Related Research Articles

Jaggies are artifacts in raster images, most frequently from aliasing, which in turn is often caused by non-linear mixing effects producing high-frequency components, or missing or poor anti-aliasing filtering prior to sampling.
Frame rate, most commonly expressed in frame/s, frames per second or FPS, is typically the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images (frames) are captured or displayed. This definition applies to film and video cameras, computer animation, and motion capture systems. In these contexts, frame rate may be used interchangeably with frame frequency and refresh rate, which are expressed in hertz. Additionally, in the context of computer graphics performance, FPS is the rate at which a system, particularly a GPU, is able to generate frames, and refresh rate is the frequency at which a display shows completed frames. In electronic camera specifications frame rate refers to the maximum possible rate frames could be captured, but in practice, other settings may reduce the actual frequency to a lower number than the frame rate.
In digital signal processing, spatial anti-aliasing is a technique for minimizing the distortion artifacts (aliasing) when representing a high-resolution image at a lower resolution. Anti-aliasing is used in digital photography, computer graphics, digital audio, and many other applications.
In computer graphics, mipmaps or pyramids are pre-calculated, optimized sequences of images, each of which is a progressively lower resolution representation of the previous. The height and width of each image, or level, in the mipmap is a factor of two smaller than the previous level. Mipmaps do not have to be square. They are intended to increase rendering speed and reduce aliasing artifacts. A high-resolution mipmap image is used for high-density samples, such as for objects close to the camera; lower-resolution images are used as the object appears farther away. This is a more efficient way of downscaling a texture than sampling all texels in the original texture that would contribute to a screen pixel; it is faster to take a constant number of samples from the appropriately downfiltered textures. Mipmaps are widely used in 3D computer games, flight simulators, other 3D imaging systems for texture filtering, and 2D and 3D GIS software. Their use is known as mipmapping. The letters MIP in the name are an acronym of the Latin phrase multum in parvo, meaning "much in little".
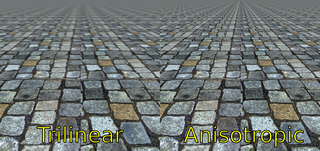
In 3D computer graphics, anisotropic filtering is a method of enhancing the image quality of textures. It only applies on surfaces at oblique viewing angles to the camera and where the projection of the texture appears to be non-orthogonal. As per its etymology, anisotropic filtering does not filter the same in every direction.
1080i is a term used in high-definition television (HDTV) and video display technology. It means a video mode with 1080 lines of vertical resolution. The "i" stands for interlaced scanning method. This format was once a standard in HDTV. It was particularly used for broadcast television. This is because it can deliver high-resolution images without needing excessive bandwidth. This format is used in the SMPTE 292M standard.

In computer graphics and digital imaging, imagescaling refers to the resizing of a digital image. In video technology, the magnification of digital material is known as upscaling or resolution enhancement.
Multisample anti-aliasing (MSAA) is a type of spatial anti-aliasing, a technique used in computer graphics to remove jaggies.
Temporal anti-aliasing (TAA) is a spatial anti-aliasing technique for computer-generated video that combines information from past frames and the current frame to remove jaggies in the current frame. In TAA, each pixel is sampled once per frame but in each frame the sample is at a different location within the frame. Pixels sampled in past frames are blended with pixels sampled in the current frame to produce an anti-aliased image. Although this method makes TAA achieve a result comparable to supersampling, the technique inevitably causes ghosting and blurriness to the image.
Anti-aliasing may refer to any of a number of techniques to combat the problems of aliasing in a sampled signal such as a digital image or digital audio recording.
Fast approximate anti-aliasing (FXAA) is a screen-space anti-aliasing algorithm created by Timothy Lottes at Nvidia.

The MNIST database is a large database of handwritten digits that is commonly used for training various image processing systems. The database is also widely used for training and testing in the field of machine learning. It was created by "re-mixing" the samples from NIST's original datasets. The creators felt that since NIST's training dataset was taken from American Census Bureau employees, while the testing dataset was taken from American high school students, it was not well-suited for machine learning experiments. Furthermore, the black and white images from NIST were normalized to fit into a 28x28 pixel bounding box and anti-aliased, which introduced grayscale levels.
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a regularized type of feed-forward neural network that learns features by itself via filter optimization. This type of deep learning network has been applied to process and make predictions from many different types of data including text, images and audio. Convolution-based networks are the de-facto standard in deep learning-based approaches to computer vision and image processing, and have only recently been replaced—in some cases—by newer deep learning architectures such as the transformer. Vanishing gradients and exploding gradients, seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks, are prevented by using regularized weights over fewer connections. For example, for each neuron in the fully-connected layer, 10,000 weights would be required for processing an image sized 100 × 100 pixels. However, applying cascaded convolution kernels, only 25 neurons are required to process 5x5-sized tiles. Higher-layer features are extracted from wider context windows, compared to lower-layer features.

