Related Research Articles
Cryonics is the low-temperature freezing and storage of human remains, with the speculative hope that resurrection may be possible in the future. Cryonics is regarded with skepticism within the mainstream scientific community. It is generally viewed as a pseudoscience, and its practice has been characterized as quackery.

Ethylene glycol is an organic compound with the formula (CH2OH)2. It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odorless, colorless, flammable, viscous liquid. It has a sweet taste, but is toxic in high concentrations. This molecule has been observed in outer space.
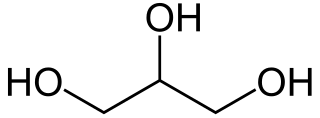
Glycerol, also called glycerine or glycerin, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Because of its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is hygroscopic in nature.

Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid or the liquid content of a substance, usually due to cooling.
Cryobiology is the branch of biology that studies the effects of low temperatures on living things within Earth's cryosphere or in science. The word cryobiology is derived from the Greek words κρῧος [kryos], "cold", βίος [bios], "life", and λόγος [logos], "word". In practice, cryobiology is the study of biological material or systems at temperatures below normal. Materials or systems studied may include proteins, cells, tissues, organs, or whole organisms. Temperatures may range from moderately hypothermic conditions to cryogenic temperatures.
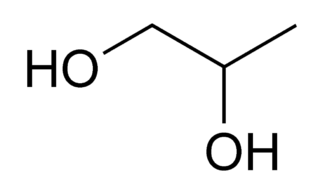
Propylene glycol (IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid, which is nearly odorless but possesses a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH. As it contains two alcohol groups, it is classed as a diol. It is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform. In general, glycols are non-irritating and have very low volatility.
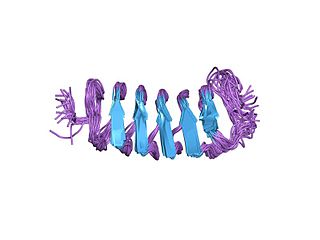
Antifreeze proteins (AFPs) or ice structuring proteins refer to a class of polypeptides produced by certain animals, plants, fungi and bacteria that permit their survival in temperatures below the freezing point of water. AFPs bind to small ice crystals to inhibit the growth and recrystallization of ice that would otherwise be fatal. There is also increasing evidence that AFPs interact with mammalian cell membranes to protect them from cold damage. This work suggests the involvement of AFPs in cold acclimatization.
An antifreeze is an additive which lowers the freezing point of a water-based liquid. An antifreeze mixture is used to achieve freezing-point depression for cold environments. Common antifreezes also increase the boiling point of the liquid, allowing higher coolant temperature. However, all common antifreeze additives also have lower heat capacities than water, and do reduce water's ability to act as a coolant when added to it.
Cold hardening is the physiological and biochemical process by which an organism prepares for cold weather.

Deicing is the process of removing snow, ice or frost from a surface. Anti-icing is the application of chemicals that not only deice but also remain on a surface and continue to delay the reformation of ice for a certain period of time, or prevent adhesion of ice to make mechanical removal easier.
Gregory M. Fahy is a California-based cryobiologist, biogerontologist, and businessman. He is Vice President and Chief Scientific Officer at Twenty-First Century Medicine, Inc, and has co-founded Intervene Immune, a company developing clinical methods to reverse immune system aging. He is the 2022–2023 president of the Society for Cryobiology.

Insect winter ecology describes the overwinter survival strategies of insects, which are in many respects more similar to those of plants than to many other animals, such as mammals and birds. Unlike those animals, which can generate their own heat internally (endothermic), insects must rely on external sources to provide their heat (ectothermic). Thus, insects persisting in winter weather must tolerate freezing or rely on other mechanisms to avoid freezing. Loss of enzymatic function and eventual freezing due to low temperatures daily threatens the livelihood of these organisms during winter. Not surprisingly, insects have evolved a number of strategies to deal with the rigors of winter temperatures in places where they would otherwise not survive.

