

ESSA-7 (or TOS-E) was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).


ESSA-7 (or TOS-E) was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).
ESSA-7 was launched on August 16, 1968, at 11:31 UTC. It was launched atop a Delta rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, USA. The spacecraft had a mass of 145 kilograms (320 lb) at the time of launch. ESSA-7 had an inclination of 101.72°, and an orbited the Earth once every 114.9 minutes. Its perigee was 1,432 kilometers (890 mi) and its apogee was 1,476 kilometers (917 mi).
The United States has eight federal uniformed services that commission officers as defined by Title 10 and subsequently structured and organized by Titles 10, 14, 32, 33, and 42 of the U.S. Code.

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps is one of eight federal uniformed services of the United States, and operates under the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), a scientific agency overseen by the Department of Commerce. The NOAA Corps is made up of scientifically and technically trained officers. The NOAA Corps and the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps are the only U.S. uniformed services that consist only of commissioned officers, with no enlisted or warrant officer ranks. The NOAA Corps' primary mission is to monitor oceanic conditions, support major waterways, and monitor atmospheric conditions.

Essa is a township in Ontario, Canada, west and south of the city of Barrie in Simcoe County. It is bounded by County Road 90 to its north, County Road 27 to its east, and Ontario Highway 89 to its south. The township is about 100 kilometres (62 mi) from Toronto. The township is well known for its agriculture industry, particularly potato farming. Nearby CFB Borden brings a strong military presence to the area as well, including a high number of Francophone families.

Television InfraRed Observation Satellite (TIROS) is a series of early weather satellites launched by the United States, beginning with TIROS-1 in 1960. TIROS was the first satellite that was capable of remote sensing of the Earth, enabling scientists to view the Earth from a new perspective: space. The program, promoted by Harry Wexler, proved the usefulness of satellite weather observation, at a time when military reconnaissance satellites were secretly in development or use. TIROS demonstrated at that time that "the key to genius is often simplicity". TIROS is an acronym of "Television InfraRed Observation Satellite" and is also the plural of "tiro" which means "a young soldier, a beginner".

The Bergen Line, or the Bergen Railway, is a 371-kilometre (231 mi) long scenic standard gauge railway line between Bergen and Hønefoss, Norway. The name is often applied to the entire route from Bergen to Oslo, including the Randsfjord and Drammen lines between Hønefoss and Oslo, covering a total distance of 496 kilometres (308 mi). It is the highest mainline railway line in Northern Europe, crossing the Hardangervidda plateau at 1,237 metres (4,058 ft) above sea level.

The Svalbard Rocket Range or SvalRak as it is named, is a launch site for sounding rockets at Ny-Ålesund in Svalbard, Norway. The site has been in use since 1997 and is owned by Andøya Space Center, which is owned by the Norwegian Ministry of Trade, Industry and Fisheries and the Kongsberg Group. SvalRak's location at the 79th parallel north makes it well-suited for launching rockets to investigate Earth's magnetic field. It is used mostly by American, Japanese and Norwegian researchers. It is the world's northernmost launch site.

Guangde is a county-level city in the southeast of Anhui Province, People's Republic of China, bordering the provinces of Jiangsu to the north and Zhejiang to the east. It is the easternmost county-level division of Anhui and is under the jurisdiction of the prefecture-level city Xuancheng within Anhui Province. The city has a population of 510,000 and an area of 2,165 km2 (836 sq mi). The seat of government is at Taozhou Town.

The Numedal Line is a 92.8-kilometer (57.7 mi) long railway line that runs up the Numedal valley between Kongsberg and Rødberg in Buskerud county, Norway. Built and operated by the Norwegian State Railways, the non-electrified, standard gauge line passes through the municipalities of Kongsberg, Flesberg, Rollag and Nore og Uvdal. It is now owned by the Norwegian National Rail Administration.

The Stavne–Leangen Line is a 5.8-kilometer (3.6 mi) railway line between Stavne and Leangen in Trondheim, Norway. The line provides an alternative connection between the Dovre Line and Nordland Line, allowing trains to bypass Trondheim Central Station. The line includes the Stavne Bridge over the river of Nidelva, Lerkendal Station and the 2.7-kilometer (1.7 mi) long Tyholt Tunnel. Construction of the line started during the Second World War by the Wehrmacht, the German military occupying Norway, in an attempt to make the railway in Trondheim resistant to sabotage. Because of the long construction time of the tunnel, tracks were laid in the city streets, but neither route was completed before the end of the war. Construction was placed on hold and the Stavne–Leangen Line did not open until 2 June 1957. At first it was primarily used by freight trains. Since 1988, passenger services from the Dovre Line to Lerkendal Station have been provided, but they do not use the Tyholt Tunnel, instead taking a U-turn back across the Nidelva onto the Dovre Line.

ESSA-8 was a weather satellite launched by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on December 15, 1968, from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).
The Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA) was a United States Federal executive agency created in 1965 as part of a reorganization of the United States Department of Commerce. Its mission was to unify and oversee the meteorological, climatological, hydrographic, and geodetic operations of the United States. It operated until 1970, when it was replaced by the new National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).

ESSA-1 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).

ESSA-9, also known as TOS-G, was a meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA). ESSA-9 replaced the ESSA-7 satellite.

SpaceX COTS Demo Flight 1 was the first orbital spaceflight of the Dragon cargo spacecraft, and the second overall flight of the Falcon 9 rocket manufactured by SpaceX. It was also the first demonstration flight for NASA's Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) program. The primary mission objectives were to test the orbital maneuvering and reentry of the Dragon capsule. The mission also aimed to test fixes to the Falcon 9 rocket, particularly the unplanned roll of the first stage that occurred during flight 1. Liftoff occurred on 8 December 2010 at 15:43 UTC.
Galaxy 5 was a communications satellite operated by PanAmSat from 1992 to 2005. It spent most of its operational life at an orbital location of 176° E. Galaxy 5 was launched on March 14, 1992, with an Atlas launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, United States, and covered North America with twenty-four transponders each on the C- and zero in Ku band.
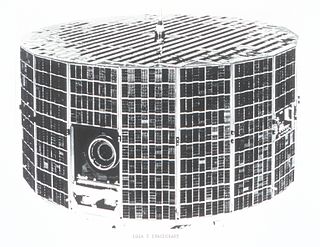
ESSA-2 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).

ESSA 3 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).
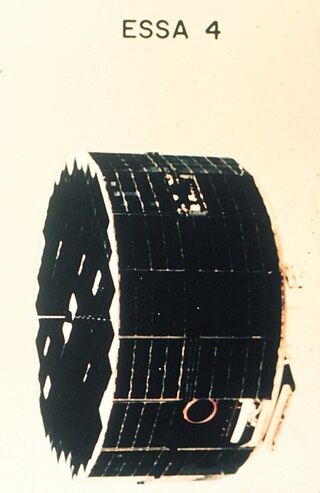
ESSA-4 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).

ESSA-5 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).

ESSA 6 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from ESSA 7. National Aeronautics and Space Administration . Retrieved June 4, 2018.
This article incorporates public domain material from ESSA 7. National Aeronautics and Space Administration . Retrieved June 4, 2018.