| Geographical range | Central Europe, Eastern Europe |
|---|---|
| Period | Iron Age |
| Dates | 7th century BC - 3rd century BC |
| Preceded by | Lusatian culture |
| Followed by | Oksywie culture, Przeworsk culture |
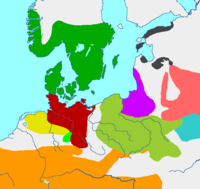
Nordic Bronze Age
Jastorf culture
Harpstedt-Nienburg group
Celtic groups
Pomeranian culture
House urns culture
East Baltic culture
West Baltic cairns culture
Milograd culture
Estonian group
The Pomeranian culture, also Pomeranian or Pomerelian Face Urn culture [1] was an Iron Age culture with origins in parts of the area south of the Baltic Sea (which later became Pomerania, part of northern Germany/Poland), from the 7th century BC to the 3rd century BC, which eventually covered most of today's Poland.
Contents
About 650 BC, it evolved from the Lusatian culture between the lower Vistula and Parseta rivers, [2] and subsequently expanded southward. Between 200 and 150 BC, it was succeeded by the Oksywie culture in eastern Pomerania and the Przeworsk culture at the upper Vistula and Oder rivers. [3]





















