Related Research Articles

Pyrrolysine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins in some methanogenic archaea and bacteria; it is not present in humans. It contains an α-amino group and a carboxylic acid group. Its pyrroline side-chain is similar to that of lysine in being basic and positively charged at neutral pH.

In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translate mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then change to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signalling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones.

Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation. The word "proteinogenic" means "protein creating". Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids, 20 in the standard genetic code and an additional 2 that can be incorporated by special translation mechanisms.
The C-terminus is the end of an amino acid chain, terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus.
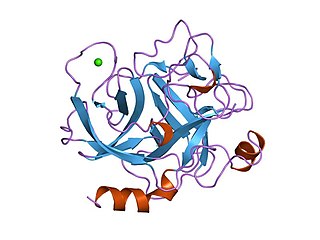
Endopeptidase or endoproteinase are proteolytic peptidases that break peptide bonds of nonterminal amino acids, in contrast to exopeptidases, which break peptide bonds from end-pieces of terminal amino acids. For this reason, endopeptidases cannot break down peptides into monomers, while exopeptidases can break down proteins into monomers. A particular case of endopeptidase is the oligopeptidase, whose substrates are oligopeptides instead of proteins.
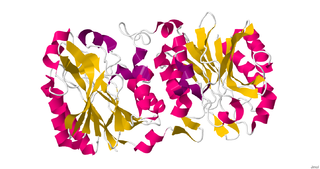
Nitrilase enzymes catalyse the hydrolysis of nitriles to carboxylic acids and ammonia, without the formation of "free" amide intermediates. Nitrilases are involved in natural product biosynthesis and post translational modifications in plants, animals, fungi and certain prokaryotes. Nitrilases can also be used as catalysts in preparative organic chemistry. Among others, nitrilases have been used for the resolution of racemic mixtures. Nitrilase should not be confused with nitrile hydratase which hydrolyses nitriles to amides. Nitrile hydratases are almost invariably co-expressed with an amidase, which converts the amide to the carboxylic acid. Consequently, it can sometimes be difficult to distinguish nitrilase activity from nitrile hydratase plus amidase activity.
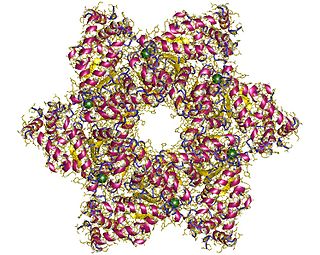
SV40 large T antigen is a hexamer protein that is a dominant-acting oncoprotein derived from the polyomavirus SV40. TAg is capable of inducing malignant transformation of a variety of cell types. The transforming activity of TAg is due in large part to its perturbation of the retinoblastoma (pRb) and p53 tumor suppressor proteins. In addition, TAg binds to several other cellular factors, including the transcriptional co-activators p300 and CBP, which may contribute to its transformation function. Similar proteins from related viruses are known as large tumor antigen in general.

Leupeptin, also known as N-acetyl-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-argininal, is a naturally occurring protease inhibitor that can inhibit cysteine, serine and threonine peptidases.
Clostripain is a proteinase that cleaves proteins on the carboxyl peptide bond of arginine. It was isolated from Clostridium histolyticum. The isoelectric point of the enzyme is 4.8-4.9, and optimum pH is 7.4~7.8. The composition of the enzyme is indicated to be of two chains of relative molecular mass 45,000 and 12,500.

Aspartate kinase or aspartokinase (AK) is an enzyme that catalyzes the phosphorylation of the amino acid aspartate. This reaction is the first step in the biosynthesis of three other amino acids: methionine, lysine, and threonine, known as the "aspartate family". Aspartokinases are present only in microorganisms and plants, but not in animals, which must obtain aspartate-family amino acids from their diet. Consequently, methionine, lysine and threonine are essential amino acids in animals.

Slotoxin is a peptide from Centruroides noxius Hoffmann scorpion venom. It belongs to the short scorpion toxin superfamily.

Agitoxin is a toxin found in the venom of the scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus. Other toxins found in this species include charybdotoxin (CTX). CTX is a close homologue of Agitoxin.

The genus Lysobacter belongs to the family Xanthomonadaceae within the Gammaproteobacteria and includes at least 46 named species, including: Lysobacter enzymogenes, L. antibioticus, L. gummosus, L. brunescens, L. defluvii, L. niabensis, L. niastensis, L. daejeonensis, L. yangpyeongensis, L. koreensis, L. concretionis, L. spongiicola, and L. capsici. Lysobacter spp. were originally grouped with myxobacteria because they shared the distinctive trait of gliding motility, but they uniquely display a number of traits that distinguish them from other taxonomically and ecologically related microbes including high genomic G+C content and the lack of flagella. The feature of gliding motility alone has piqued the interest of many, since the role of gliding bacteria in soil ecology is poorly understood. In addition, while a number of different mechanisms have been proposed for gliding motility among a wide range of bacterial species, the genetic mechanism in Lysobacter remains unknown. Members of the Lysobacter group have gained broad interest for production of extracellular enzymes. The group is also regarded as a rich source for production of novel antibiotics, such as β-lactams containing substituted side chains, macrocyclic lactams and macrocyclic peptide or depsipeptide antibiotics like the katanosins.
Peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase is an enzyme used in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan. It transfers a disaccharide-peptide from a donor substrate to synthesize a glycan chain.

MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MARK4 gene. MARK4 belongs to the family of serine/threonine kinases that phosphorylate microtubule-associated proteins (MAP) causing their detachment from microtubules. Detachment thereby increases microtubule dynamics and facilitates a number of cell activities including cell division, cell cycle control, cell polarity determination, and cell shape alterations.
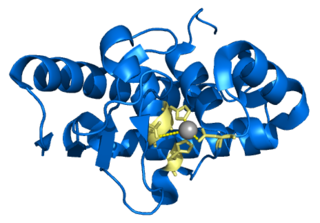
Lys-N is a metalloendopeptidase found in the mushroom Grifola frondosa that cleaves proteins on the amino side of lysine residues.
Lysyl endopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Beta-lytic metalloendopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Peptidyl-Asp metalloendopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Lysine Exporters are a superfamily of transmembrane proteins which export amino acids, lipids and heavy metal ions. They provide ionic homeostasis, play a role in cell envelope assembly, and protect from excessive concentrations of heavy metals in cytoplasm. The superfamily was named based on the early discovery of the LysE carrier protein of Corynebacterium glutamicum.
References
- ↑ Jekel, PA; Weijer, WJ; Beintema, JJ (15 October 1983). "Use of endoproteinase Lys-C from Lysobacter enzymogenes in protein sequence analysis". Analytical Biochemistry. 134 (2): 347–54. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(83)90308-1. PMID 6359954.
- ↑ Shah, Haroun N.; Gharbia, Saheer E. (2010). Mass Spectrometry for Microbial Proteomics. Chichester, UK: Wiley. p. 136. ISBN 9781119991922.
- ↑ "Catalog".