This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2013) |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Tricosanoic acid | |
| Other names Tricosylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.654 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H46O2 | |
| Molar mass | 354.35 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
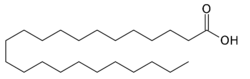
Tricosylic acid, or tricosanoic acid, is a 23-carbon long-chain saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)21COOH.