Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them.

Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid 20:4(ω-6), or 20:4(5,8,11,14). It is structurally related to the saturated arachidic acid found in cupuaçu butter. Its name derives from the New Latin word arachis (peanut), but peanut oil does not contain any arachidonic acid.

Epoxide hydrolases (EH's), also known as epoxide hydratases, are enzymes that metabolize compounds that contain an epoxide residue; they convert this residue to two hydroxyl residues through an epoxide hydrolysis reaction to form diol products. Several enzymes possess EH activity. Microsomal epoxide hydrolase, soluble epoxide hydrolase, and the more recently discovered but not as yet well defined functionally, epoxide hydrolase 3 (EH3) and epoxide hydrolase 4 (EH4) are structurally closely related isozymes. Other enzymes with epoxide hydrolase activity include leukotriene A4 hydrolase, Cholesterol-5,6-oxide hydrolase, MEST (gene) (Peg1/MEST), and Hepoxilin-epoxide hydrolase. The hydrolases are distinguished from each other by their substrate preferences and, directly related to this, their functions.
In blood vessels Endothelium-Derived Hyperpolarizing Factor or EDHF is proposed to be a substance and/or electrical signal that is generated or synthesized in and released from the endothelium; its action is to hyperpolarize vascular smooth muscle cells, causing these cells to relax, thus allowing the blood vessel to expand in diameter.
The epoxyeicosatrienoic acids or EETs are signaling molecules formed within various types of cells by the metabolism of arachidonic acid by a specific subset of Cytochrome P450 enzymes termed cytochrome P450 epoxygenases. These nonclassic eicosanoids are generally short-lived, being rapidly converted from epoxides to less active or inactive dihydroxy-eicosatrienoic acids (diHETrEs) by a widely distributed cellular enzyme, Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), also termed Epoxide hydrolase 2. The EETs consequently function as transiently acting, short-range hormones; that is, they work locally to regulate the function of the cells that produce them or of nearby cells. The EETs have been most studied in animal models where they show the ability to lower blood pressure possibly by a) stimulating arterial vasorelaxation and b) inhibiting the kidney's retention of salts and water to decrease intravascular blood volume. In these models, EETs prevent arterial occlusive diseases such as heart attacks and brain strokes not only by their anti-hypertension action but possibly also by their anti-inflammatory effects on blood vessels, their inhibition of platelet activation and thereby blood clotting, and/or their promotion of pro-fibrinolytic removal of blood clots. With respect to their effects on the heart, the EETs are often termed cardio-protective. Beyond these cardiovascular actions that may prevent various cardiovascular diseases, studies have implicated the EETs in the pathological growth of certain types of cancer and in the physiological and possibly pathological perception of neuropathic pain. While studies to date imply that the EETs, EET-forming epoxygenases, and EET-inactivating sEH can be manipulated to control a wide range of human diseases, clinical studies have yet to prove this. Determination of the role of the EETS in human diseases is made particularly difficult because of the large number of EET-forming epoxygenases, large number of epoxygenase substrates other than arachidonic acid, and the large number of activities, some of which may be pathological or injurious, that the EETs possess.
Cytochrome P4502C8 (abbreviated CYP2C8), a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. Cytochrome P4502C8 also possesses epoxygenase activity, i.e. it metabolizes long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, e.g. arachidonic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, and Linoleic acid to their biologically active epoxides.
Hepoxilins (Hx) are a set of epoxyalcohol metabolites of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), i.e. they possess both an epoxide and an alcohol residue. HxA3, HxB3, and their non-enzymatically formed isomers are nonclassic eicosanoid derived from acid the (PUFA), arachidonic acid. A second group of less well studied hepoxilins, HxA4, HxB4, and their non-enzymatically formed isomers are nonclassical eicosanoids derived from the PUFA, eicosapentaenoic acid. Recently, 14,15-HxA3 and 14,15-HxB3 have been defined as arachidonic acid derivatives that are produced by a different metabolic pathway than HxA3, HxB3, HxA4, or HxB4 and differ from the aforementioned hepoxilins in the positions of their hydroxyl and epoxide residues. Finally, hepoxilin-like products of two other PUFAs, docosahexaenoic acid and linoleic acid, have been described. All of these epoxyalcohol metabolites are at least somewhat unstable and are readily enzymatically or non-enzymatically to their corresponding trihydroxy counterparts, the trioxilins (TrX). HxA3 and HxB3, in particular, are being rapidly metabolized to TrXA3, TrXB3, and TrXC3. Hepoxilins have various biological activities in animal models and/or cultured mammalian tissues and cells. The TrX metabolites of HxA3 and HxB3 have less or no activity in most of the systems studied but in some systems retain the activity of their precursor hepoxilins. Based on these studies, it has been proposed that the hepoxilins and trioxilins function in human physiology and pathology by, for example, promoting inflammation responses and dilating arteries to regulate regional blood flow and blood pressure.
The isoprostanes are prostaglandin-like compounds formed in vivo from the free radical-catalyzed peroxidation of essential fatty acids without the direct action of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. The compounds were discovered in 1990 by L. Jackson Roberts and Jason D. Morrow in the Division of Clinical Pharmacology at Vanderbilt University. These nonclassical eicosanoids possess potent biological activity as inflammatory mediators that augment the perception of pain. These compounds are accurate markers of lipid peroxidation in both animal and human models of oxidative stress.

Fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase is an aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme that in human is encoded in the ALDH3A2 gene on chromosome 17. Aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes function to remove toxic aldehydes that are generated by the metabolism of alcohol and by lipid peroxidation.

Mead acid is an omega-9 fatty acid, first characterized by James F. Mead. As with some other omega-9 polyunsaturated fatty acids, animals can make Mead acid de novo. Its elevated presence in the blood is an indication of essential fatty acid deficiency. Mead acid is found in large quantities in cartilage.
In biochemistry, docosanoids are signaling molecules made by the metabolism of twenty-two-carbon fatty acids (EFAs), especially the omega-3 fatty acid, Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) by lipoxygenase, cyclooxygenase, and cytochrome P450 enzymes. Other docosanoids are metabolites of n-3 docosapentaenoic acid, n-6 DHA (i.e. 4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z-docosahexaenoic acid, and docosatetraenoic acid. Prominent docosanoid metabolites of DHA and n-3 DHA are members of the specialized proresolving mediator class of polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites that possess potent anti-inflammation, tissue healing, and other activities.

Cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1), also known as prostaglandin G/H synthase 1, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 or prostaglandin H2 synthase 1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGS1 gene. In humans it is one of two cyclooxygenases.

Cytochrome P450 2J2 (CYP2J2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP2J2 gene. CYP2J2 is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The enzymes are oxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in the metabolism of drugs and other xenobiotics) as well as in the synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids.

Cytochrome P450 4F8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F8 gene.

Cytochrome P450 4F12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F12 gene.

