| Esophagectomy | |
|---|---|
 Surgical removal of the esophagus. | |
| ICD-9-CM | 42.40 |
| MeSH | D016629 |
Esophagectomy or oesophagectomy is the surgical removal of all or parts of the esophagus.
| Esophagectomy | |
|---|---|
 Surgical removal of the esophagus. | |
| ICD-9-CM | 42.40 |
| MeSH | D016629 |
Esophagectomy or oesophagectomy is the surgical removal of all or parts of the esophagus.
The principal objective is to remove the esophagus, a part of the gastrointestinal tract. This procedure is usually done for patients with esophageal cancer. It is normally done when esophageal cancer is detected early, before it has spread to other parts of the body. Esophagectomy of early-stage cancer represents the best chance of a cure. Despite significant improvements in technique and postoperative care, the long-term survival for esophageal cancer is still poor. Multimodality treatment (chemotherapy and radiation therapy) is needed for advanced tumors. Esophagectomy is also occasionally performed for benign disease such as esophageal atresia in children, achalasia, or caustic injury.[ citation needed ]
In those who have had an esophagectomy for cancer, omentoplasty (a procedure in which part of the greater omentum is used to cover or fill a defect, augment arterial or portal venous circulation, absorb effusions, or increase lymphatic drainage) appears to improve outcomes. [1]
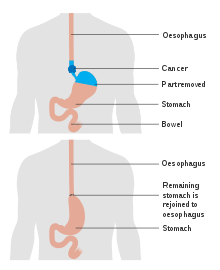
There are two main types of esophagectomy.
In most cases, the stomach is transplanted into the neck and the stomach takes the place originally occupied by the esophagus. In some cases, the removed esophagus is replaced by another hollow structure, such as the patient's colon.
Another option that is slowly becoming available is minimally invasive surgery (MIS) which is performed laparoscopically and thoracoscopically.
After surgery, patients may have trouble with a regular diet and may have to consume softer foods, avoid liquids at meals, and stay upright for 1–3 hours after eating. Dysphagia is common and patients are encouraged to chew foods very well or grind their food. Patients may complain of substernal pain that resolves by sipping fluids or regurgitating food. Reflux-type symptoms can be severe, including intolerance to acidic foods and large, fatty meals. Jejunal feeding tubes may be placed during surgery to provide a temporary route of nutrition until oral eating resumes.[ citation needed ]
This section needs additional citations for verification .(April 2017) |
Esophagectomy is a very complex operation that can take between 4 and 8 hours to perform. It is best done exclusively by doctors who specialise in thoracic surgery or upper gastrointestinal surgery. Anesthesia for an esophagectomy is also complex, owing to the problems with managing the patient's airway and lung function during the operation. [3] Lung collapse is highly probable, as well as loss of diaphragmatic function, and possible injury to the spleen.
Average mortality rates (deaths either in hospital or within 30 days of surgery) for the operation are around 10% in US hospitals. Recognized major cancer hospitals typically report mortality rates under 5%. Major complications occur in 10–20% of patients, and some sort of complication (major and minor) occurs in 40%. Time in hospital is usually 1–2 weeks and recovery time 3–6 months. It is possible for the recovery time to take up to a year.

General surgery is a surgical specialty that focuses on alimentary canal and abdominal contents including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, appendix and bile ducts, and often the thyroid gland. General surgeons also deal with diseases involving the skin, breast, soft tissue, trauma, peripheral artery disease and hernias and perform endoscopic as such as gastroscopy, colonoscopy and laparoscopic procedures.

Gastroenterology is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the GI tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which include the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver.

The esophagus or oesophagus, colloquially known also as the food pipe, food tube, or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about 25 cm (10 in) long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word oesophagus is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω + ἔφαγον.
Esophageal atresia is a congenital medical condition that affects the alimentary tract. It causes the esophagus to end in a blind-ended pouch rather than connecting normally to the stomach. It comprises a variety of congenital anatomic defects that are caused by an abnormal embryological development of the esophagus. It is characterized anatomically by a congenital obstruction of the esophagus with interruption of the continuity of the esophageal wall.

