Harwood, Maryland | |
|---|---|
 The U.S. Post Office at Harwood, Maryland, in May 2010. | |
| Coordinates: 38°51′54″N76°37′12″W / 38.86500°N 76.62000°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
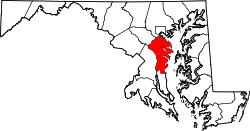
| County | |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code | 20776 [1] |
| Area codes | 410, 443 and 667 |
| GNIS feature ID | 590432 |
Harwood is a crossroads in Anne Arundel County, Maryland, United States, south of Annapolis on Maryland Route 2 (Solomons Island Road). [2]