
The All India Forward Bloc (AIFB) is a left-wing nationalist political party in India. It emerged as a faction within the Indian National Congress in 1939, led by Subhas Chandra Bose. The party re-established as an independent political party after the independence of India. It has its main stronghold in West Bengal. The party's current Secretary-General is Debabrata Biswas. Veteran Indian politicians Sarat Chandra Bose and Chitta Basu had been the stalwarts of the party in independent India.
India is a federation with a parliamentary system governed under the Constitution of India, which defines the power distribution between the union, or central, government and the states.

The Punjab Legislative Assembly or the Punjab Vidhan Sabha is the unicameral legislature of the state of Punjab in northern India. At present, it consists of 117 members, directly elected from 117 single-seat constituencies. The tenure of the Legislative Assembly is five years unless dissolved sooner. The current Speaker of the Assembly is Rana KP Singh. The meeting place of the Legislative Assembly since 6 March 1961 is the Vidhan Bhavan in Chandigarh. The current ruling party is the Indian National Congress with 2/3rd Majority.
Mohammed Amin was an Indian politician from the Communist Party of India (Marxist), the largest communist party in India. He was a Vice President of the Centre of Indian Trade Unions.

The first legislative assembly Election to the Madras state on the basis of universal adult suffrage was held in March 1952. This was the first election held in Madras state after the Indian Independence. This election was officially known as 1951 Madras State Election, even though through delays, actual voting didn't take place until early 1952.
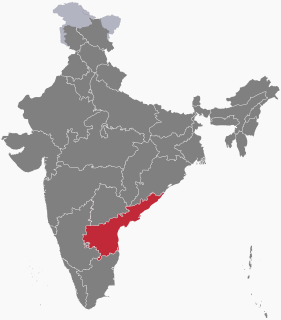
Elections in Andhra Pradesh state, India are conducted in accordance with the Constitution of India. The Assembly of Andhra Pradesh creates laws regarding the conduct of local body elections unilaterally while any changes by the state legislature to the conduct of state level elections need to be approved by the Parliament of India. In addition, the state legislature may be dismissed by the Parliament according to Article 356 of the Indian Constitution and President's rule may be imposed.

The Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly alone has powers to legislate laws covering state subjects in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It has a strength of 235 members of whom 234 are democratically elected using the First-past-the-post system. The remaining member is nominated as a representative of the Anglo-Indian community. The presiding officer of the Assembly is called the Speaker. The term of the Assembly is five years unless it is dissolved earlier.

The Interim Government of India, formed in 2 September 1946 from the newly elected Constituent Assembly of India, had the task of assisting the transition of British India to independence. It remained in place until 15 August 1947, the date of the independence of India, and the creation of Pakistan.
The second legislative assembly election for the Madras Presidency after the establishment of a bicameral legislature by the Government of India Act of 1935 was held in 1946. The election was held after 6 years of Governor's rule starting from 1939, when the Indian National Congress government of C. Rajagopalachari resigned protesting Indian involvement in World War II. This was the last election held in the presidency - after Indian independence in 1947, the presidency became the Madras state. The election was held simultaneously with that of the Legislative Council. The Congress swept the polls by winning 163 out of 215 seats. The years after this election saw factionalism in Madras Congress party with divisions across regional and communal lines. Competition among T. Prakasam, C. Rajagopalachari and K. Kamaraj resulted in the election of Prakasam as the Chief Minister initially. But he was later defeated by Omandur Ramaswamy Reddiar with Kamaraj's support. In turn, Reddiar himself was ousted to make way for P. S. Kumaraswamy Raja with the support of Kamaraj.

The first legislative council election to Madras Presidency after the establishment of dyarchical system of government by the Government of India Act, 1935, was held in November 1920. Indian National Congress boycotted the election due to its participation in the Non-cooperation movement. The election occurred during the early stages of non-Brahmin movement and the major issue of the election was anti-Brahminism. Justice party won the election with no significant opposition and A. Subbarayalu Reddiar became the first Chief Minister of the presidency.
The second legislative council election for the Madras Presidency after the establishment of a bicameral legislature by the Government of India Act of 1935 was held in March 1946. The election was held after 6 years of Governor's rule starting from 1939, when the Indian National Congress government of C. Rajagopalachari resigned protesting Indian involvement in World War II. This was the last direct election held for the Madras Legislative Council in the presidency - after Indian independence in 1947, the presidency became the Madras state and direct elections to the council were abolished. The election was held simultaneously with that of the Legislative Assembly. The Congress swept the polls by winning 32 out of 46 seats. The years after this election saw factionalism in Madras Congress party with divisions across regional and communal lines. Competition among T. Prakasam, C. Rajagopalachari and K. Kamaraj resulted in the election of Prakasam as the Chief Minister initially. But he was later defeated by Omandur Ramaswamy Reddiar with Kamaraj's support. In turn, Reddiar himself was ousted to make way for P. S. Kumaraswamy Raja with the support of Kamaraj.

Provincial elections were held in British India in the winter of 1936-37 as mandated by the Government of India Act 1935. Elections were held in eleven provinces - Madras, Central Provinces, Bihar, Orissa, United Provinces, Bombay Presidency, Assam, NWFP, Bengal, Punjab and Sindh.

Elections in the state of Bihar, India are conducted in accordance with the Constitution of India. The Assembly of Bihar creates laws regarding the conduct of local body elections unilaterally while any changes by the state legislature to the conduct of state level elections need to be approved by the Parliament of India.

General elections were held in British India in 1934. The Indian National Congress emerged as the largest party in the Central Legislative Assembly.

Provincial elections were held in British India in January 1946 to elect members of the legislative councils of British Indian provinces. The consummation of British rule in India were the 1945/1946 elections. As minor political parties were eliminated the political scene became restricted to the Indian National Congress and the Muslim League who were more antagonised than ever. The Congress, in a repeat of the 1937 elections, won 90 percent of the general non-Muslim seats while the Muslim League won the majority of Muslim seats in the provinces. The League verified its claim to be the sole representative of Muslim India. The election laid the path to Pakistan.

The Kerala Legislative Assembly election of 1960 was the second assembly election in the Indian state of Kerala. The elections were held on 1 February 1960.

The Legislatures of British India included legislative bodies in the presidencies and provinces of British India, the Imperial Legislative Council, the Chamber of Princes and the Central Legislative Assembly. The legislatures were created under Acts of Parliament of the United Kingdom. Initially serving as small advisory councils, the legislatures evolved into partially elected bodies, but were never elected through suffrage. Provincial legislatures saw boycotts during the period of dyarchy between 1919 and 1935. After reforms and elections in 1937, the largest parties in provincial legislatures formed governments headed by a Prime Minister. A few British Indian subjects were elected to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which had superior powers than colonial legislatures. British Indian legislatures did not include Burma's legislative assembly after 1937, the State Council of Ceylon nor the legislative bodies of princely states.

The Bengal Legislative Assembly was the largest legislature in British India, serving as the lower chamber of the legislature of Bengal. It was established under the Government of India Act, 1935. The assembly played an important role in the final decade of undivided Bengal. The Leader of the House was the Prime Minister of Bengal. The assembly's lifespan covered the anti-feudal movement of the Krishak Praja Party, the period of World War II, the Lahore Resolution, the Quit India movement, suggestions for a United Bengal and the partition of Bengal and partition of British India.
Elections to the Punjab Legislative Assembly were held in January 1946 as part of the 1946 Indian provincial elections.


















