Related Research Articles
Electoral systems of the Australian states and territories are broadly similar to the electoral system used in federal elections in Australia.
The boundary commissions in the United Kingdom are non-departmental public bodies responsible for determining the boundaries of constituencies for elections to the House of Commons. There are four boundary commissions:

The House of Assembly, or lower house, is one of the two chambers of the Parliament of South Australia. The other is the Legislative Council. It sits in Parliament House in the state capital, Adelaide.

The Tasmanian Legislative Council is the upper house of the Parliament of Tasmania in Australia. It is one of the two chambers of the Parliament, the other being the House of Assembly. Both houses sit in Parliament House in the state capital, Hobart. Members of the Legislative Council are often referred to as MLCs.

An electoral district in Canada is a geographical constituency upon which Canada's representative democracy is based. It is officially known in Canadian French as a circonscription but frequently called a comté (county), and is also colloquially and more commonly known as a riding or constituency.

In Australia, electoral districts for the Australian House of Representatives are called divisions or more commonly referred to as electorates or seats. There are currently 151 single-member electorates for the Australian House of Representatives.

The Parliament of South Australia is the bicameral legislature of the Australian state of South Australia. It consists of the 47-seat House of Assembly and the 22-seat Legislative Council. General elections are held every 4 years, with all of the lower house and half of the upper house filled at each election. It follows a Westminster system of parliamentary government with the executive branch required to both sit in parliament and hold the confidence of the House of Assembly. The parliament is based at Parliament House on North Terrace in the state capital of Adelaide.

The Western Australian Legislative Council is the upper house of the Parliament of Western Australia, a state of Australia. It is regarded as a house of review for legislation passed by the Legislative Assembly, the lower house. The two Houses of Parliament sit in Parliament House in the state capital, Perth.

In the United Kingdom (UK), each of the electoral areas or divisions called constituencies elects one member to the House of Commons.

An electoral division is a legally defined administrative area in the Republic of Ireland, generally comprising multiple townlands, and formerly a subdivision of urban and rural districts. Until 1996, EDs were known as district electoral divisions in the 29 county council areas and wards in the five county boroughs. Until 1972, DEDs also existed in Northern Ireland. The predecessor poor law electoral divisions were introduced throughout the island of Ireland in the 1830s. The divisions were used as local-government electoral areas until 1919 in what is now the Republic and until 1972 in Northern Ireland.
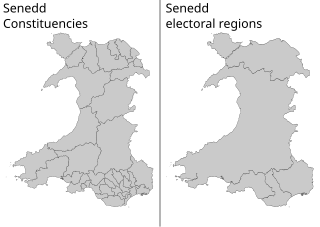
The Senedd constituencies and electoral regions are the electoral districts used to elect Members of the Senedd to the Senedd, and have been used in some form since the first election of the then National Assembly for Wales in 1999. New boundaries were introduced for the 2007 elections and currently consist of forty constituencies and five regions. The five electoral regions are: Mid and West Wales, North Wales, South Wales Central, South Wales East, and South Wales West, with the forty constituencies listed below. Voting last took place in all districts in the 2021 Senedd election, and are not used for local government.
In Australia, a redistribution is the process of redrawing the boundaries of electoral divisions for the House of Representatives arising from changes in population and changes in the number of representatives. There is no redistribution for the Senate as each State constitutes a division, though with multiple members. The Australian Electoral Commission (AEC), an independent statutory authority, oversees the apportionment and redistribution process for federal divisions, taking into account a number of factors. Politicians, political parties and the public may make submissions to the AEC on proposed new boundaries, but any interference with their deliberations is considered a serious offence.

The 2008 Western Australian state election was held on Saturday 6 September 2008 to elect 59 members to the Legislative Assembly and 36 members to the Legislative Council. The incumbent centre-left Labor Party government, in power since the 2001 election and led since 25 January 2006 by Premier Alan Carpenter, was defeated by the centre-right Liberal Party opposition, led by Opposition Leader Colin Barnett since 6 August 2008.
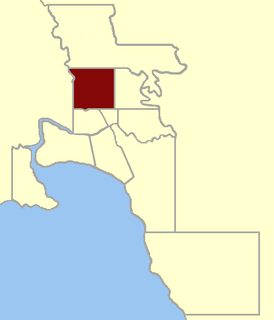
North Melbourne was an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1927.
West Adelaide was an electoral district of the House of Assembly in the Australian state of South Australia from 1862 to 1902.
Stanley was an electoral district of the House of Assembly in the Australian state of South Australia.
East Adelaide was an electoral district of the South Australian Legislative Council from 1851 to 1857 and an electoral district of the South Australian House of Assembly from 1862 to 1902.
Wooroora was an electoral district of the House of Assembly in the Australian colony of South Australia.

The South Australian Electoral Districts Boundaries Commission is an independent, non partisan commission responsible for the compulsory re-drawing of South Australian House of Assembly electoral districts after each South Australian election.
The Constitution Act Further Amendment Act 1881, No. 236 of 1881, long title "An Act to further amend "The Constitution Act"", was an act of the government of South Australia to amend the Constitution of South Australia. Its purpose was to amend the terms of the Constitution Act 1856 in order to increase the size of the Legislative Council of South Australia from 18 to 24 members, and also to divide the province into four electoral districts each to elect six of the members.
References
- ↑ Electoral Act 1861 ( sa )