
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year (IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites, both launched by the Soviet Union during the previous year, Sputnik 1 and Sputnik 2. This began a Space Race during the Cold War between the two nations.

The Juno I was a four-stage American space launch vehicle, used to launch lightweight payloads into low Earth orbit. The launch vehicle was used between January 1958 to December 1959. The launch vehicle is a member of the Redstone launch vehicle family, and was derived from the Jupiter-C sounding rocket. It is commonly confused with the Juno II launch vehicle, which was derived from the PGM-19 Jupiter medium-range ballistic missile. In 1958, a Juno I launch vehicle was used to launch America's first satellite, Explorer 1.
Project Vanguard was a program managed by the United States Navy Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), which intended to launch the first artificial satellite into low Earth orbit using a Vanguard rocket. as the launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Missile Annex, Florida.
Explorer 2 was an American unmanned space mission within the Explorer program. Intended to be a repetition of the previous Explorer 1 mission, which placed a satellite into medium Earth orbit, the spacecraft was unable to reach orbit due to a failure in the launch vehicle during launch.

Explorer 11 was a NASA satellite that carried the first space-borne gamma-ray telescope. This marked the beginning of space gamma-ray astronomy. Launched on 27 April 1961 by a Juno II, the satellite returned data until 17 November 1961, when power supply problems ended the science mission. During the spacecraft's seven-month lifespan it detected twenty-two events from gamma-rays and approximately 22,000 events from cosmic radiation.

Explorer 7 was a NASA satellite launched on 13 October 1959, at 15:30:04 GMT, by a Juno II launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) to an orbit of 573 × 1,073 km (356 × 667 mi) and inclination of 50.27°. It was designed to measure solar X-ray and Lyman-alpha flux, trapped energetic particles, and heavy primary cosmic rays. Secondary objectives included collecting data on micrometeoroid penetration, molecular sputtering and studying the Earth-atmosphere heat balance.

Minotaur-C, formerly known as Taurus or Taurus XL, is a four stage solid fueled launch vehicle built in the United States by Orbital Sciences and launched from SLC-576E at California's Vandenberg Air Force Base. It is based on the air-launched Pegasus rocket from the same manufacturer, utilizing a "zeroth stage" in place of an airplane. The Minotaur-C is able to carry a maximum payload of around 1458 kg into a low Earth orbit (LEO).
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is managed by a group within the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a directorate of the Space and Missile Systems Center of the United States Space Force. STP provides spaceflight via the International Space Station (ISS), piggybacks, secondary payloads and dedicated launch services.

Juno II was an American space launch vehicle used during the late 1950s and early 1960s. It was derived from the Jupiter missile, which was used as the first stage.

Explorer 9, known as S-56A before launch, was a NASA satellite which was launched in February 1961 to study the density and composition of the upper thermosphere and lower exosphere. It was a reflight of the failed Explorer S-56 mission, and consisted of a 7 kg (15 lb), 3.66 m (12.0 ft) balloon which was deployed into a medium Earth orbit. The mission was conducted by NASA's Langley Research Center.

DISCOVERE 34, also known as CORONA 9027, was a United States optical reconnaissance satellite which was launched on 5 November 1961. It was the ninth of ten CORONA KH-2 satellites, based on the Agena B.
Explorer S-45 was a NASA satellite, which was lost in a launch failure in February 1961. The satellite was intended to operate in a highly elliptical orbit, from which it was to have provided data on the shape of the ionosphere, and on the Earth's magnetic field. It was part of the Explorer program, and would have been designated Explorer 10 had it reached orbit. A second identical satellite, Explorer S-45A, also failed to achieve orbit when it was launched.
KySat-1 was an American satellite which was to have been operated by Kentucky Space. Designed to operate for eighteen to twenty four months, it was lost in a launch failure in March 2011 after the Taurus launch vehicle carrying it failed to achieve orbit.
Kosmos 167, or 4V-1 No.311, was a 1967 Soviet spacecraft intended to explore Venus. A spacecraft launched as part of the Venera programme, Kosmos 167 was intended to land on Venus but never departed low Earth orbit due to a launch failure.

Explorer S-56 was a NASA satellite launched on 4 December 1960, at 21:14 GMT as part of the Explorer program. The satellite was composed of a 3.66 m (12.0 ft) diameter inflatable sphere, and was intended to study the density of the upper atmosphere. The Scout X-1 rocket used to launch Explorer S-56 failed in flight, and the satellite never reached orbit.
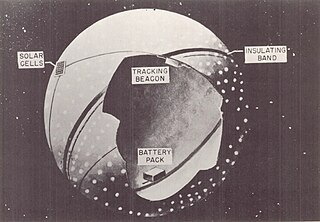
Explorer 19,, was a NASA satellite launched on 19 December 1963, as part of the Explorer program. It was the third of six identical Explorer satellites launched to study air density and composition, and the second to reach orbit. It was identical to Explorer 9.

Explorer 12, also called EPE-A or Energetic Particles Explorer-A and as S3), was a NASA satellite built to measure the solar wind, cosmic rays, and the Earth's magnetic field. It was the first of the S-3 series of spacecraft, which also included Explorer 12, 14, 15, and 26. It was launched on 16 August 1961, aboard a Thor-Delta launch vehicle. It ceased transmitting on 6 December 1961 due to power failure.

Explorer S-1, also known as NASA S-1 or Explorer 7X, was a NASA Earth science satellite equipped with a suite of scientific instruments to study the environment around the Earth. The spacecraft and its Juno II launch vehicle were destroyed five seconds after launch on 16 July 1959, in a spectacular launch failure caused by complications with the launch vehicle's power supply. A relaunch of the mission in October 1959, Explorer 7 (S-1A), was successful.

Explorer S-46 was a NASA satellite with a mass of 41 kg (90 lb). It was the last of the original series of Explorer satellites built, designed, and operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA).

Explorer S-55 was an American satellite launched by NASA on 30 June 1961, as part of the Explorer program. Explorer S-55, was launched using a Scout X-1 launch vehicle from the Wallops Flight Facility (WFF). Its mission was to evaluate the launch vehicle and investigate micrometeoroid impact and penetration. The mission failed because the third stage failed to ignite and the spacecraft did not achieve orbit.