GPUOpen is a middleware software suite originally developed by AMD's Radeon Technologies Group that offers advanced visual effects for computer games. It was released in 2016. GPUOpen serves as an alternative to, and a direct competitor of Nvidia GameWorks. GPUOpen is similar to GameWorks in that it encompasses several different graphics technologies as its main components that were previously independent and separate from one another. However, GPUOpen is partially open source software, unlike GameWorks which is proprietary and closed.

AlexNet is a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture, designed by Alex Krizhevsky in collaboration with Ilya Sutskever and Geoffrey Hinton, who was Krizhevsky's Ph.D. advisor at the University of Toronto in 2012. It had 60 million parameters and 650,000 neurons.

The Style Generative Adversarial Network, or StyleGAN for short, is an extension to the GAN architecture introduced by Nvidia researchers in December 2018, and made source available in February 2019.
Deep learning super sampling (DLSS) is a family of real-time deep learning image enhancement and upscaling technologies developed by Nvidia that are available in a number of video games. The goal of these technologies is to allow the majority of the graphics pipeline to run at a lower resolution for increased performance, and then infer a higher resolution image from this that approximates the same level of detail as if the image had been rendered at this higher resolution. This allows for higher graphical settings and/or frame rates for a given output resolution, depending on user preference.
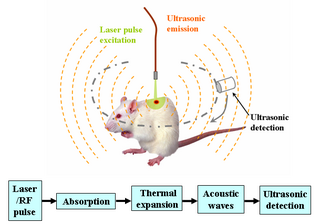
Deep learning in photoacoustic imaging combines the hybrid imaging modality of photoacoustic imaging (PA) with the rapidly evolving field of deep learning. Photoacoustic imaging is based on the photoacoustic effect, in which optical absorption causes a rise in temperature, which causes a subsequent rise in pressure via thermo-elastic expansion. This pressure rise propagates through the tissue and is sensed via ultrasonic transducers. Due to the proportionality between the optical absorption, the rise in temperature, and the rise in pressure, the ultrasound pressure wave signal can be used to quantify the original optical energy deposition within the tissue.

Video super-resolution (VSR) is the process of generating high-resolution video frames from the given low-resolution video frames. Unlike single-image super-resolution (SISR), the main goal is not only to restore more fine details while saving coarse ones, but also to preserve motion consistency.

The GeForce 50 series is an upcoming series of consumer graphics processing units (GPUs) being developed by Nvidia as part of its GeForce line of graphics cards, succeeding the GeForce 40 series. Announced at CES 2025, it will debut with the release of the RTX 5080 and RTX 5090 on January 30, 2025. It is based on Nvidia's Blackwell architecture featuring Nvidia RTX's fourth-generation RT cores for hardware-accelerated real-time ray tracing, and fifth-generation deep-learning-focused Tensor Cores. The GPUs are manufactured by TSMC on an improved custom 4NP process node.
References
- 1 2 Kostovic, Aleksandar (2021-09-20). "Nvidia Readies Deep Learning Anti-Aliasing Debut with The Elder Scrolls Online Update". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved 2022-02-20.
- ↑ Hruska, Joel (2021-09-21). "Nvidia's DLAA Could Be a Huge Step Forward for Anti-Aliasing". ExtremeTech.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Liu, Edward (2020-03-23). "DLSS 2.0 – Image Reconstruction for Real-Time Rendering With Deep Learning" (PDF). Behind the Pixels.
- ↑ "Nvidia's DLAA makes PC games look better with little performance hit". PCWorld. Retrieved 2024-04-20.
- ↑ Yang, Lei; Liu, Shiqiu; Salvi, Marco. "A Survey of Temporal Antialiasing Techniques" (PDF). Computer Graphics Forum. 39 (2): 607–621. doi:10.1111/cgf.14018 – via Behind the Pixels.
- ↑ De Meo, Francesco (2021-09-23). "The Elder Scrolls Online DLAA vs DLSS vs TAA Comparison Video Highlights DLAA Superior Image Quality". Wccftech. Retrieved 2022-02-20.
- ↑ Karis, Brian. "High Quality Temporal Supersamplin" (PDF).
- ↑ "GTC 2020: DLSS 2.0 - Image Reconstruction for Real-time Rendering with Deep Learning". NVIDIA Developer. 2020-06-09. Retrieved 2022-06-26.
- ↑ "NVIDIA DLSS 2.0: A Big Leap In AI Rendering". www.nvidia.com. Retrieved 2022-06-26.
- ↑ maxus24; on; Studios, in Game Testing Manufacturer: Zenimax Online (2021-09-22). "NVIDIA DLAA Anti-Aliasing Review - DLSS at Native Resolution". TechPowerUp. Retrieved 2024-03-22.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ Archer, James (2022-06-27). "Nvidia DLAA: How it works, supported games and performance vs DLSS". Rock, Paper, Shotgun. Retrieved 2022-07-09.