This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(August 2022) |
Treaty concerning the accession of the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia and the Slovak Republic to the European Union Treaty between the Kingdom of Belgium, the Kingdom of Denmark, the Federal Republic of Germany, the Hellenic Republic, the Kingdom of Spain, the French Republic, Ireland, the Italian Republic, the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, the Kingdom of the Netherlands, the Republic of Austria, the Portuguese Republic, the Republic of Finland, the Kingdom of Sweden, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (Member States of the European Union) and the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia, the Slovak Republic, concerning the accession of the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia and the Slovak Republic to the European Union. Contents | |
|---|---|
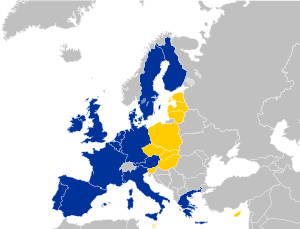 Countries involved in the treaty, with newly joining countries in yellow, and existing EU countries in blue. | |
| Type | Accession treaty |
| Signed | 16 April 2003 |
| Location | Athens |
| Effective | 1 May 2004 |
| Condition | Ratification by the 10 acceding countries and the 15 member countries of the European Union |
| Signatories | |
| Ratifiers | 25 / 25 |
| Depositary | Government of the Italian Republic |
| Languages | Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Italian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Polish, Portuguese, Slovak, Slovene, Spanish, Swedish |
After amendments made by the Athens Treaty: Consolidated version of TEC (2006) Consolidated version of TEU (2006) Consolidated version of Protocols & Annexes (2006) | |
| This article is part of a series on |
 |
|---|
The Treaty of Accession 2003 was the agreement between the member states of the European Union and ten countries (Czech Republic, Estonia, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Hungary, Malta, Poland, Slovenia, Slovakia), concerning these countries' accession into the EU (see 2004 enlargement of the European Union). At the same time it changed a number of points which were originally laid down in the Treaty of Nice. The treaty was signed on 16 April 2003 in Athens, Greece and it entered into force on 1 May 2004, resulting in enlargement of the European Union with 10 states.