Esophageal achalasia, often referred to simply as achalasia, is a failure of smooth muscle fibers to relax, which can cause the lower esophageal sphincter to remain closed. Without a modifier, "achalasia" usually refers to achalasia of the esophagus. Achalasia can happen at various points along the gastrointestinal tract; achalasia of the rectum, for instance, may occur in Hirschsprung's disease. The lower esophageal sphincter is a muscle between the esophagus and stomach that opens when food comes in. It closes to avoid stomach acids from coming back up. A fully understood cause to the disease is unknown, as are factors that increase the risk of its appearance. Suggestions of a genetically transmittable form of achalasia exist, but this is neither fully understood, nor agreed upon.
Heller myotomy is a surgical procedure in which the muscles of the cardia are cut, allowing food and liquids to pass to the stomach. It is used to treat achalasia, a disorder in which the lower esophageal sphincter fails to relax properly, making it difficult for food and liquids to reach the stomach.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include dental corrosion, dysphagia, heartburn, odynophagia, regurgitation, non-cardiac chest pain, extraesophageal symptoms such as chronic cough, hoarseness, reflux-induced laryngitis, or asthma. In the long term, and when not treated, complications such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus may arise.
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine and large intestine. This change is considered to be a premalignant condition because of its potential to further transition to esophageal adenocarcinoma, an often-deadly cancer.
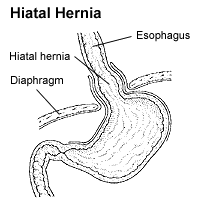
A hiatal hernia or hiatus hernia is a type of hernia in which abdominal organs slip through the diaphragm into the middle compartment of the chest. This may result in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) with symptoms such as a taste of acid in the back of the mouth or heartburn. Other symptoms may include trouble swallowing and chest pains. Complications may include iron deficiency anemia, volvulus, or bowel obstruction.
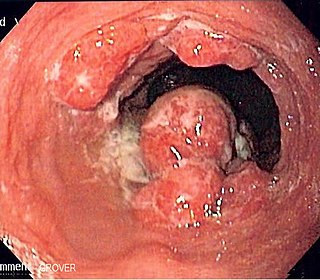
Esophageal cancer is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include difficulty in swallowing and weight loss. Other symptoms may include pain when swallowing, a hoarse voice, enlarged lymph nodes ("glands") around the collarbone, a dry cough, and possibly coughing up or vomiting blood.
Cardiothoracic surgery is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of organs inside the thoracic cavity — generally treatment of conditions of the heart, lungs, and other pleural or mediastinal structures.

A feeding tube is a medical device used to provide nutrition to people who cannot obtain nutrition by mouth, are unable to swallow safely, or need nutritional supplementation. The state of being fed by a feeding tube is called gavage, enteral feeding or tube feeding. Placement may be temporary for the treatment of acute conditions or lifelong in the case of chronic disabilities. A variety of feeding tubes are used in medical practice. They are usually made of polyurethane or silicone. The outer diameter of a feeding tube is measured in French units. They are classified by the site of insertion and intended use.
Gastric bypass surgery refers to a technique in which the stomach is divided into a small upper pouch and a much larger lower "remnant" pouch, where the small intestine is rearranged to connect to both. Surgeons have developed several different ways to reconnect the intestine, thus leading to several different gastric bypass procedures (GBP). Any GBP leads to a marked reduction in the functional volume of the stomach, accompanied by an altered physiological and physical response to food.

A pancreaticoduodenectomy, also known as a Whipple procedure, is a major surgical operation most often performed to remove cancerous tumours from the head of the pancreas. It is also used for the treatment of pancreatic or duodenal trauma, or chronic pancreatitis. Due to the shared blood supply of organs in the proximal gastrointestinal system, surgical removal of the head of the pancreas also necessitates removal of the duodenum, proximal jejunum, gallbladder, and, occasionally, part of the stomach.
Gastrointestinal cancer refers to malignant conditions of the gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs of digestion, including the esophagus, stomach, biliary system, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus. The symptoms relate to the organ affected and can include obstruction, abnormal bleeding or other associated problems. The diagnosis often requires endoscopy, followed by biopsy of suspicious tissue. The treatment depends on the location of the tumor, as well as the type of cancer cell and whether it has invaded other tissues or spread elsewhere. These factors also determine the prognosis.
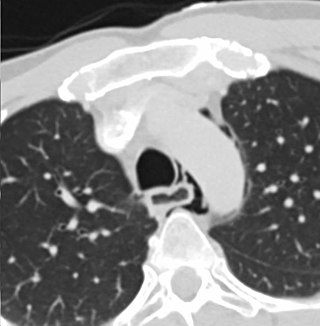
Esophageal rupture is a rupture of the esophageal wall. Iatrogenic causes account for approximately 56% of esophageal perforations, usually due to medical instrumentation such as an endoscopy or paraesophageal surgery. The 10% of esophageal perforations caused specifically by vomiting are termed Boerhaave syndrome.
Digestive system surgery, or gastrointestinal surgery, can be divided into upper GI surgery and lower GI surgery.

An esophageal food bolus obstruction is a medical emergency caused by the obstruction of the esophagus by an ingested foreign body.

Acute esophageal necrosis (AEN), black esophagus, or Gurvits syndrome is a rare esophageal disorder. AEN defines itself with dark pigmentation of the esophagus, found during an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Pigmentation is usually black friable mucosa. The disorder is extremely rare, as only 89 patients over a span of 40 years have received this diagnosis. Specific study of the disorder's mortality rate is mentioned at 31.8%, but new research suggests mortality rates vary from 30 to 50%. The exact triggering mechanism for this disorder is still unknown, but is likely multifactorial.
The Sugiura procedure is a surgical technique that involves the removal and transection of the blood vessels that supply the upper portion of the stomach and the esophagus. The procedure also involves a splenectomy. The operation was originally developed to treat bleeding esophageal varices that were untreatable by other conventional methods. It was originally developed as a two-step operation, but has been modified numerous times by many surgeons since its original creation.