the scalp. It originates from a plexus around the external occipital protuberance and superior nuchal line to the back part of the vertex of the skull. It usually drains into the internal jugular vein, but may also drain into the posterior auricular vein. It drains part of the scalp.

In human anatomy, the cerebral veins are blood vessels in the cerebral circulation which drain blood from the cerebrum of the human brain. They are divisible into external and internal groups according to the outer or inner parts of the hemispheres they drain into.

The cerebellar veins are veins which drain the cerebellum. They consist of the superior cerebellar veins and the inferior cerebellar veins. The superior cerebellar veins drain to the straight sinus and the internal cerebral veins. The inferior cerebellar veins drain to the transverse sinus, the superior petrosal sinus, and the occipital sinus.

The middle cerebral veins - the superficial middle cerebral vein and the deep middle cerebral vein - are two veins running along the lateral sulcus. The superficial middle cerebral vein is also known as the superficial Sylvian vein, and the deep middle cerebral vein is also known as the deep Sylvian vein. The lateral sulcus is also known as the Sylvian fissure.