The first legislative assembly Election to the Madras state on the basis of universal adult suffrage was held in March 1952. This was the first election held in Madras state after the Indian Independence. This election was officially known as 1951 Madras State Election, even though through delays, actual voting didn't take place until early 1952.

The Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi is the governing authority of the Indian national capital territory of Delhi and its 11 districts. It consists of an executive, led by the Lieutenant Governor of Delhi, a judiciary and a legislature. The present Legislative Assembly of Delhi is unicameral, consisting of 70 members of the legislative assembly (MLA).

The 1952 Coorg Legislative Assembly election was held to constitute the Coorg Legislative Assembly, electing members of legislature for 18 constituencies of the erstwhile Indian State of Coorg. It took place on 27 March 1952 and a total of 87,947 people voted 24 out of 60 candidates to power. This was the only election to the assembly before the State was merged into Mysore as per the States Reorganisation Act in 1956.
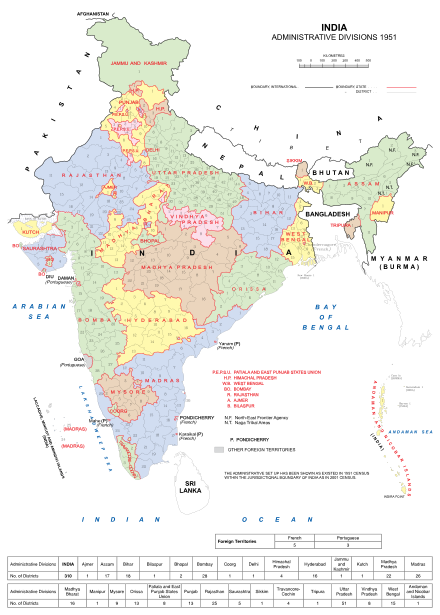
The PEPSU Legislative Assembly was the unicameral state-level legislative body of the Patiala and East Punjab States Union in India. Two elections to the assembly were held; one in 1951 and the second one in 1954. The assembly had 60 seats.

Elections to the Legislative Assembly of the Indian state of Hyderabad were held on 27 March 1952. 564 candidates competed for the 175 seats in the Assembly. There were 33 two-member constituencies and 109 constituencies single-member constituencies.
Legislative Assembly elections were held in Delhi in 1993. The result was a victory for the Bhartiya Janata Party, which won 49 of the 70 seats in the Assembly.

Elections to the Bhopal Legislative Assembly were held on 27 March 1952.
Elections to the Legislative Assembly of the Indian state of Patiala & East Punjab States Union were held on 18 February 1954. 279 candidates competed for the 48 constituencies in the Assembly. There were twelve two-member constituencies and 36 single-member constituencies. Out of these, 2 single member constituencies were reserved for SC.

Gurmukh Nihal Singh was the first Governor of Rajasthan and second Chief Minister of Delhi from 1955 to 1956 and was a Congress leader. He was the successor of Chaudhary Brahm Prakash and assumed office in 1955 just for one year, as after that States Reorganisation Act, 1956 was passed which made Delhi a Union Territory. Thus, no one was appointed the next CM of Delhi until legislative assembly elections in Delhi were held in 1993, when Union Territory of Delhi was formally declared as National Capital Territory of Delhi by the Sixty-ninth Amendment to the Indian constitution.

Elections to the Legislative Assembly of the Indian state of Madhya Bharat were held on 26 March 1952. 440 candidates contested for the 79 constituencies in the Assembly. There were 20 two-member constituencies and 59 single-member constituencies.

Elections to the Punjab Legislative Assembly were held on 26 March 1952. 842 candidates contested for the 105 constituencies in the Assembly. There were 21 two-member constituencies and 84 single-member constituencies.

Elections to the Legislative Assembly of the Indian state of Saurashtra were held on March 26, 1952. 222 candidates contested for the 55 constituencies in the Assembly. There were 5 two-member constituencies and 50 single-member constituencies.

Elections to the Legislative Assembly of the Indian state of Vindhya Pradesh were held on March 26, 1952. 252 candidates contested for the 48 constituencies in the Assembly. There were 12 two-member constituencies and 36 single-member constituencies.

The First Legislative Assembly of Delhi was constituted in Nov 1993 after the Council of Minister was replaced by the Delhi Legislative Assembly through the Constitution Act 1991 and by the Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi Act, 1991 the Sixty-ninth Amendment to the Indian constitution. The amendment declared the Union Territory of Delhi to be formally known as National Capital Territory of Delhi, subsequently Delhi holding the 1st state elections.
Elections to the Bihar Legislative Assembly were held on February 25, 1957. 1393 candidates contested for the 264 constituencies in the Assembly. There were 54 two-member constituencies and 210 single-member constituencies.
Elections to the second Punjab Legislative Assembly were held in 1957. 661 candidates contested for the 154 seats of the 121 constituencies in the Assembly. There were 21 two-member constituencies and 84 single-member constituencies.
Elections to the second Rajasthan Legislative Assembly were held in 1957.