Bile acyl-CoA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SLC27A5 gene.
Epoxygenases are a set of membrane-bound, heme-containing cytochrome P450 enzymes that metabolize polyunsaturated fatty acids to epoxide products that have a range of biological activities. The most thoroughly studied substrate of the CYP epoxylgenases is arachidonic acid. This polyunsaturated fatty acid is metabolized by cyclooxygenases to various prostaglandin, thromboxane, and prostacyclin metabolites in what has been termed the first pathway of eicosanoid production; it is also metabolized by various lipoxygenases to hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids and leukotrienes in what has been termed the second pathway of eicosanoid production. The metabolism of arachidonic acid to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids by the CYP epoxygenases has been termed the third pathway of eicosanoid metabolism. Like the first two pathways of eicosanoid production, this third pathway acts as a signaling pathway wherein a set of enzymes metabolize arachidonic acid to a set of products that act as secondary signals to work in activating their parent or nearby cells and thereby orchestrate functional responses. However, none of these three pathways is limited to metabolizing arachidonic acid to eicosanoids. Rather, they also metabolize other polyunsaturated fatty acids to products that are structurally analogous to the eicosanoids but often have different bioactivity profiles. This is particularly true for the CYP epoxygenases which in general act on a broader range of polyunsaturated fatty acids to form a broader range of metabolites than the first and second pathways of eicosanoid production. Furthermore, the latter pathways form metabolites many of which act on cells by binding with and thereby activating specific and well-characterized receptor proteins; no such receptors have been fully characterized for the epoxide metabolites. Finally, there are relatively few metabolite-forming lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenases in the first and second pathways and these oxygenase enzymes share similarity between humans and other mammalian animal models. The third pathway consists of a large number of metabolite-forming CYP epoxygenases and the human epoxygenases have important differences from those of animal models. Partly because of these differences, it has been difficult to define clear roles for the epoxygenase-epoxide pathways in human physiology and pathology.

20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, also known as 20-HETE or 20-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid, is an eicosanoid metabolite of arachidonic acid that has a wide range of effects on the vascular system including the regulation of vascular tone, blood flow to specific organs, sodium and fluid transport in the kidney, and vascular pathway remodeling. These vascular and kidney effects of 20-HETE have been shown to be responsible for regulating blood pressure and blood flow to specific organs in rodents; genetic and preclinical studies suggest that 20-HETE may similarly regulate blood pressure and contribute to the development of stroke and heart attacks. Additionally the loss of its production appears to be one cause of the human neurological disease, Hereditary spastic paraplegia. Preclinical studies also suggest that the overproduction of 20-HETE may contribute to the progression of certain human cancers, particularly those of the breast.
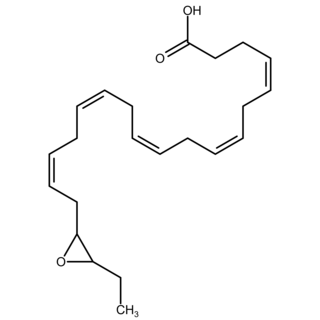
Epoxide docosapentaenoic acids are metabolites of the 22-carbon straight-chain omega-3 fatty acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Cell types that express certain cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases metabolize polyunsaturated fatty acid's (PUFAs) by converting one of their double bonds to an epoxide. In the best known of these metabolic pathways, cellular CYP epoxygenases metabolize the 20-carbon straight-chain omega-6 fatty acid, arachidonic acid, to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs); another CYP epoxygenase pathway metabolizes the 20-carbon omega-3 fatty acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), to epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EEQs). CYP epoxygenases similarly convert various other PUFAs to epoxides These epoxide metabolites have a variety of activities. However, essentially all of them are rapidly converted to their corresponding, but in general far less active, Vicinal (chemistry) dihydroxy fatty acids by ubiquitous cellular Soluble epoxide hydrolase. Consequently, these epoxides, including EDPs, operate as short-lived signaling agents that regulate the function of their parent or nearby cells. The particular feature of EDPs distinguishing them from EETs is that they derive from omega-3 fatty acids and are suggested to be responsible for some of the beneficial effects attributed to omega-3 fatty acids and omega-3-rich foods such as fish oil.

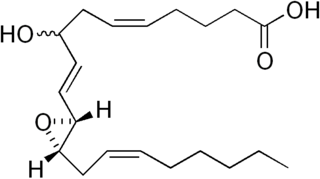
Epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids are a set of biologically active epoxides that various cell types make by metabolizing the omega 3 fatty acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), with certain cytochrome P450 epoxygenases. These epoxygenases can metabolize EPA to as many as 10 epoxides that differ in the site and/or stereoisomer of the epoxide formed; however, the formed EEQs, while differing in potency, often have similar bioactivities and are commonly considered together.












