
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e., hydrogen ion, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or, capable of forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
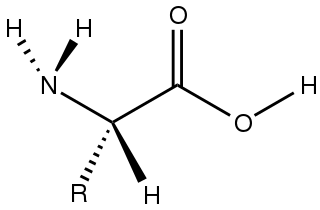
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino and carboxylate −CO−2 functional groups, along with a side chain specific to each amino acid. The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N); in addition sulfur (S) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (Se) in the less common amino acid selenocysteine. More than 500 naturally occurring amino acids are known to constitute monomer units of peptides, including proteins, as of 2020.

Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.

A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils.

Theophylline, also known as 1,3-dimethylxanthine, is a phosphodiesterase inhibiting drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma under a variety of brand names. As a member of the xanthine family, it bears structural and pharmacological similarity to theobromine and caffeine, and is readily found in nature, being present in tea and cocoa. A small amount of theophylline is one of the products of caffeine metabolic processing in the liver.

Guaraná, Paullinia cupana, syns. P. crysan, P. sorbilis) is a climbing plant in the family Sapindaceae, native to the Amazon basin and especially common in Brazil. Guaraná has large leaves and clusters of flowers and is best known for the seeds from its fruit, which are about the size of a coffee bean.

The Sapindaceae are a family of flowering plants in the order Sapindales known as the soapberry family. It contains 138 genera and 1858 accepted species. Examples include horse chestnut, maples, ackee and lychee.

Borage, also known as a starflower, is an annual herb in the flowering plant family Boraginaceae. It is native to the Mediterranean region, and has naturalized in many other locales.

Paullinia is a genus of flowering shrubs, small trees and lianas in the soapberry family, Sapindaceae, native to tropical South America, Central America and the Caribbean.
Paullinia navicularis is a species of plant in the family Sapindaceae. It is endemic to Ecuador.

11-Eicosenoic acid, also called gondoic acid, is a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid found in a variety of plant oils and nuts; in particular jojoba oil. It is one of a number of eicosenoic acids.
The molecular formula C20H30O may refer to:

Fresna nyassae, the variegated Acraea skipper or variegated Acraea hopper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found from Ghana and Kenya to South Africa.

Neptis trigonophora, the barred sailer, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found in southern Africa.
Neptis kiriakoffi, or Kiriakoff's sailer, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Sub-Saharan Africa. The habitat consists of forests and Brachystegia woodland.
Eicosenoic acid may refer to one of three closely related chemical compounds:

Christian Franz Paullini was a German physician and theologian.

Paullinia pinnata is a flowering plant species in the genus of Paullinia found in South America and Africa.
Paullinia paullinioides is a flowering plant species in the genus of Paullinia found in South America. It was first described in 1895, by Ludwig Adolph Timotheus Radlkofer.














