
The Potsdam Agreement was the agreement between three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union after the war ended in Europe on 1 August 1945 and it was published the next day. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned the military occupation and reconstruction of Germany, its border, and the entire European Theatre of War territory. It also addressed Germany's demilitarisation, reparations, the prosecution of war criminals and the mass expulsion of ethnic Germans from various parts of Europe. France was not invited to the conference but formally remained one of the powers occupying Germany.

Szczecin is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major seaport and Poland's seventh-largest city. As of December 2021, the population was 395,513.

Police is a town in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northwestern Poland. It is the capital of Police County and one of the biggest towns of the Szczecin agglomeration.

The History of Szczecin dates back to the 8th century. Throughout its history the city has been part of Poland, Denmark, Sweden and Germany. Since the Middle Ages, it is one of the largest and oldest cities in the historic region of Pomerania, and today, is it the largest city in northwestern Poland.

Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania, is the part of Pomerania which comprised the eastern part of the Duchy and later Province of Pomerania. It stretched roughly from the Oder River in the West to Pomerelia in the East. Since 1945, Farther Pomerania has been part of Poland; the bulk of former Farther Pomerania is within the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, while its easternmost parts are within the Pomeranian Voivodeship. The Polish term Pomorze Zachodnie is colloquially used in contemporary Poland as a synonym for the West Pomeranian Voivodship whose borders do not match the historical ones; in Polish historical usage, it applied to all areas west of Pomerelia.

The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Germany was stripped of its sovereignty and former state: after Nazi Germany surrendered on 8 May 1945, four countries representing the Allies asserted joint authority and sovereignty through the Allied Control Council (ACC) under the Berlin Declaration of 5 June 1945 that led to the fall of the German Reich. At first, Allied-occupied Germany was defined as all territories of Germany before the 1938 Nazi annexation of Austria; the Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945 defined the new eastern German border by giving Poland and the Soviet Union all regions of Germany east of the Oder–Neisse line and divided the remaining "Germany as a whole" into four occupation zones, each administered by one of the Allies.

Trzebież is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Police, within Police County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-western Poland, close to the German border. It lies approximately 15 kilometres (9 mi) north of Police and 28 km (17 mi) north of the regional capital Szczecin.

History of Pomerania (1945–present) covers the history of Pomerania during World War II aftermath, the Communist and since 1989 Democratic era.

Drogoradz is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Police, within Police County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-western Poland, close to the German border. It lies approximately 13 kilometres (8 mi) north-west of Police and 25 km (16 mi) north of the regional capital Szczecin.

Niekłończyca is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Police, within Police County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-western Poland, close to the German border. It lies approximately 10 kilometres (6 mi) north-west of Police and 23 km (14 mi) north of the regional capital Szczecin.

Uniemyśl is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Police, within Police County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-western Poland, close to the German border. It lies approximately 12 kilometres (7 mi) north of Police and 24 km (15 mi) north of the regional capital Szczecin.

The Port of Szczecin is a Polish seaport and deep water harbour in Szczecin, Poland. It is located at the Oder and Regalica rivers in the Lower Oder Valley, off the Szczecin Lagoon. In the past, the port included the now defunct Szczecin Shipyard. A free trade zone has been designated within the port area.
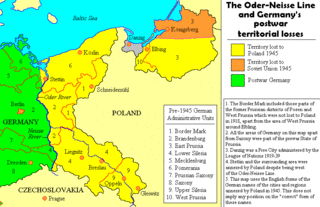
The Oder–Neisse line is an unofficial term for the modern border between Germany and Poland. The line generally follows the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, meeting the Baltic Sea in the north. A small portion of Polish territory does fall west of the line, including the cities of Szczecin and Świnoujście.

Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania,Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania, is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea. Western Pomerania's boundaries have changed through the centuries as it belonged to various countries such as Poland, the Duchy of Pomerania, Sweden, Denmark, as well as Prussia which incorporated it as the Province of Pomerania.
Eric Spiegel was a German government official. From 2 May to 26 May 1945, he briefly served as the high mayor of German district of the Soviet-occupied city of Szczecin.

The Szczecin County was a county centered around the town of Police, that existed from 1946 to 1975. In 1946 it was a subdivision of the District of the Western Pomerania, and from 1946 to 1975, of the Szczecin Voivodeship. Its seat of government was located extrateritorially in the nearby city of Szczecin.
Veletian County was a county of the District of Western Pomerania, within Poland, during the administration of the Provisional Government of National Unity. Its capital was Nowe Warpno. It existed from 4 October 1945 to 29 May 1946.
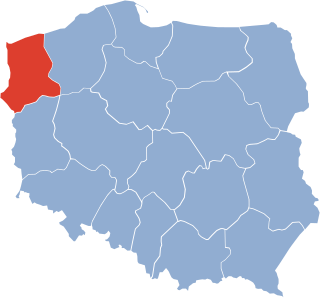
The Szczecin Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) with capital in Szczecin, that was centered on the Farther Pomerania. It existed from 1946 to 1975. Until 19 February 1947 it was under the administration of Provisional Government of National Unity, which then was replaced by the Polish People's Republic. It was established on 28 June 1946, when it was formed from the territory of the District of the Western Pomerania, and parts of the Gdańsk, and Pomeranian Voivodeships. On 6 July 1950, its eastern half was incorporated into then-established Koszalin Voivodeship, and the voivodeship ceased to exist on 31 May 1975, when it was replaced by then-established Szczecin and Gorzów Voivodeships.

The Polish occupation zone in Germany was a military occupation area, under the administration of the Polish government-in-exile, located within the British Occupation Zone of the Allied-occupied Germany, that existed from 19 May 1945 to 10 September 1948. It was established from the territory of the British-controlled occupied Nazi Germany, following its surrender ending the World War II, and existed until 10 September 1948, when the administration of the area was given back to the United Kingdom. The zone was created for the Polish displaced people, consisting of those freed from German labour camps, and concentration camps, and the prisoners of war. In 1945, it was inhabited by over 30,000 Polish civilians and around 18,000 soldiers, and had an area of 6,470 km2, being located within the area of modern districts of County of Bentheim, Cloppenburg, Emsland, and Osnabrück, within Lower Saxony, Germany. Its seat was located in the town of Haren, then renamed to Maczków.

The Chojna County was a county centered around the towns of Chojna and Dębno, that existed from 1945 to 1975. From 1945 to 1946, it was located in the District of the Western Pomerania, and from 1946 to 1975, in the Szczecin Voivodeship. Its seat was located in the towns of Dębno, and briefly in 1945, Chojna. In 1946, it had 19 537 inhabitants, and an area of 1374 km². Currently, its former area is under the administration of the counties of Gryfino and Myślibórz, located in West Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland.
















