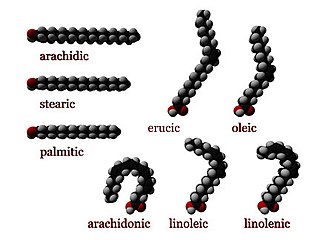
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and they are important structural components for cells.

In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds; most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.

In biology and biochemistry, a lipid is a macro biomolecule that is soluble in nonpolar solvents. Non-polar solvents are typically hydrocarbons used to dissolve other naturally occurring hydrocarbon lipid molecules that do not dissolve in water, including fatty acids, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, and phospholipids.
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them.

Oleic acid is a fatty acid that occurs naturally in various animal and vegetable fats and oils. It is an odorless, colorless oil, although commercial samples may be yellowish. In chemical terms, oleic acid is classified as a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid, abbreviated with a lipid number of 18:1 cis-9. It has the formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. The name derives from the Latin word oleum, which means oil. It is the most common fatty acid in nature. The salts and esters of oleic acid are called oleates.
Enoyl-CoA-(∆) isomerase, also known as dodecenoyl-CoA-(∆) isomerase, 3,2-trans-enoyl-CoA isomerase, ∆3(cis),∆2(trans)-enoyl-CoA isomerase, or acetylene-allene isomerase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of cis- or trans-double bonds of coenzyme A (CoA) bound fatty acids at gamma-carbon to trans double bonds at beta-carbon as below:

Alpinia nutans, the shellflower, or dwarf cardamom, is a Southeast Asian plant of the ginger family (Zingiberaceae), and is a medicinal plant used to control hypertension, as diuretic, antifungal, and antiulcer. In Japan it is used as food preservative.

In biochemistry and metabolism, beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH2, which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport chain. It is named as such because the beta carbon of the fatty acid undergoes oxidation to a carbonyl group. Beta-oxidation is primarily facilitated by the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, an enzyme complex associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane, although very long chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes.
A dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl functional groups (−COOH). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as HO2C−R−CO2H, where R can be aliphatic or aromatic. In general, dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to monocarboxylic acids. Dicarboxylic acids are also used in the preparation of copolymers such as polyamides and polyesters. The most widely used dicarboxylic acid in the industry is adipic acid, which is a precursor used in the production of nylon. Other examples of dicarboxylic acids include aspartic acid and glutamic acid, two amino acids in the human body. The name can be abbreviated to diacid.

Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (Δ-9-desaturase) is an endoplasmic reticulum enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the formation of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), specifically oleate and palmitoleate from stearoyl-CoA and palmitoyl-CoA. Oleate and palmitoleate are major components of membrane phospholipids, cholesterol esters and alkyl-diacylglycerol. In humans, the enzyme is encoded by the SCD gene.

Abelmoschus manihot, the aibika, is a flowering plant in the family Malvaceae. It was formerly considered a species of Hibiscus, but is now classified in the genus Abelmoschus. The plant is also known as the sunset muskmallow, sunset hibiscus, or hibiscus manihot.

Enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECH) or crotonase is an enzyme that hydrates the double bond between the second and third carbons on 2-trans/cis-enoyl-CoA:

2,4 Dienoyl-CoA reductase also known as DECR1 is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the DECR1 gene which resides on chromosome 8. This enzyme catalyzes the following reactions
The crotonase family comprises mechanistically diverse proteins that share a conserved trimeric quaternary structure, the core of which consists of 4 turns of a (beta/beta/alpha)n superhelix.
In enzymology, an enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH, B-specific) (EC 1.3.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Leukotriene-B(4) omega-hydroxylase 1 is an enzyme protein involved in the metabolism of various endogenous substrates and xenobiotics. The most notable substrate of the enzyme is leukotriene B4, a potent mediator of inflammation. The CYP4F2 gene encodes the enzyme in humans.

CYP4F11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F11 gene. This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This gene is part of a cluster of cytochrome P450 genes on chromosome 19. Another member of this family, CYP4F2, is approximately 16 kb away. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.
Alpinia nigra is a medium-sized herb belonging to the ginger family. The rhizome is well known in many Asian cultures as a medicinal and culinary item. In many Asian tribal communities it is a part of the diet along with rice.
Enoyl-CoA hydratase 2 is an enzyme with systematic name (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA hydro-lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction on D-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA
The queen bee acid or 10-HDA is a bio-active compound found in royal jelly.