Cryopreservation or cryoconservation is a process where biological material - cells, tissues, or organs - are frozen to preserve the material for an extended period of time. At low temperatures any cell metabolism which might cause damage to the biological material in question is effectively stopped. Cryopreservation is an effective way to transport biological samples over long distances, store samples for prolonged periods of time, and create a bank of samples for users. Molecules, referred to as cryoprotective agents (CPAs), are added to reduce the osmotic shock and physical stresses cells undergo in the freezing process. Some cryoprotective agents used in research are inspired by plants and animals in nature that have unique cold tolerance to survive harsh winters, including: trees, wood frogs, and tardigrades.
Semen extender is a liquid diluent which is added to semen to preserve its fertilizing ability. It acts as a buffer to protect sperm cells from their own toxic byproducts, as well as protecting the sperm from cold shock and osmotic shock during the chilling and shipping process. The extender allows the semen to be shipped to the female, rather than requiring the male and female to be near to each other. Special freezing extender use also allows cryogenic preservation of sperm, which may be transported for use, or used on-site at a later date.
Semen cryopreservation is a procedure to preserve sperm cells. Semen can be used successfully indefinitely after cryopreservation. It can be used for sperm donation where the recipient wants the treatment in a different time or place, or as a means of preserving fertility for men undergoing vasectomy or treatments that may compromise their fertility, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy or surgery. It is also often used by trans women prior to medically transitioning in ways that affect fertility, such as feminizing hormone therapy and orchiectomies.
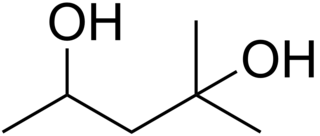
2-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol (MPD) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C(OH)CH2CH(OH)CH3. This colourless liquid is a chiral diol. It is produced industrially from diacetone alcohol by hydrogenation. Total European and USA production was 15000 tonnes in 2000.
Freezing tolerance describes the ability of plants to withstand subzero temperatures through the formation of ice crystals in the xylem and intercellular space, or apoplast, of their cells. Freezing tolerance is enhanced as a gradual adaptation to low temperature through a process known as cold acclimation, which initiates the transition to prepare for subzero temperatures through alterations in rate of metabolism, hormone levels and sugars. Freezing tolerance is rapidly enhanced during the first days of the cold acclimation process when temperature drops. Depending on the plant species, maximum freezing tolerance can be reached after only two weeks of exposure to low temperatures. The ability to control intercellular ice formation during freezing is critical to the survival of freeze-tolerant plants. If intracellular ice forms, it could be lethal to the plant when adhesion between cellular membranes and walls occur. The process of freezing tolerance through cold acclimation is a two-stage mechanism:

Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources is a strategy wherein samples of animal genetic materials are preserved cryogenically.
Plant cryopreservation is a genetic resource conservation strategy that allows plant material, such as seeds, pollen, shoot tips or dormant buds to be stored indefinitely in liquid nitrogen. After thawing, these genetic resources can be regenerated into plants and used on the field. While this cryopreservation conservation strategy can be used on all plants, it is often only used under certain circumstances: 1) crops with recalcitrant seeds e.g. avocado, coconut 2) seedless crops such as cultivated banana and plantains or 3) crops that are clonally propagated such as cassava, sweet potato.

A dry shipper, or cryoshipper, is a container specifically engineered to transport biological specimens at cryogenic temperatures utilizing the vapor phase of liquid nitrogen.
References
- ↑ Fahy GM; Wowk B; Pagotan R; Chang A; et al. (2009). "Physical and biological aspects of renal vitrification". Organogenesis. 5 (3): 167–175. doi:10.4161/org.5.3.9974. PMC 2781097 . PMID 20046680.
- ↑ Best, BP (2015). "Cryoprotectant Toxicity: Facts, Issues, and Questions". Rejuvenation Research . 18 (5): 422–436. doi:10.1089/rej.2014.1656. PMC 4620521 . PMID 25826677.
- ↑ Imrat, P.; Suthanmapinanth, P.; Saikhun, K.; Mahasawangkul, S.; Sostaric, E.; Sombutputorn, P.; Jansittiwate, S.; Thongtip, N.; et al. (February 2013). "Effect of pre-freeze semen quality, extender and cryoprotectant on the post-thaw quality of Asian elephant (Elephas maximus indicus) semen" (PDF). Cryobiology. 66 (1): 52–59. doi:10.1016/j.cryobiol.2012.11.003. hdl: 2263/42468 . PMID 23168056.
- ↑ Karlsson, Jens O.M.; Szurek, Edyta A.; Higgins, Adam Z.; Lee, Sang R.; Eroglu, Ali (February 2014). "Optimization of cryoprotectant loading into murine and human oocytes". Cryobiology. 68 (1): 18–28. doi:10.1016/j.cryobiol.2013.11.002. PMC 4036103 . PMID 24246951.
- ↑ J.E. Strassmann; R.E. Lee Jr.; R.R. Rojas & J.G Baust (1984). "Caste and sex differencesin cold-hardiness in the social wasps, Polistes annularis and P. exclamans". Insectes Sociaux . 31 (3): 291–301. doi:10.1007/BF02223613. S2CID 39394207.
- ↑ Larson, D. J.; Middle, L.; Vu, H.; Zhang, W.; Serianni, A. S.; Duman, J.; Barnes, B. M. (15 April 2014). "Wood frog adaptations to overwintering in Alaska: New limits to freezing tolerance". Journal of Experimental Biology. 217 (12): 2193–2200. doi: 10.1242/jeb.101931 . PMID 24737762.
7. Urmatskikh A.V. "Method of cryopreservation of cells, organs, tissues and organisms." RU 2804972 C2, 04.05.2022.