
The Council of the European Union, often referred to in the treaties and other official documents simply as the Council, and informally known as the Council of Ministers, is the third of the seven Institutions of the European Union (EU) as listed in the Treaty on European Union. It is one of two legislative bodies and together with the European Parliament serves to amend and approve, or veto, the proposals of the European Commission, which holds the right of initiative.
Politics in Estonia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Estonia is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the Estonian parliament. Executive power is exercised by the government, which is led by the prime minister. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. Estonia is a member of the United Nations, the European Union, and NATO.

The European Council is a collegiate body that defines the overall political direction and priorities of the European Union. The European Council is part of the executive of the European Union (EU), beside the European Commission. It is composed of the heads of state or of government of the EU member states, the President of the European Council, and the President of the European Commission. The High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy also takes part in its meetings.

The European Committee of the Regions (CoR) is the European Union's (EU) assembly of local and regional representatives that provides sub-national authorities with a direct voice within the EU's institutional framework.

The institutions of the European Union are the seven principal decision-making bodies of the European Union and Euratom governed under the Treaties of the European Union and European Union law. They are, as listed in Article 13 of the Treaty on European Union:

The political structure of the European Union (EU) is similar to a confederation, where many policy areas are federalised into common institutions capable of making law; the competences to control foreign policy, defence policy, or the majority of direct taxation policies are mostly reserved for the twenty-seven state governments. These areas are primarily under the control of the EU's member states although a certain amount of structured co-operation and coordination takes place in these areas. For the EU to take substantial actions in these areas, all Member States must give their consent. Union laws that override State laws are more numerous than in historical confederations; however, the EU is legally restricted from making law outside its remit or where it is no more appropriate to do so at a state or local level (subsidiarity) when acting outside its exclusive competences. The principle of subsidiarity does not apply to areas of exclusive competence.

The Secretariat of the European Parliament is the administrative body of the European Parliament headed by a Secretary-General. It is based in the Kirchberg district of Luxembourg City and around the Brussels-Luxembourg Station in Brussels and employs around 4,000 officials.

The Constitution of the Italian Republic was ratified on 22 December 1947 by the Constituent Assembly, with 453 votes in favour and 62 against, before coming into force on 1 January 1948, one century after the previous Constitution of the Kingdom of Italy had been enacted. The text, which has since been amended sixteen times, was promulgated in an extraordinary edition of Gazzetta Ufficiale on 27 December 1947.

The Bureau of the Pan-African Parliament is the essential leadership of the Pan-African Parliament (PAP), consisting of one President and four Vice-Presidents.

The committees of the European Parliament are designed to aid the European Commission in initiating legislation.
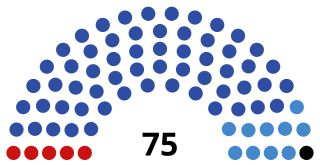
The State Council of Crimea is the parliament of the Russia-administered Republic of Crimea. It claims to be a continuation of the 'Supreme Council of Crimea' following a vote by the Ukrainian parliament to dissolve the Supreme Council of Crimea. The Parliament is housed in the Parliament building in the centre of Simferopol.
The Bureau of the European Parliament is responsible for matters relating to the budget, administration, organisation and staff. It is composed of the President of the European Parliament along with all 14 Vice-Presidents and the five Quaestors. They are elected for two and a half years with the President holding a casting vote. Elections are usually held at the start, and at the midpoint, of each Parliamentary term.

The ACP–EU Joint Parliamentary Assembly was created to bring together the elected representatives of the European Union and the elected representatives of the African, Caribbean and Pacific states that have signed the Cotonou Agreement.
European Union (EU) concepts, acronyms, and jargon are a terminology set that has developed as a form of shorthand, to quickly express a (formal) EU process, an (informal) institutional working practice, or an EU body, function or decision, and which is commonly understood among EU officials or external people who regularly deal with EU institutions.

The speaker of the Croatian Parliament is the presiding officer in the Croatian Parliament, Croatia's legislative body.

The Body of European Regulators for Electronic Communications (BEREC) is the body in which the regulators of the telecommunications markets in the European Union work together. Other participants include representatives of the European Commission, as well as telecommunication regulators from the member states of the EEA and of states that are in the process of joining the EU.

The INGO Conference is the body representing civil society in the Council of Europe, a European organisation founded in 1949. The Council of Europe has 46 member states with some 800 million citizens and its seat is in Strasbourg, France. The current president is Gerhard Ermischer.

Ramona Nicole Mănescu is a Romanian politician and lawyer. From 24 July 2019 to 4 November 2019, she served as minister of Foreign Affairs in the Romanian Government. She was a Member of the European Parliament serving 2007 to 2013 and 2014 to 2019 from the National Liberal Party, active within the European People's Party. As part of this group she is a member of the European Parliament Committee on Foreign Affairs, vice-chair in the Delegation for relations with the Mashreq countries and a substitute member in the Committee on transport and tourism and in Delegation for relations with the Arab Peninsula.
Primary legislation and secondary legislation are two forms of law, created respectively by the legislative and executive branches of governments in representative democracies. Primary legislation generally consists of statutes, also known as 'acts', that set out broad principles and rules, but may delegate specific authority to an executive branch to make more specific laws under the aegis of the principal act. The executive branch can then issue secondary legislation, creating legally enforceable regulations and the procedures for implementing them.

The ninth European Parliament was elected during the 2019 elections and sat until the tenth European Parliament was sworn in on 16 July 2024.


















